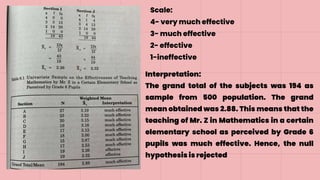
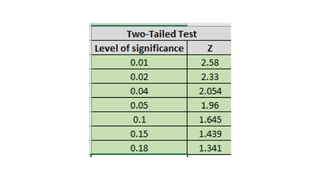
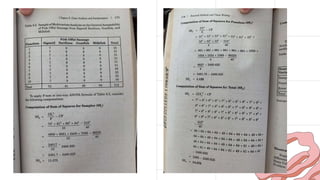
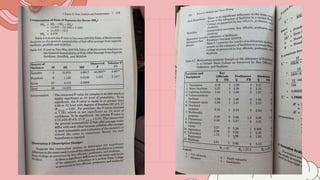
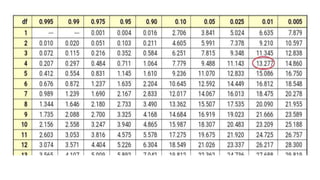
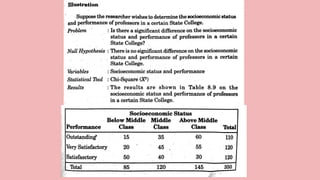
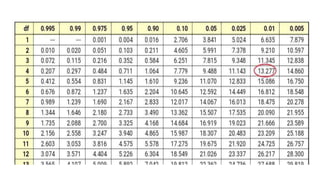
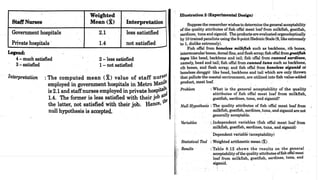
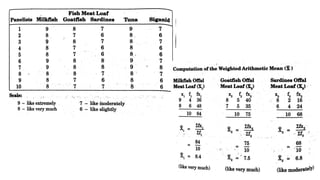
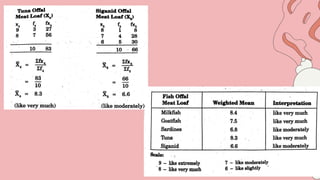
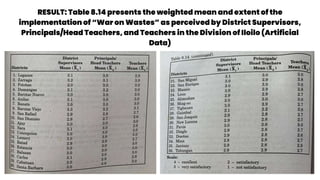
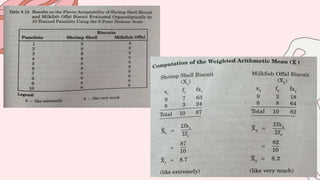
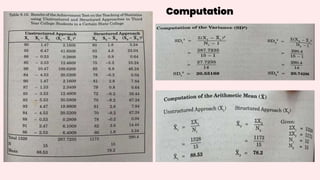
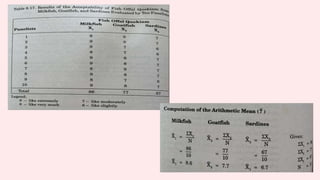
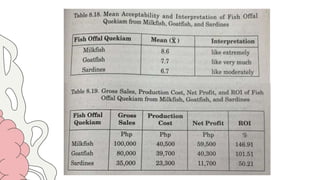
This document discusses 10 different types of data analysis: univariate, bivariate, multivariate, normative, descriptive, classification, evaluative, comparative, and cost-effective analysis. For each type of analysis, the document provides examples of how each could be used to analyze data from research studies, including specifying the variables and statistical tools that could be used. It focuses on explaining the purpose and application of each analytical technique.