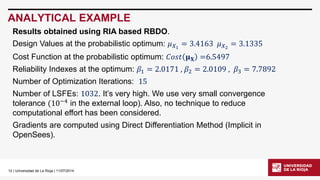
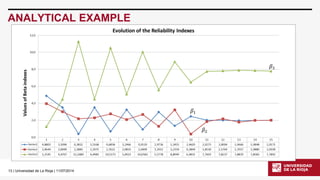
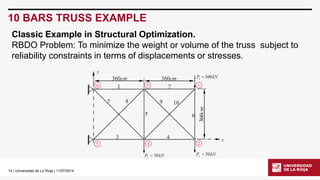
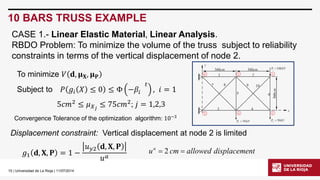
The document discusses the application of OpenSees in reliability-based design optimization (RBDO) of structures, outlining recent updates and methods for analyzing reliability and sensitivity. It details RBDO problems, methods, including both double and single loop approaches, and presents analytical examples, such as a ten-bar truss optimization problem. The document emphasizes the integration of OpenSees with MATLAB for addressing complex RBDO tasks, highlighting structural analyses under uncertain conditions.


![8| Universidad de La Rioja | 11/07/2014
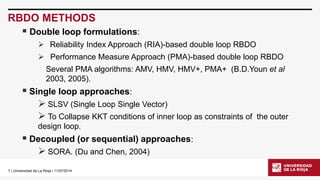
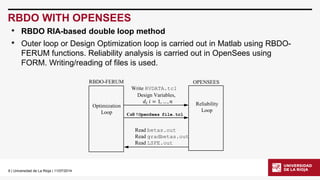
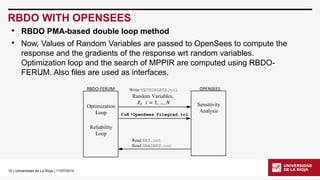
RBDO WITH OPENSEES
•Structural Reliability applications are useful when large structures supporting extreme actions are considered. These extreme actions are wind loads, seismic ground motions or wave loads.
•Then, nonlinear structural behavior must be considered. Also dynamic analysis is necessary when load are time variant. Because that an advanced finite element analysis software is needed.
•OpenSeesis a powerful software with advanced structural analysis capabilities. Also reliability and sensibility functions have been recently modified. Because that OpenSeesbecomes a powerful FEA tool.
•Here some RBDO problems are solved combining some MATLAB functions with the power of OpenSees. These MATLAB functions were originally integrated with FERUM and forming the RBDO –FERUM toolbox. [1]
[1]L.Celorrio-Barragué,“DevelopmentofaReliability-BasedDesignOptimizationToolboxfortheFERUMSoftware”,
SUM2012,LNAI7520,pp.273–286,2012.Springer-VerlagBerlinHeidelberg2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d2007celeriobarragueosdpt2014-140910165427-phpapp02/85/Application-of-OpenSees-in-Reliability-based-Design-Optimization-of-Structures-8-320.jpg)

![21| Universidad de La Rioja | 11/07/2014
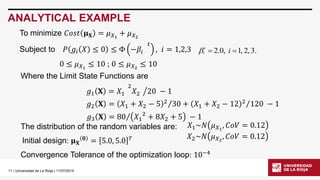
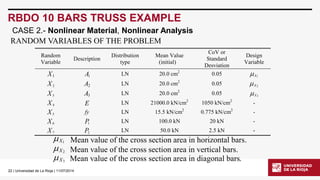
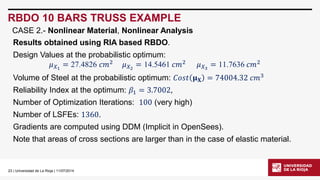
RBDO 10 BARS TRUSS EXAMPLE
uniaxialMaterial Hardening1 $E $fy0.0 [expr$b/(1-$b)*$E]
A random variable is added: fy(elastic limit) ~퐿푁휇=15.5 푘푁푐푚2,퐶표푉=0.05.
$b is the hardening ratio and is considered determinist: set b 0.02
CASE 2.-Nonlinear Material, Nonlinear Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d2007celeriobarragueosdpt2014-140910165427-phpapp02/85/Application-of-OpenSees-in-Reliability-based-Design-Optimization-of-Structures-21-320.jpg)
![24| Universidad de La Rioja | 11/07/2014
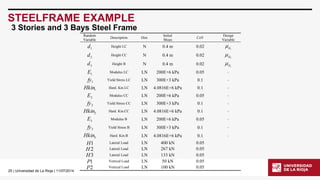
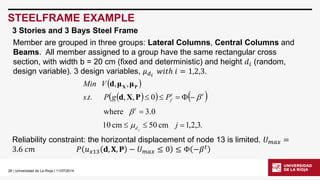
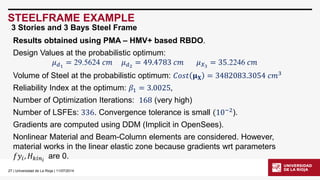
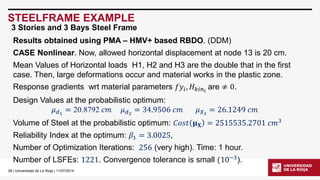
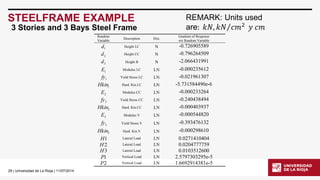
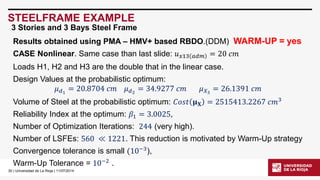
STEELFRAME EXAMPLE
3 Stories and 3 Bays Steel Frame
Modified version of the structural model in the file steelframe.tcl[2] downloaded from OpenSeesforum.
[2]T.HaukaasandM.H.Scott,ShapeSensitivitiesintheReliabilityAnalysisofNonlinearFrameStructures,ComputerandStructures,v.84,15-16,p964-977,2006
1 2 3 1 1 2 2 5 5 5 4 4 4 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d2007celeriobarragueosdpt2014-140910165427-phpapp02/85/Application-of-OpenSees-in-Reliability-based-Design-Optimization-of-Structures-24-320.jpg)