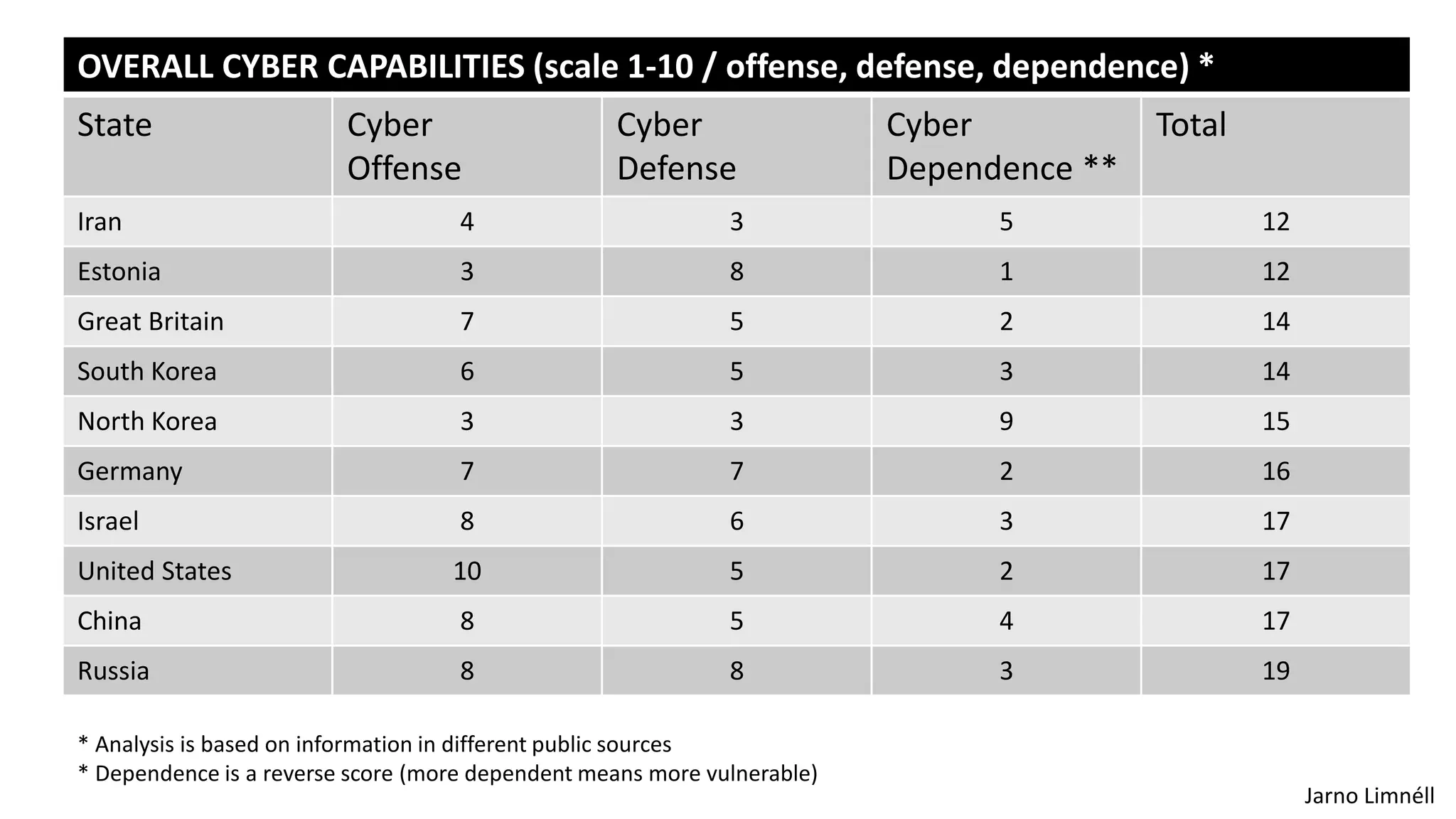
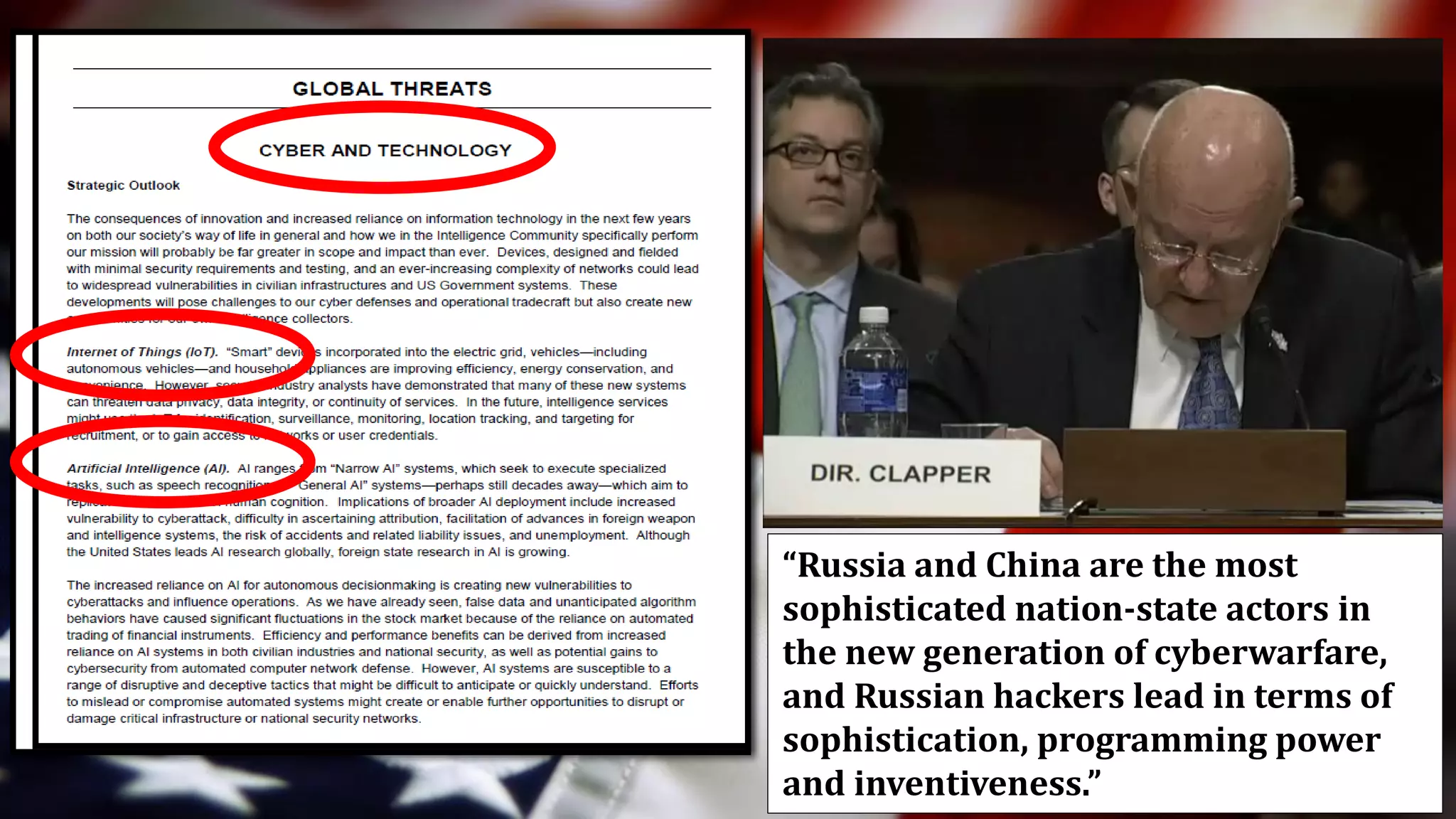
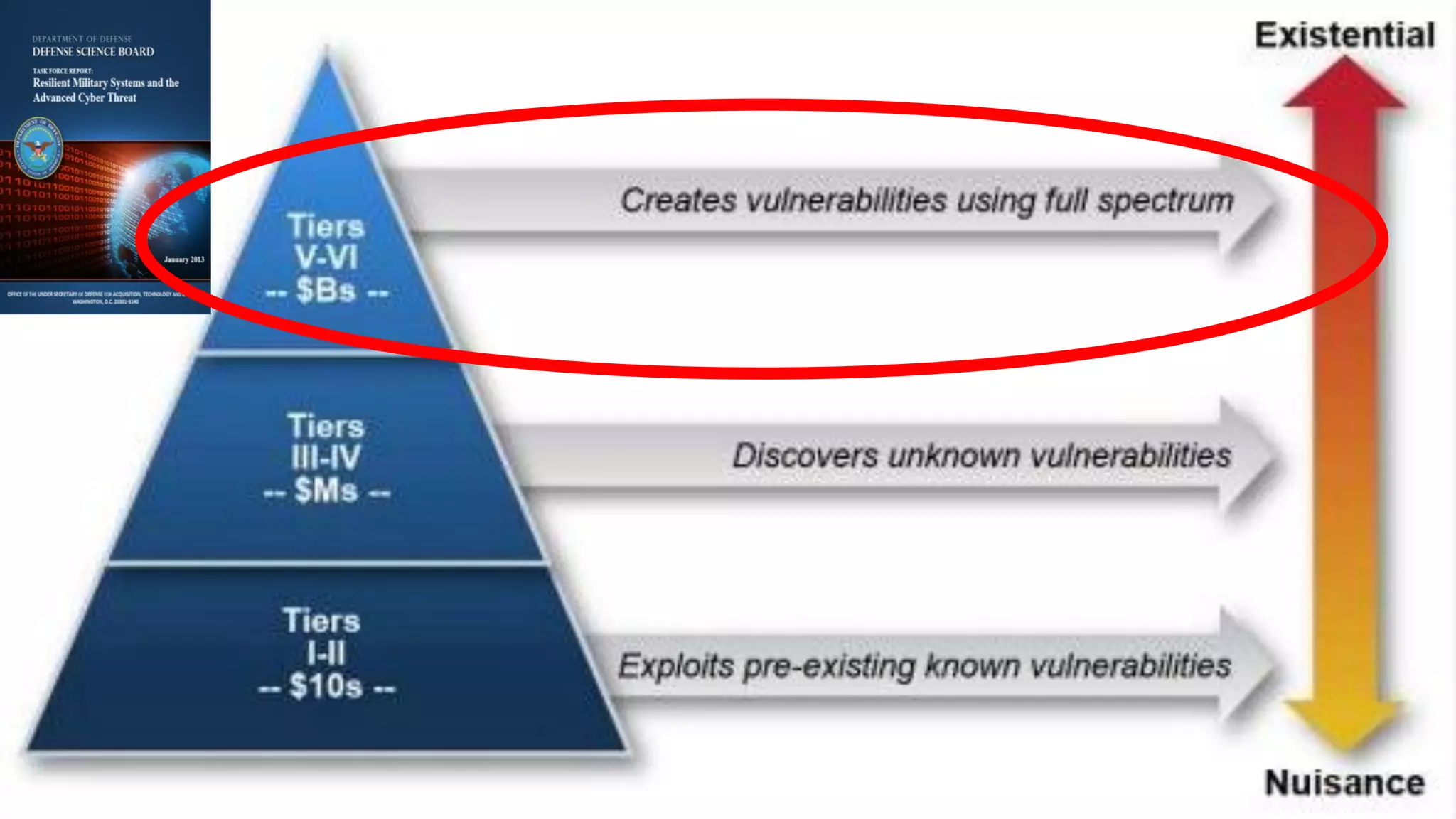
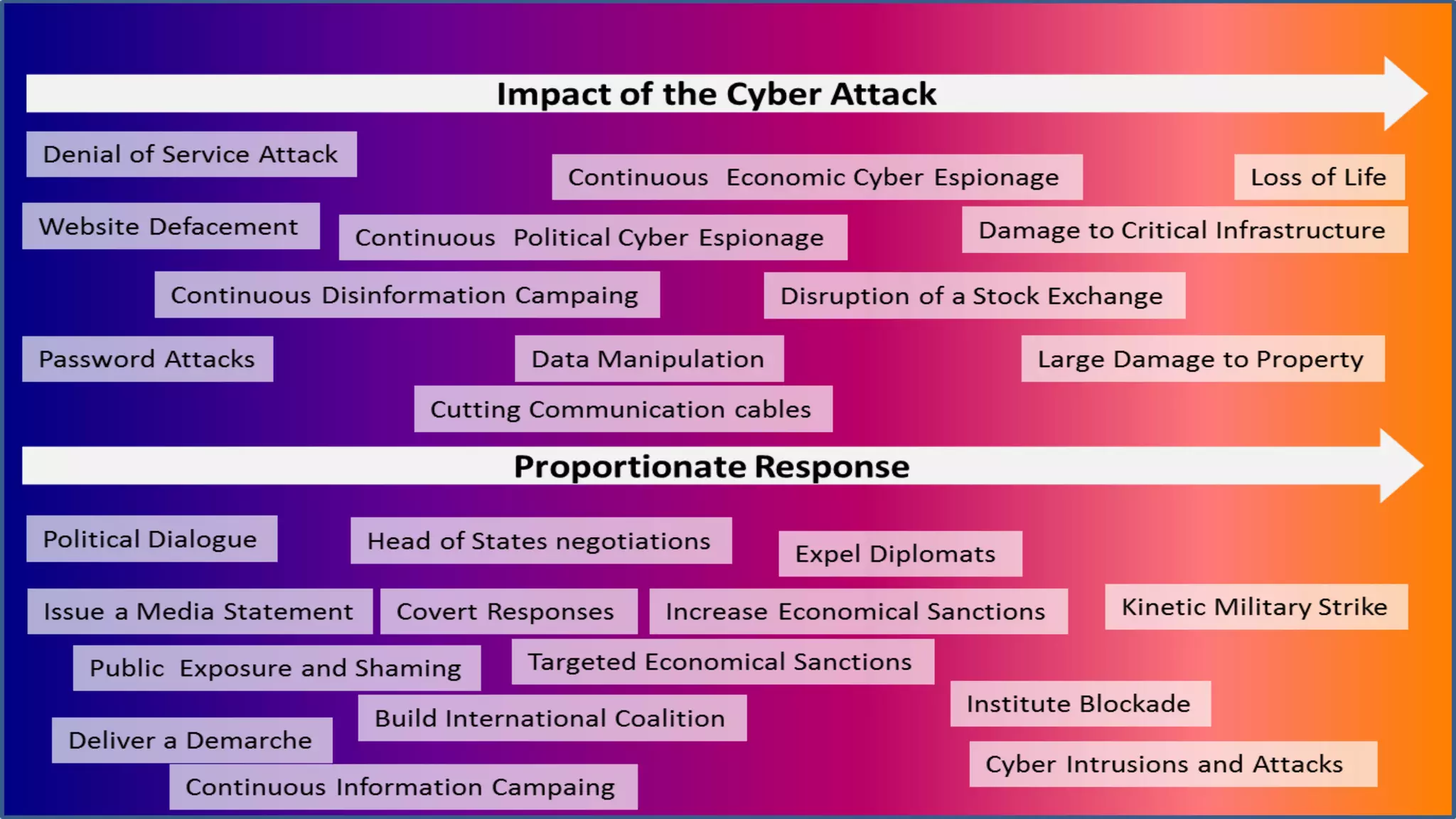
The document discusses the evolving landscape of cyberwarfare, highlighting Russia and China's advanced cyber capabilities and strategies in military operations. It emphasizes the integration of cyber capabilities into broader military and political tactics, with a focus on intelligence gathering, critical infrastructure attacks, and the blurring lines between state actors and cybercriminals. Recommendations include enhancing cybersecurity resilience, education, and integrating cyber and physical operations to counter aggression in the cyber domain.