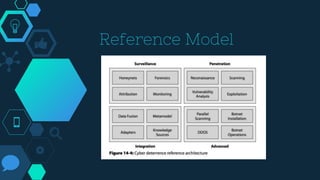
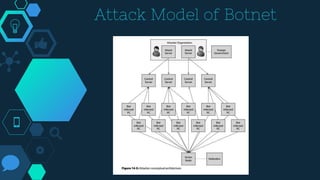
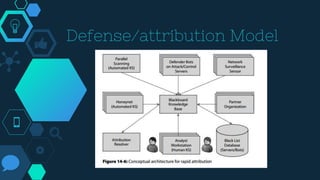
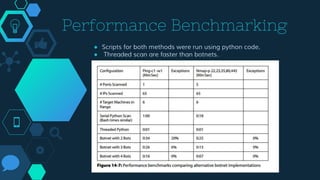
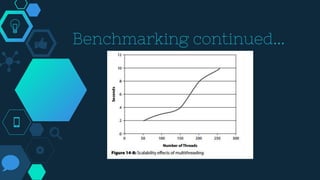
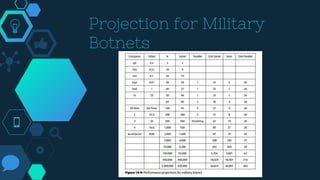
This chapter discusses cyber deterrence strategies and architectures. It outlines the objectives of cyber deterrence as preventing attacks, denying enemies freedom in cyberspace, and using cyber space for counterattacks. It discusses challenges like attribution and unpredictability. The chapter summarizes Libicki's cyber deterrence strategy of situational awareness, identification, analysis, attribution assessment, and retaliation considerations. It proposes a solution architecture using military botnets for effective distributed scanning and proposes prototypes and performance benchmarking of threaded and botnet-based scanning.