CVD-Report-V1.pdf
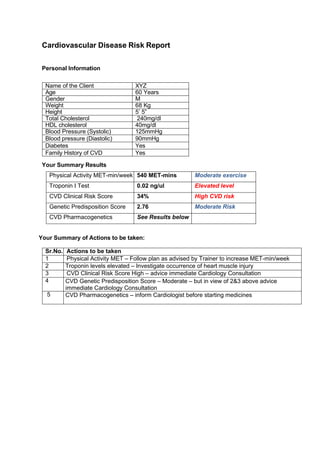
- 1. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Report Personal Information Name of the Client XYZ Age 60 Years Gender M Weight 68 Kg Height 5’ 5” Total Cholesterol 240mg/dl HDL cholesterol 40mg/dl Blood Pressure (Systolic) 125mmHg Blood pressure (Diastolic) 90mmHg Diabetes Yes Family History of CVD Yes Your Summary Results Physical Activity MET-min/week 540 MET-mins Moderate exercise Troponin I Test 0.02 ng/ul Elevated level CVD Clinical Risk Score 34% High CVD risk Genetic Predisposition Score 2.76 Moderate Risk CVD Pharmacogenetics See Results below Your Summary of Actions to be taken: Sr.No. Actions to be taken 1 Physical Activity MET – Follow plan as advised by Trainer to increase MET-min/week 2 Troponin levels elevated – Investigate occurrence of heart muscle injury 3 CVD Clinical Risk Score High – advice immediate Cardiology Consultation 4 CVD Genetic Predisposition Score – Moderate – but in view of 2&3 above advice immediate Cardiology Consultation 5 CVD Pharmacogenetics – inform Cardiologist before starting medicines
- 2. Detailed Report 1.0 Physical activity Report Regular physical activity reduces the risk of obesity, blood lipid abnormalities, hypertension, and non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and has been shown to reduce substantially the risk of coronary heart disease (PMID:15044412). Leisure-time exercise, including as much as 35-40 minutes per day of brisk walking, was protective for CHD risk. Reduced sedentary behaviour and TV time also makes positive impact on lowering the risk. Physical activity can be measured in terms of MET-min. One MET minute equals one minute spent at a MET score of 1 (inactivity). To reach 1,000 MET minutes, a person could combine brisk walking and low-impact aerobics, both with a MET score of 5, for 200 minutes a week (5 x 200 = 1,000). Generally, an improvement in health requires 500-1000 MET minutes a week. We have developed a calculator to measure number of calories burnt through the physical activity. You Met-min per week is 540 which is moderate. You need to increase the physical activity till it achieves MET-min in the range of 6000 to 1000. This achievement will improve your lipid profile and blood sugar levels and thereby decrease the clinical risk of CVD. 2.0 Troponin I Test Report This test measures the levels of cardiac biomarkers in your blood. These markers include enzymes, hormones, and proteins. Cardiac biomarkers show up in your blood after your heart has been under severe stress and becomes injured because it isn't getting enough oxygen. These markers start appearing in individuals who are apparently healthy. This might be because of silent cardiac events or these levels can be elevated for other reasons. The levels of biomarkers are often used to provide an indication of cardiac events in your body. The following cardiac biomarkers can be used to diagnose cardiac events: Cardiac Troponin. This protein is by far the most commonly used biomarker. It has the highest known sensitivity. It enters into your bloodstream soon after a heart attack. It also stays in your bloodstream days after all other biomarkers go back to normal levels. Two forms of troponin may be measured: Troponin T and Troponin I. Troponin I is highly specific to the heart and stays higher longer than Creatinine Kinase-Myocardial Band (CK-MB). Current guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) say this is the best biomarker for characterizing a cardiac event. Troponin I Test Report Name: XXYZ Age: 65 years Sex: Male Referred by: Dr. Cardio, MD Sample Receipt Date: 27-08-2022 Reporting Date: 27-08-2022
- 3. Test Name Results Biological Range Units Troponin I 0.01 0.0 to 0.01 ng/ul Signed by Dr. ABC, MD (Cardio)
- 4. 3.0 CVD Clinical Risk Score Report We have developed a Cardiac Clinical Risk Calculator for the Indian population aged between 25 to 74. This risk score is applicable to those who had not yet had any known previous heart disease or event. The score predicts 10-year risk for heart attack, stroke and Cardio Vascular Disease (CVD). CVD Clinical Risk score is based on Age, raised Cholesterol and Lipid profile, raised blood pressure, Body Mass Index (BMI), Type 2 Diabetes, smoking & tobacco use, physical activity and family history of cardiac events. Your CVD Clinical Risk Score is 34% CVD Clinical Risk Score: 1) Risk score < 10 - Low risk 2) Risk score > 10 and < 20 - Moderate risk 3) Risk score > 20 - High risk 3.2 Risk Factors for CVD clinical Risk Smoking: Number of cigarettes smoked per day Cholesterol: Lipid profile including total cholesterol, HDL, LDL and triglyceride levels and HDL to total cholesterol ratio Diabetes: Type 2 Diabetes is also a risk factor included in the clinical risk score Blood Pressure: Blood pressure is one of the significant factor and Blood pressure medication is also considered for the risk calculation. Obesity: BMI is one of the risk factor included in the CVD risk calculation. Family History: indicates genetic disposition
- 5. 4.0 CVD Genetic Predisposition Risk Report Cardiac Genetic Predisposition Risk Panel is designed to highlight confounding factors barring appropriate cardiovascular risk reduction in patients. The panel focuses on 17 genetic markers affecting Coronary artery disease, Myocardial infarction, Myocardial Ischemia, Stroke, hypertension, total cholesterol, LDL (low-density lipoproteins) and HDL (high-density lipoproteins) cholesterol, triglycerides, thrombotic risk, homocysteinemia, insulin resistance, and statin-induced myopathy risk. Your CVD GPRS is calculated based on the number of risk alleles associated with CVD predisposition in 17 SNP markers associated with the CVD risk. CVD What is GPRS? Genetic predisposition Risk Score (GPRS) give cumulative risk score based on the number of SNP risk alleles associated with a trait. GPRS is not significant as Genetic Predisposition can be overcome with suitable lifestyle and nutritional modifications. GPRS= Genetic Predisposition Risk Score GPRS Scale 0.1 to 1.5: Typical normal risk 1.51 to 3.00: Moderate risk 3.10 o 5.0: Increased risk CVD Genetic Predisposition Risk Results Cumulative CVD Genetic predisposition risk score 2.76 CVD Type GPRS Score Atherosclerosis 1.50 Coronary artery disease 3.75 Myocardial infarction 4.00 Myocardial Ischemia 3.75 Thrombosis risk 2.60 Stroke 1.45 Hypertension 2.80 HDL 1.25 LDL 3.80 Triglycerides 2.75 Homocysteinemia 1.70 Statin risk 2.60 Genetic Markers Included Genetic Predisposition Risk Calculation 9p21 – The genetic marker 9p21 is strongly associated with coronary artery disease. Researchers believe that mutations in this region may affect uncontrolled cell proliferation leading to atherosclerosis, and eventually coronary artery disease. Carrying one variant allele
- 6. increases the risk of coronary artery disease by 25 percent, with the risk doubling in a person with two of these variant alleles. 9p21 – The genetic marker 9p21 is strongly associated with coronary artery disease. Researchers believe that mutations in this region may affect uncontrolled cell proliferation leading to atherosclerosis, and eventually coronary artery disease. Carrying one variant allele increases the risk of coronary artery disease by 25 percent, with the risk doubling in a person with two of these variant alleles. AGT – Angiotensinogen (AGT) is a protein produced by the liver, which plays a role in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This system is crucial for maintaining blood pressure and cardiovascular homeostasis, and is a target of many antihypertensive drugs. A hyperactive RAAS resulting from genetic variants, in addition to environmental factors, can lead to coronary artery disease. APOE - Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is a lipid/protein complex associated with chylomicron formation and the transport of dietary lipids via binding of the LDL (low-density lipoprotein) receptor. APOE is synthesized mainly in the liver, with a small amount of synthesis occurring in other organs such as the brain. There are three alleles of the APOE gene: E2, E3, and E4.7 E2 is a protective allele, and individuals with this variant have a reduced risk of coronary disease. E3 is considered the normal variant of APOE and not associated with any altered risk of cholesterol management. E4 is the risk allele and is associated with increased cholesterol levels, as well as coronary disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. CDKN2B‐AS1 - Cyclin‐dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1 (CDKN2B‐AS1) is a significant susceptibility locus for cardiovascular disease by regulating inflammation response and cell cycle. eNOS/NOS3 – Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) exists in three forms: neuronal, inducible, and endothelial. The form predominantly associated with cardiovascular health is the endothelial form, known as eNOS or NOS3. The eNOS/NOS3 - gene regulates vascular nitric oxide production, which helps to regulate vasodilation, vascular repair, platelet aggregation and adhesion, reduction of vascular smooth muscle proliferation, and oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles leading to atherosclerotic plaques. The homozygous variant of eNOS/NOS3 is associated with decreased nitric oxide production and a higher rate of endothelial dysfunction, leading to an increased risk of hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Factor II (Prothrombin) – Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affecting the coagulation cascade have been implicated in many cardiovascular ailments, such as venous thrombosis, ischemic stroke, pulmonary embolisms, coronary artery disease, and myocardial infarction. Prothrombin is an inherited mutation that increases the likelihood of blood clot formation. The variant allele of the prothrombin gene significantly elevates thrombin generation, and
- 7. increases risk for coronary disease, as well as embolisms. Factor V Leiden – Factor V is part of the coagulation cascade, a multi-tiered interaction of proteins and co-factors responsible for proper blood clotting. Factor V is degraded by activated protein C in the absence of hemostasis. A mutation in this gene increases the protein’s resistance to degradation, thereby increasing the risk of venous thrombosis and thromboembolisms. MTHFR – Methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme that helps convert folate into the specific form of 5-methyl-tetrahydrofolate. The key metabolic role of this form of folate is to aid homocysteine conversion to methionine. Two common mutations in the MTHFR gene (C677T and A1298C) can result in reduced enzyme functionality,20 and may contribute to increased levels of homocysteine, a known risk factor for heart disease,21 atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis. SLCO1B1 – The SLCO1B1 gene encodes a transporter that brings statin medications to the main tissues of the liver.23 Individuals who carry one or two copies of the variant allele have a reduced response to treatment for low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (a risk factor for cardiac health), and with too much statin medication in the liver, an increased risk of statin- induced myopathy. 5.0 Pharmacogenetic Screening Report CVD Drug Dosing and Prescription Investigating the genomic basis for variable responses to cardiovascular therapies has been a model for pharmacogenomics in general and has established critical pathways and specific loci modulating therapeutic responses to commonly used drugs such as clopidogrel, warfarin, and statins (PMID: 23689943). Pharmacogenomics aims to discover new therapeutic targets and understand genetic polymorphisms that determine the safety and efficacy of medications. The goal of pharmaco-genomics is customization of drug therapy with administration of a medication in an optimum dose that will be safe and effective with reduction in morbidity and mortality (PMID: 34232575). This report helps in development of initial clinical guidelines that consider how to facilitate incorporating genetic information to the bedside in order to provide better treatment and care to the patients. Clopidogrel Drug class: Antiplatelet Description: Variation in antiplatelet response leading to resistance in a subset of patients Genes and Variants: CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*3 Problem: Carriers of above variants have insufficient active metabolite formation leading to resistance
- 8. Metabolizer Type: Ultra-Rapid metabolizer Clinical Implications: Dose increase or consider newer antiplatelet agents for loss-of- function variant carriers Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet drug used in the treatment of patients with ACS, managed medically or with PCI. Clopidogrel is also used in the treatment of patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease, as indicated by a recent MI, a recent ischemic stroke, or symptomatic peripheral arterial disease. Clopidogrel has been shown to reduce the rate of subsequent MI and stroke in these patients. Clopidogrel is given to treat or to prevent further occurrences of arterial thrombosis, which occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside an artery. Diplotype results Drug Diplotype Metabolizer Type Implications for clopidogrel FDA therapeutic recommendations Clopidogrel CYP2C19*17/*1 Ultra rapid Increased platelet inhibition Dose recommended by drugs label Dose Recommendation Standard dosing of clopidogrel, as recommended in the product insert, is warranted among ACS/PCI patients with a predicted CYP2C19 extensive metabolizer or ultrarapid metabolizer phenotype (i.e., *1/*1, *1/*17, and *17/*17). Recommendation CYP2C19 Ultra Rapid Metabolizer: Clopidogrel NO action is required for this gene-drug interaction. The genetic variation results in increased conversion of clopidogrel to the active metabolite. However, this can result in both positive effects (reduction in the risk of serious cardiovascular events) and negative effects (increase in the risk of bleeding). Carvedilol Drug class: non-selective beta blocker Description: Considered to be the standard of care for patients with heart failure, particularly for patients who also have hypertension. Genes and Variants: CYP2D6*4/*4 Problem: Higher rate of dizziness during up-titration in poor metabolizers of Carvedilol Metabolizer Type: Poor metabolizer Clinical Implications: The plasma concentration of carvedilol can be elevated in case of the poor metabolizers Carvedilol is widely considered to be the standard of care for patients with heart failure, particularly for patients who also have hypertension. Carvedilol is used to treat mild to severe congestive heart failure, as well as hypertension, and left ventricular dysfunction in patients who recently had an MI, but are otherwise stable. Carvedilol is a non-selective beta blocker (blocks beta 1 and beta 2 receptors) and an alpha 1 blocker. By blocking beta receptors found in the heart, carvedilol reduces the heart rate and decreases the force of heart contractions. By blocking the alpha 1 receptors found on blood vessels, carvedilol relaxes and dilates the blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure. Diplotype results
- 9. Recommendations CYP2D6*4/*4 Carvedilol: Poor metabolizer NO action is required for this gene-drug interaction. Retrospective analysis of side effects in clinical trials showed that poor CYP2D6 metabolizers had a higher rate of dizziness during up-titration, presumably resulting from vasodilating effects. The plasma concentration of carvedilol can be elevated. This however, has no side effects in the patients. Metoprolol Drug class: Beta blocker Description: Variation in blood pressure lowering response and reduction in cardiovascular events Genes and Variants: CYP2D6*3/*4 Problem: CYP2D6*3/*4 carriers have increased sensitivity to metoprolol Metabolizer Type: Poor metabolizer Clinical Implications: Dose reduction for loss-of-function variant carriers Metoprolol is a beta blocker used in the treatment of hypertension, angina, and heart failure. Metoprolol selectively blocks beta1 adrenoreceptors mainly expressed in cardiac tissue. Blockade of these receptors reduces the heart rate and decreases the force of heart contractions. Metoprolol is primarily metabolized by the CYP2D6 enzyme. Approximately 8% of Caucasians and 2% of most other populations have absent CYP2D6 activity and are known as “CYP2D6 poor metabolizers.” In addition, a number of drugs inhibit CYP2D6 activity, such as quinidine, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and propafenone. Diplotype results Recommendations CYP2D6*3/*4 Metoprolol: Poor Metabolizer Poor metabolizers and extensive metabolizers who concomitantly use CYP2D6 inhibiting drugs will have increased (several-fold) metoprolol blood levels, decreasing metoprolol's cardioselectivity. The gene variation reduces the conversion of metoprolol to inactive metabolites. However, the clinical consequences are limited mainly to the occurrence of asymptomatic bradycardia. If a gradual reduction in heart rate is desired, or in the event of symptomatic bradycardia then Increase the dose in smaller steps and/or prescribe no more than 25% of the standard dose. Drug Diplotype Metabolizer Type Implications for Carvedilol FDA therapeutic recommendations Caevedilol CYP2D6*4/*4 Poor Meatbolizer Increased plama levels Drug Interactions, Clinical Pharmacology Drug Diplotype Metabolizer Type Implications for Metoprolol FDA Drug Labels Metoprolol CYP2D6*3/*4 Poor Meatbolizer Increased metoprolol blood levels Drug Interactions, Clinical Pharmacology
- 10. In other cases, no action is required. Warfarin Drug class: Anticoagulant Description: Variation in dose requirement for achieving and maintaining INR in therapeutic range Genes and Variants: CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, VKORC1 1639G Problem: Carriers of above variants have increased sensitivity to warfarin Metabolizer Type: Poor metabolizer Clinical Implications: Dose reduction to maintain therapeutic range Warfarin is an anticoagulant (blood thinner). Warfarin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors and is used in the prevention and treatment of various thrombotic disorders. Warfarin is a drug with narrow therapeutic index; thus, a small change in its plasma levels may result in concentration dependent adverse drug reactions or therapeutic failure. Therefore, the dose of warfarin must be tailored for each patient according to the patient’s response, measured as INR (International Normalized Ratio), and the condition being treated. Diplotype results Recommendations Calculate warfarin dosing using a published pharmacogenetic algorithm, including genotype information for VKORC1-1639G>A and CYP2C9*2 and *3. In individuals with genotypes associated with CYP2C9 poor metabolism (e.g., CYP2C9 *2/*3, *3/*3) or both increased sensitivity (VKORC1-1639 A/A) and CYP2C9 poor metabolism, an alternative oral anticoagulant might be considered. Statins Drug class: Statins includes atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin Description: Variation in lipid lowering efficacy and increased risk of myopathy Genes and Variants: SLCO1B1*5 Problem: OATP1B1*5 carriers have increased systemic exposure and risk of myotoxicity Metabolizer Type: Poor drug transport to liver Clinical Implications: Avoid using high-dose or consider using alternatives Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs . Drug Diplotype Metabolizer Type Implications for Warfarin FDA Drug Labels Warfarin CYP2C9*3/*3 Poor Meatbolizer Increased sensitivity Dosage, Drug Interactions, Clinical Pharmacology Warfarin VKORC1 AA Poor Meatbolizer Increased sensitivity Dosage, Drug Interactions, Clinical Pharmacology
- 11. The SLCO1B1*5 allele (defined as consisting of rs4149056) is assigned as a no function allele by CPIC. Patients with the *5 allele in combination with a normal, no, or increased function allele may have increased exposure to rosuvastatin as compared to patients with two normal function alleles. Other genetic and clinical factors may also influence rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics. Diplotype results Recommendations Start with a low dose of statins that can be increased not more than once every 2 to 4 weeks. Monitor the patient for muscle weakness leading to muscle myopathy. Perform liver function tests periodically to monitor side effects of liver damage. Statins may cause increase in the blood sugar or may induce Type 2 diabetes. Drug Drug Class Diplotype Metabolizer Type Implications for Statins FDA Drug Labels Statins Statins SLCO1B1*5 Poor Meatbolizer Increased systemic exposure Dosage, Drug Interactions, Clinical Pharmacology