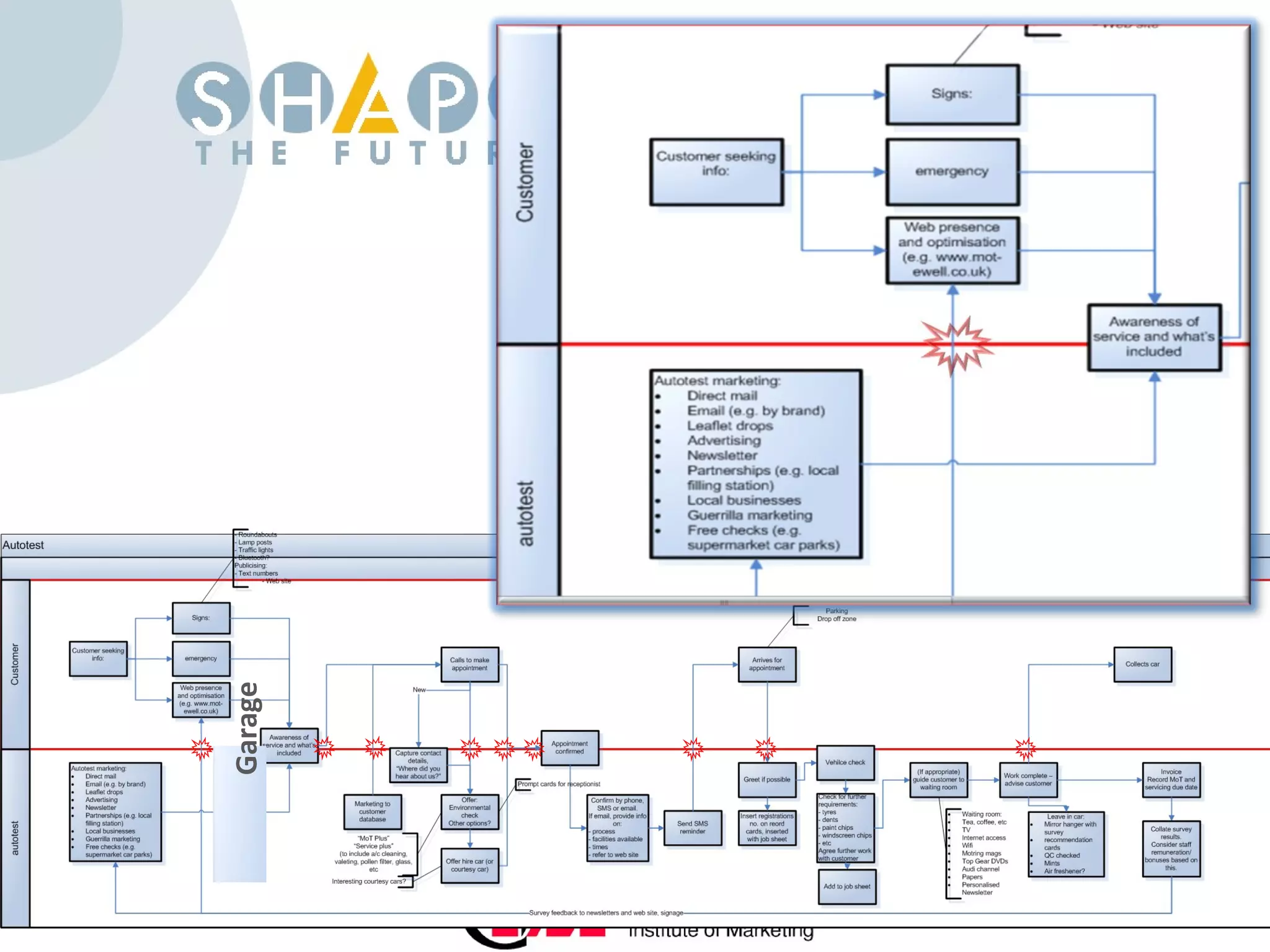
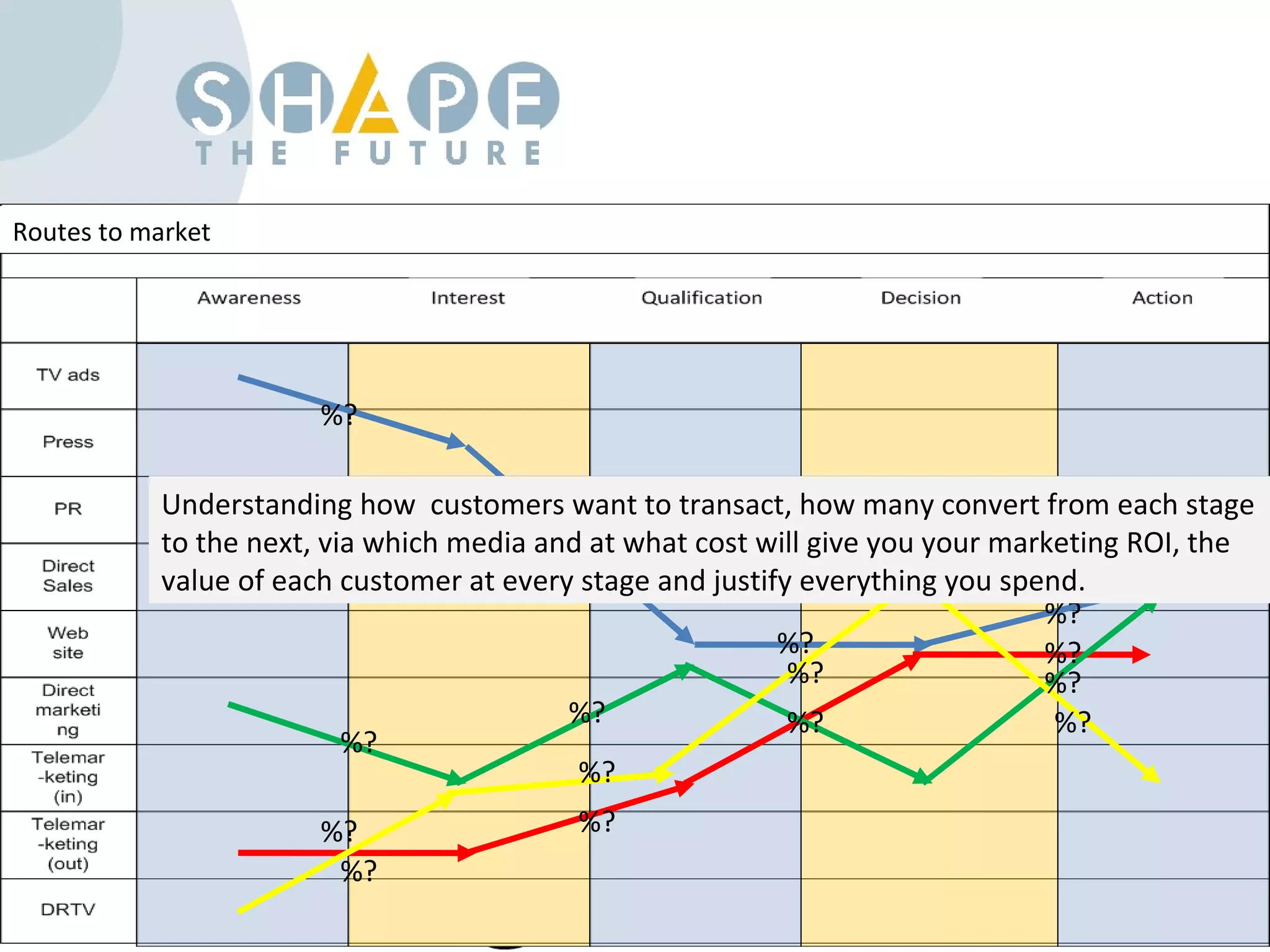
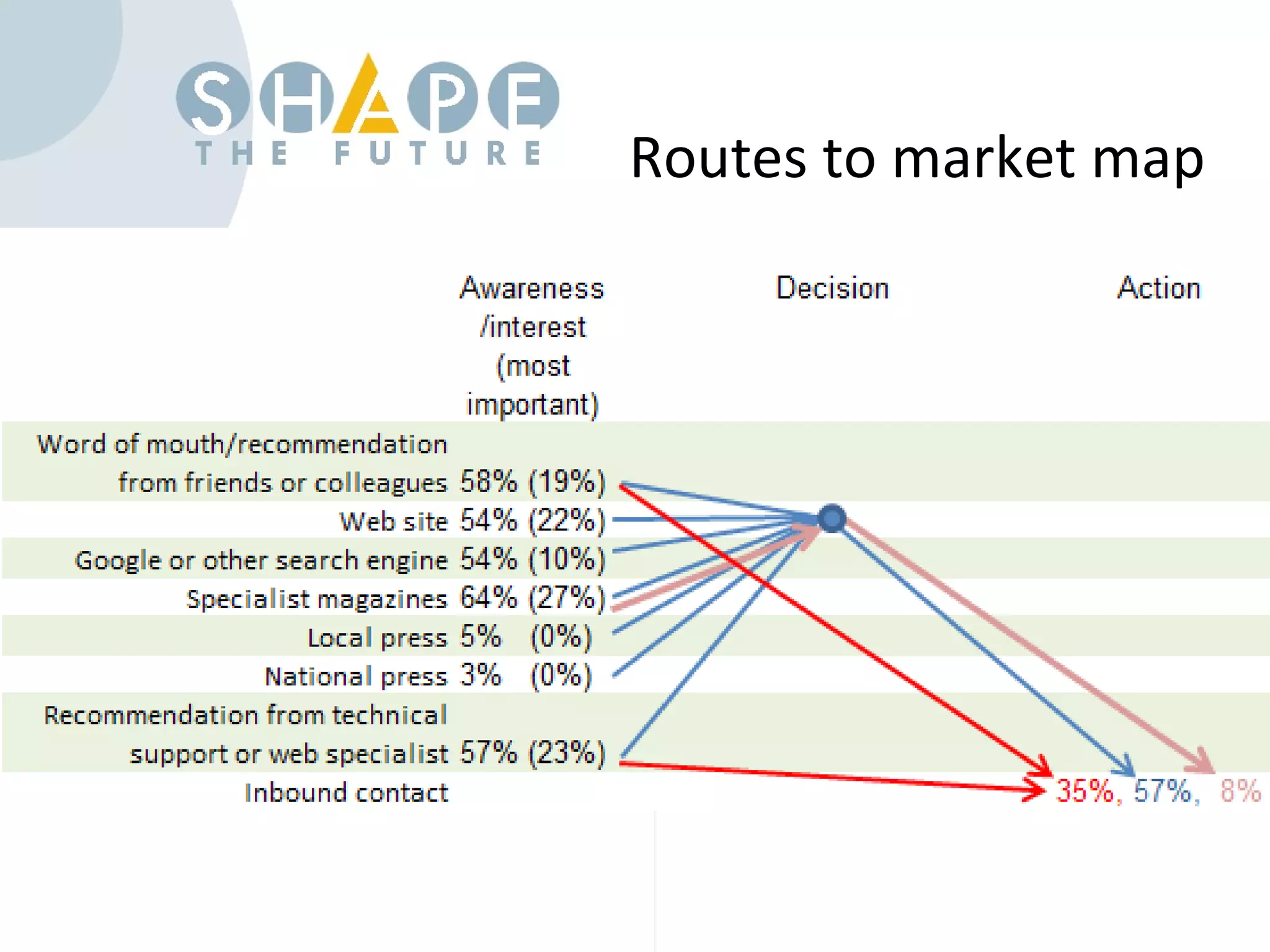
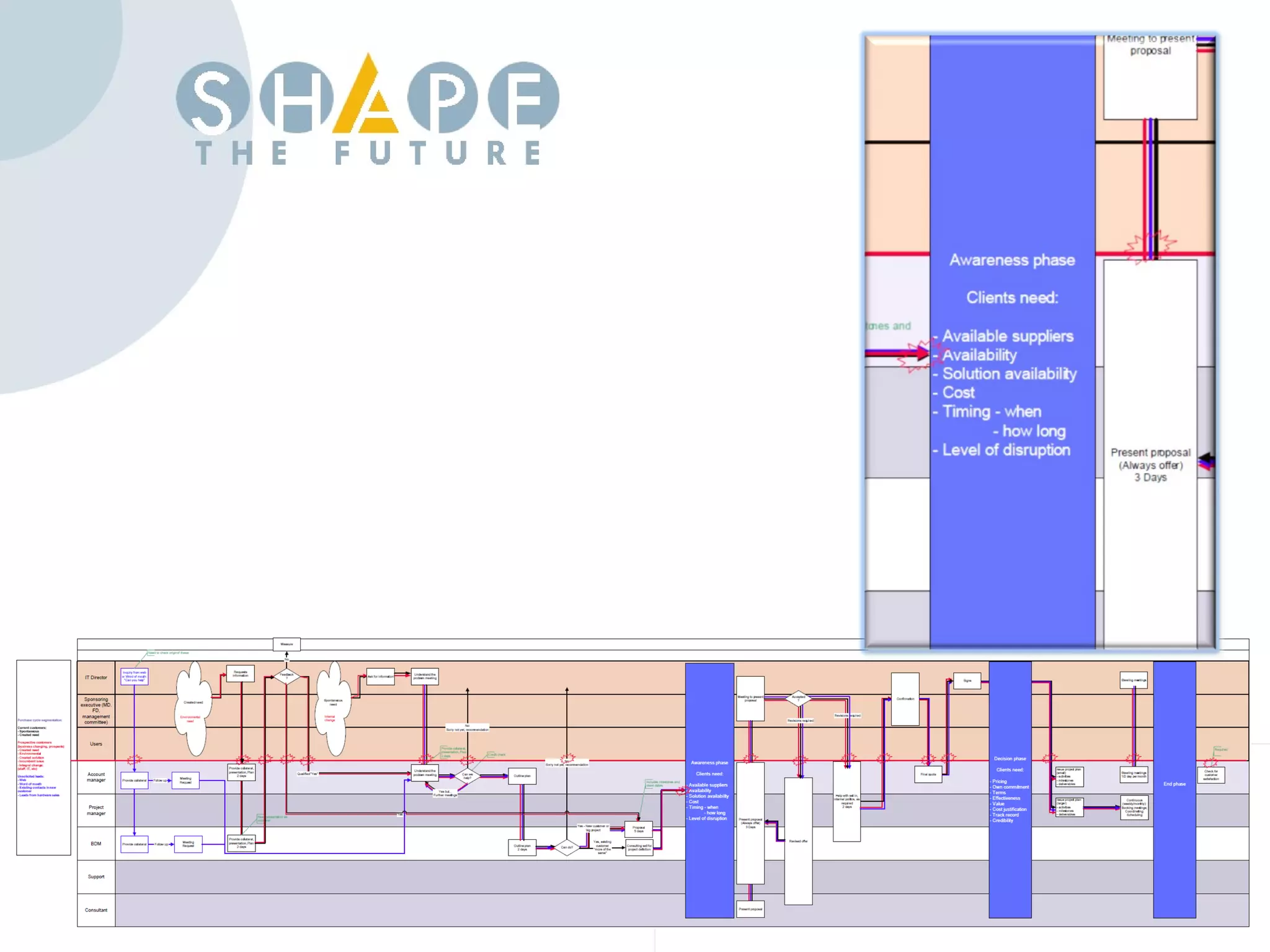
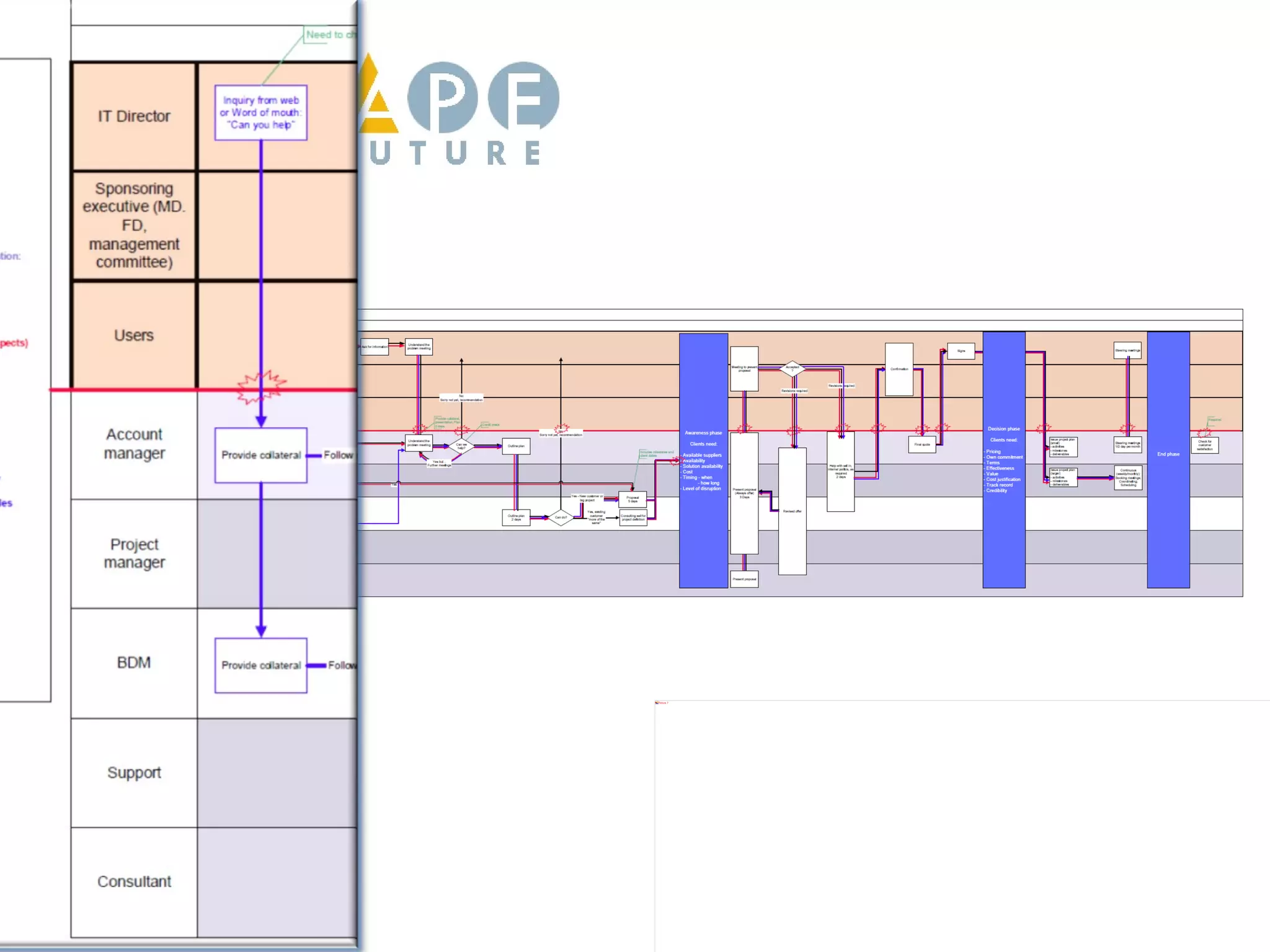
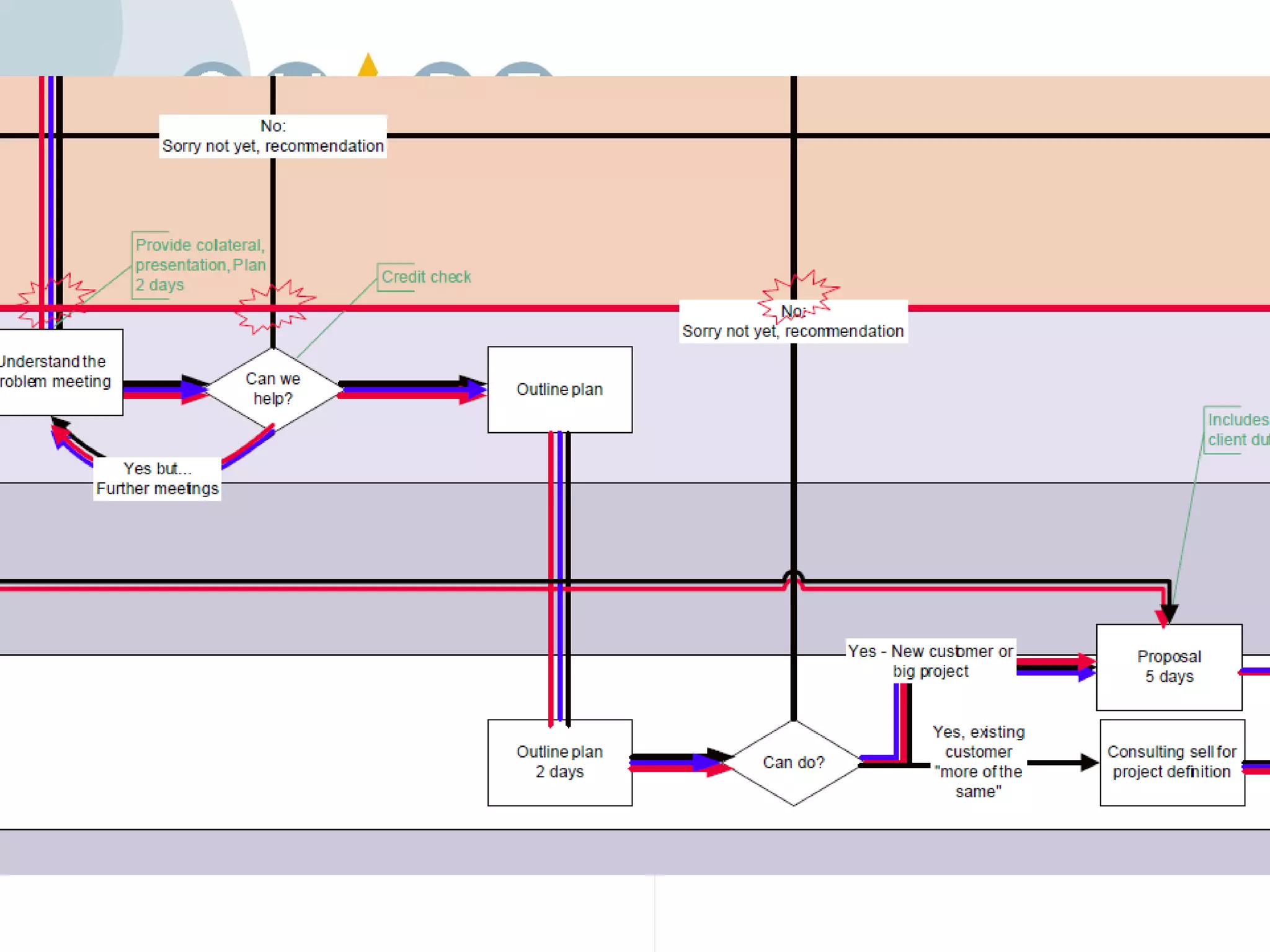
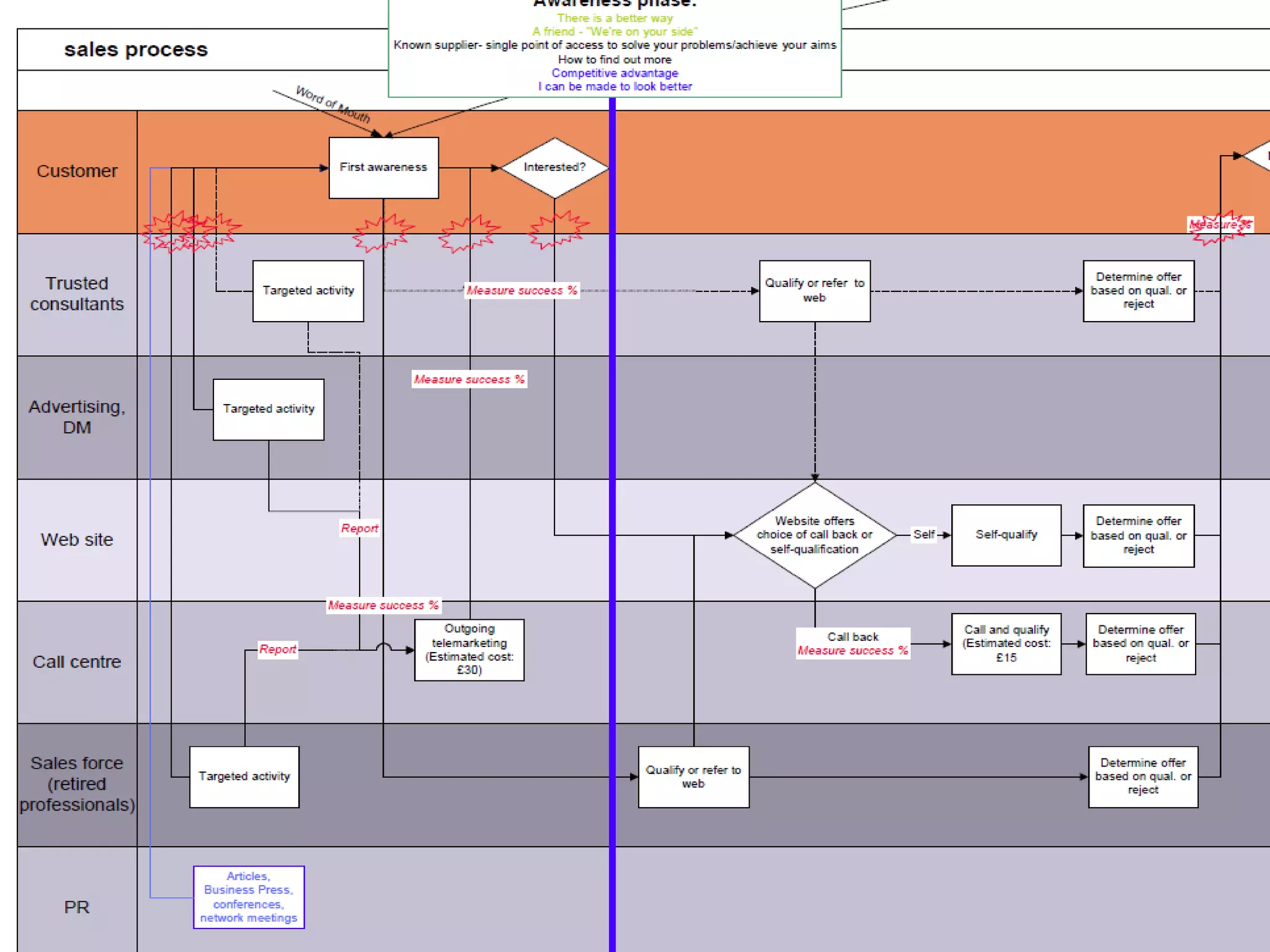
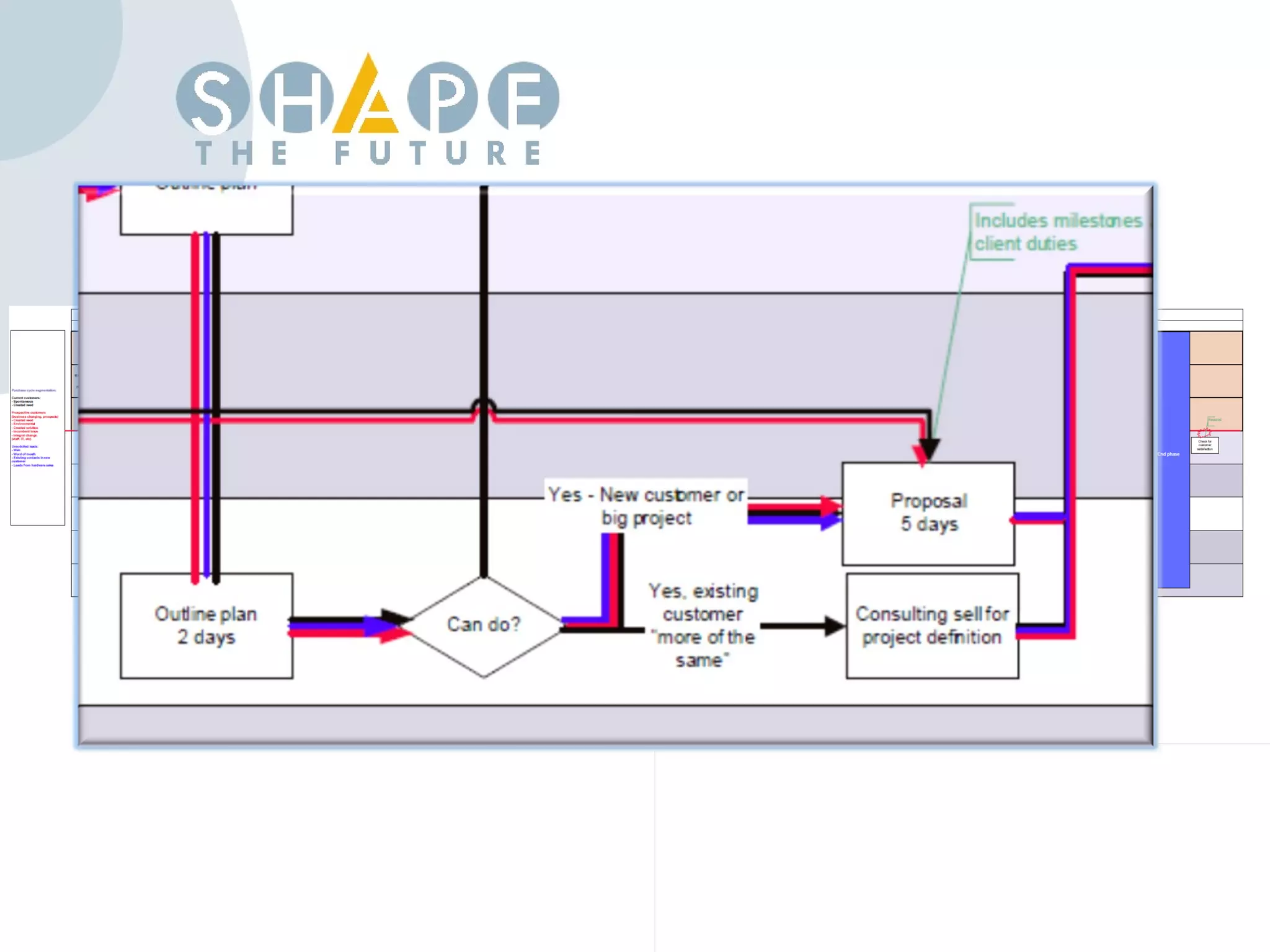
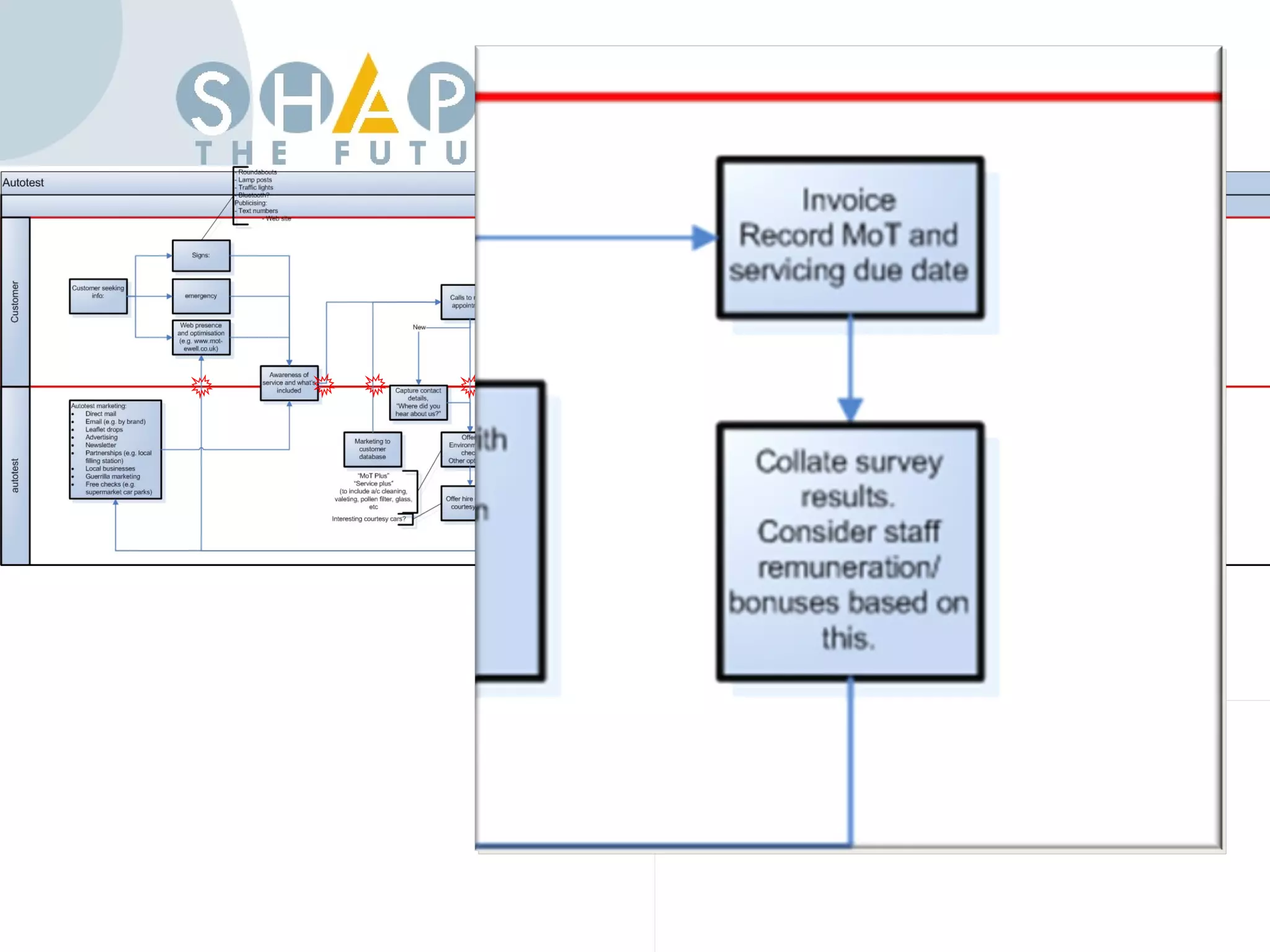
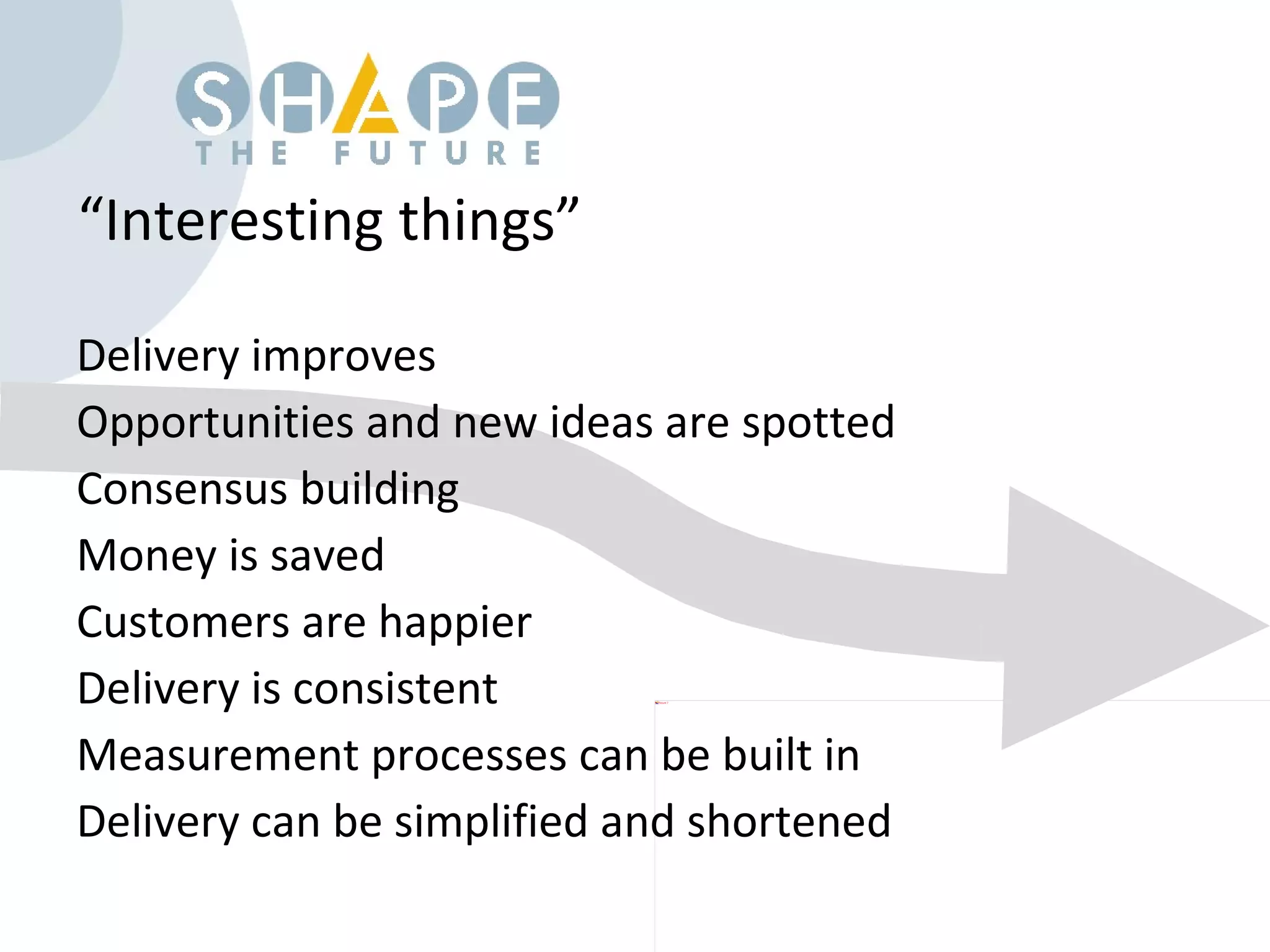
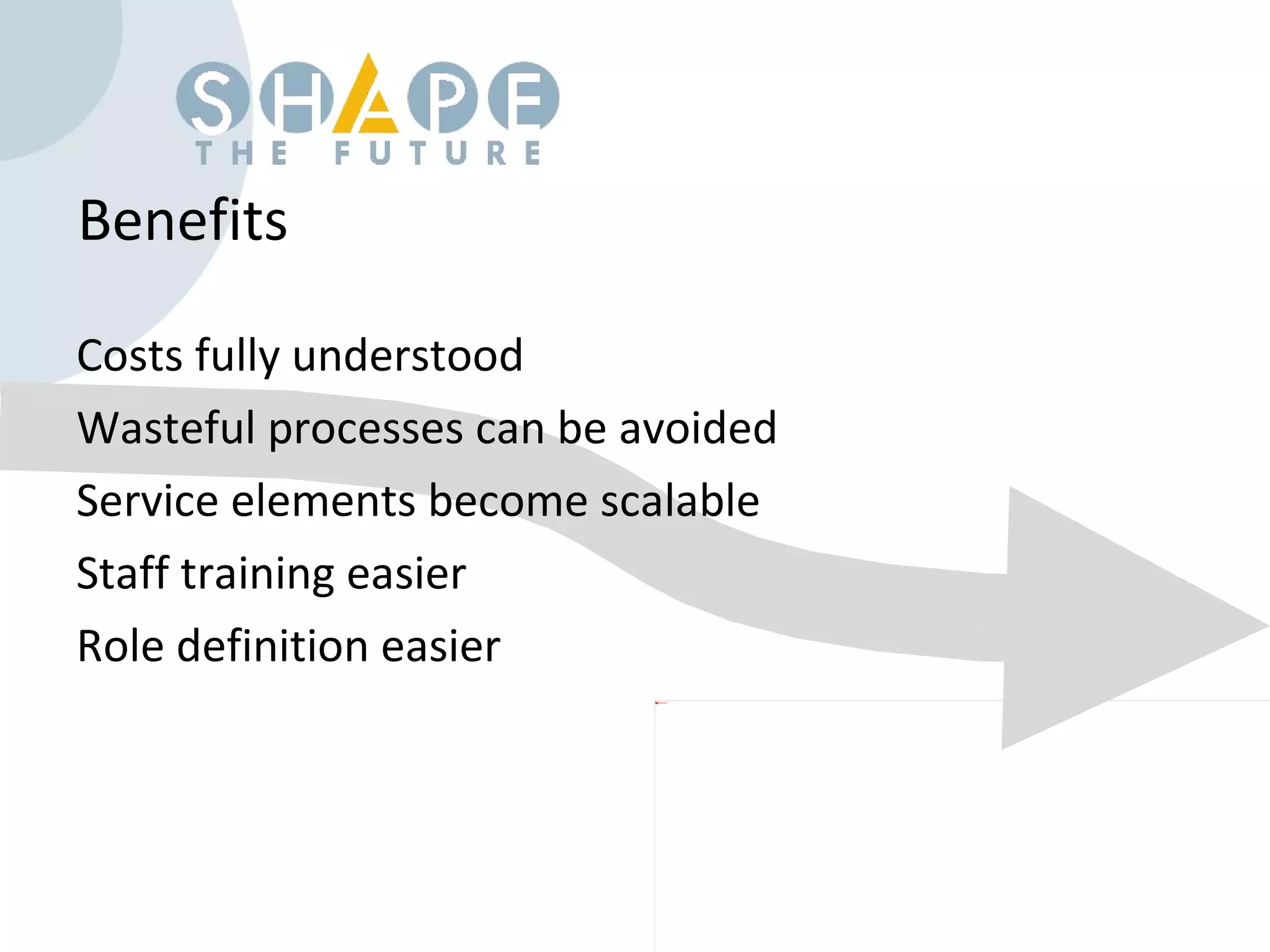
Customer journey mapping involves understanding the customer experience at each stage of their journey and dividing the journey into stages. It defines what customers need at each stage, who is involved, and plans activities to provide customers with what they want, when and where they want it. Mapping also plans for issues, assesses costs and measures effectiveness to improve the customer experience, increase satisfaction and reduce business costs.









![Thank you! Peter Martin [email_address] www.shape-the-future.com 0800 781 4045](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/customerjourneymapping290410-12-100505043204-phpapp01/75/Customer-journey-mapping-Peter-26-2048.jpg)