Embed presentation
Downloaded 32 times





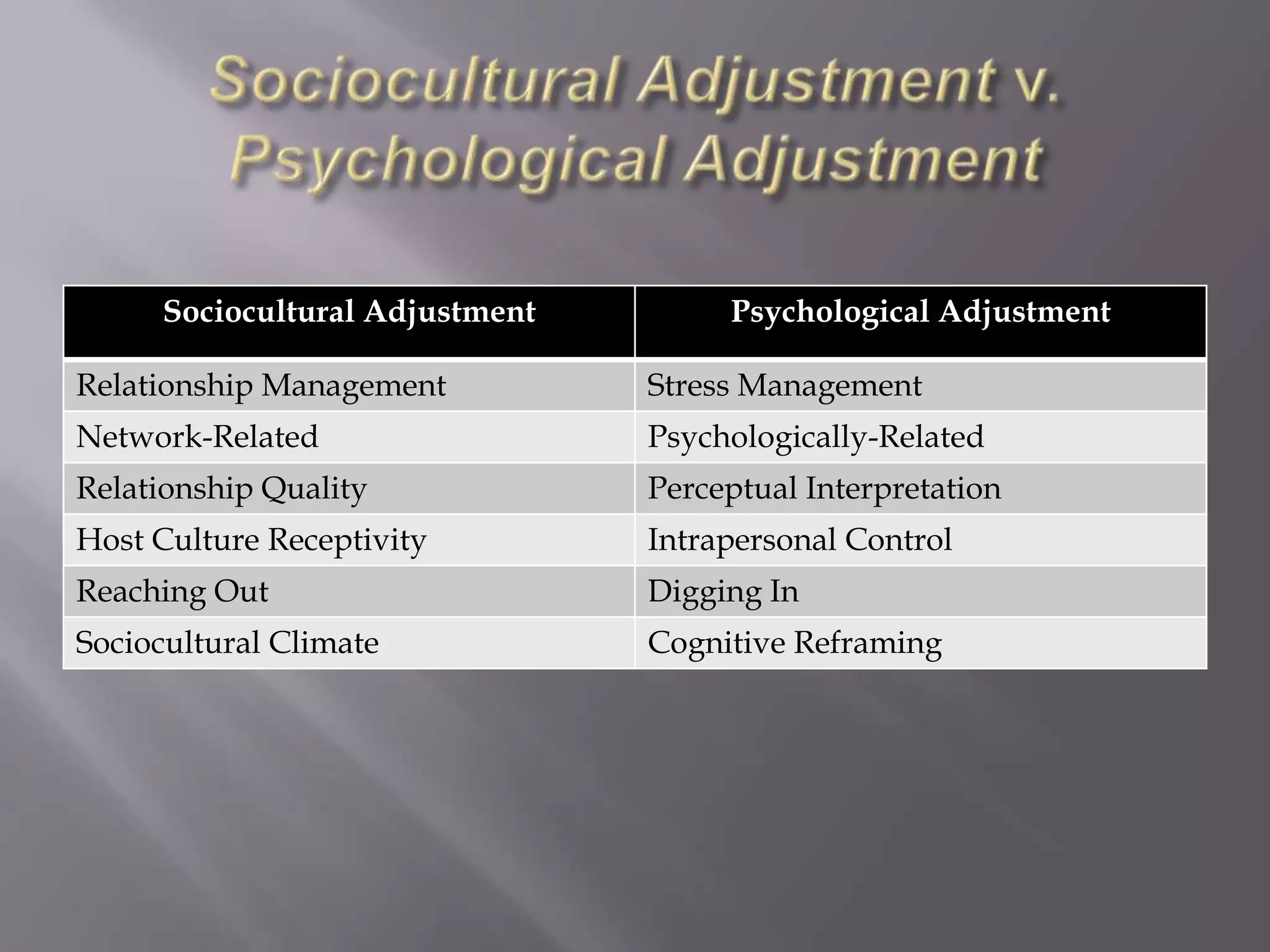
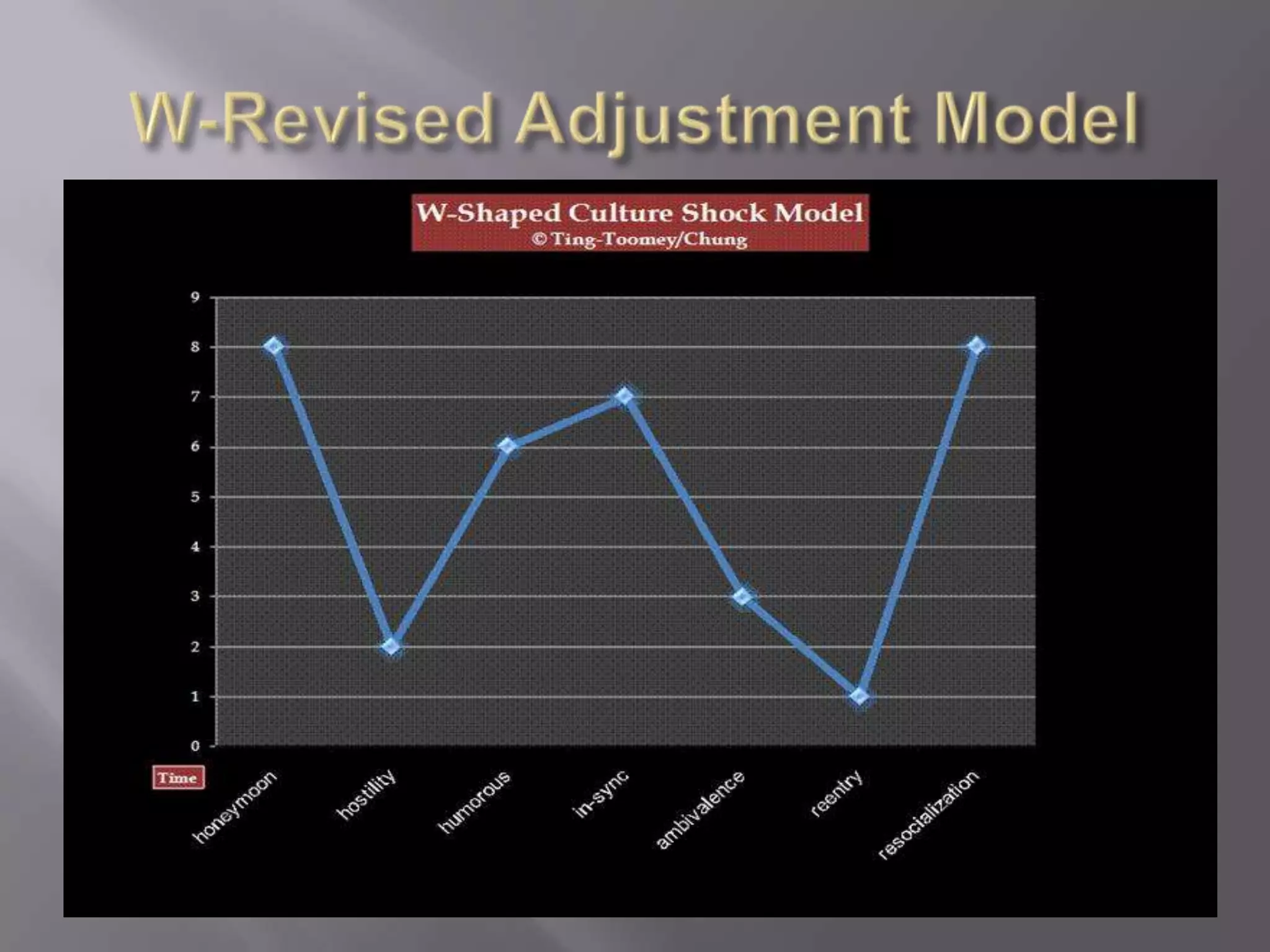

Culture shock is a stressful and disorienting experience that occurs when a person moves from a familiar culture to an unfamiliar one. It produces an identity disorientation characterized by anxiety, bewilderment, confusion over social behaviors in the new culture, and an inability to interpret unfamiliar social experiences. Several factors underlie culture shock, including motivational orientation, personal expectations, the distance between the original and new cultures, and individual personality attributes that impact sociocultural and psychological adjustment. Models of culture shock describe stages from initial excitement to feeling at home to unexpected difficulties upon returning to one's original culture.







