Cascading Style Sheets, more commonly known as CSS, is a powerful language used to control the presentation and layout of HTML documents. Since its inception in the mid-1990s by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), CSS has revolutionized web design by allowing developers to separate content from design. This separation enhances flexibility, simplifies maintenance, and provides a more consistent user experience across different platforms and devices.
CSS plays a fundamental role in web development, working in conjunction with HTML and JavaScript to create dynamic, visually appealing websites. While HTML provides the structure and content, CSS handles how that content appears. Over time, CSS has evolved significantly, and today’s web developers use advanced features like animations, responsive layouts, and grid systems that make websites more interactive and user-friendly.
---
**1. The Purpose and Philosophy of CSS**
The main goal of CSS is to separate document content from document presentation. This means keeping HTML focused on structure—like headings, paragraphs, and lists—while CSS takes care of styling aspects such as colors, fonts, spacing, and positioning.
This division of responsibilities enables a cleaner workflow. For example, designers can tweak styles without altering the HTML, and developers can modify functionality without affecting how a page looks. It also facilitates easier reusability; one CSS file can style multiple web pages, ensuring a consistent design theme across an entire website.
---
**2. The Structure of CSS**
CSS works through a set of rules. Each rule targets specific HTML elements and assigns them styles. A CSS rule consists of a selector and a declaration block. The selector identifies the HTML element to style, while the declaration block contains one or more styling instructions.
The rules themselves follow a cascading and inheritable structure. This means that styles can trickle down from parent to child elements and that rules defined later can override earlier ones if conflicts occur. This behavior is referred to as the “cascade,” and it's governed by the source order, specificity, and importance of rules.
---
**3. Selectors and Their Role**
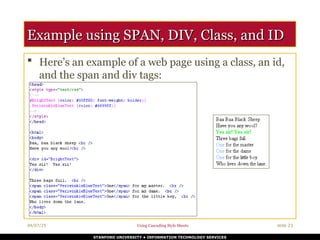
Selectors are patterns used to identify HTML elements for styling. CSS offers a wide range of selectors, which can be simple or complex depending on the desired effect. Common types include element selectors, class selectors, and ID selectors.
Element selectors target all instances of a particular HTML tag. Class selectors target elements that carry a specific class attribute, and ID selectors apply styles to a single element with a unique ID. There are also more advanced selectors, such as attribute selectors, pseudo-classes, and pseudo-elements, which enable thi







![04/07/25 Using Cascading Style Sheets slide 8
STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Grouping Styles and Selectors
Grouping Styles and Selectors
Each rule can include multiple styles by simply separating them by semicolons:
h2 { color: darkblue; font-style: italic;}
Additionally, multiple selectors that have the same styles can be grouped by separating them with commas:
h1, h2, h3 { color: darkblue; font-style: italic;}
Contextual selectors allow you to specify that something will change, but only when it is used in conjunction
with something else. With the following style, strong will be displayed in red, but only when it occurs
within li within ul.
ul li strong { color: red;}
Elements being modified by contextual selectors need not appear immediately inside one another (using
this style, blah would still be red text: <ul><ol><li><strong> blah </strong></li></ol></ul>).
Direct child selectors allow you to specify that something will change, but only those that are immediately
inside of another element. With the following style, only those strong elements that are directly inside of
an h1 will be purple; no strong tags deeper within the sheet will be purple.
h1 > strong { color: purple;}
Adjacent selectors allow you to specify that something will change, but only when preceded by something
else. With the following style, only those links (a) that are preceded by an h2 will be green.
h2 + a { color: green;}
Elements being modified by adjacent selectors appear immediately after one another. Using this style, this
link would be green: <h2>Visit Stanford!</h2><a href="http://www.stanford.edu">click here</a>.
This link would not: <h2>Visit Stanford! <a href="http://www.stanford.edu">click here</a></h2>.
You can also group selectors by attribute. With the following style, centered h2 tags (<h2 align="center">)
will be surrounded by a dotted border:
h2[align="center"] { border: dotted;}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css-presentation-250407055259-dd7dd590/85/css-presentation-for-beginner-students-ppt-8-320.jpg)









![04/07/25 Using Cascading Style Sheets slide 18
STANFORD UNIVERSITY • INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
Inline vs. Block Display (HTML)
Inline vs. Block Display (HTML)
All HTML elements (tags) are assigned a display
property value of either inline or block.
Inline elements display in browsers horizontally.
[INLINE ELEMENT 1] [INLINE ELEMENT 2] [INLINE ELEMENT 3]
Block elements display in browsers vertically (stacked
one on top of the other).
[BLOCK ELEMENT 1]
[BLOCK ELEMENT 2]
[BLOCK ELEMENT 3]
Examples of inline elements:
<a> <img> <strong> <em> <span>
Examples of block elements:
<p> <h1-h6> <div> <hr> <table> <ul> <ol>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css-presentation-250407055259-dd7dd590/85/css-presentation-for-beginner-students-ppt-18-320.jpg)