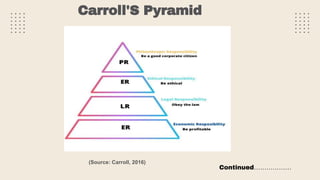
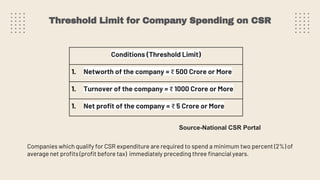
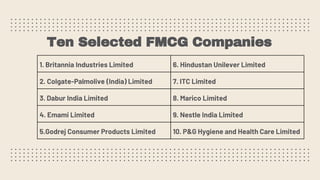
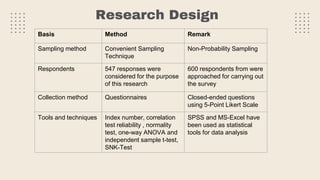
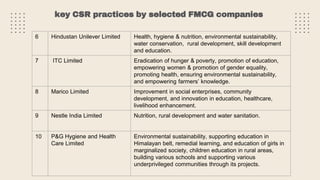
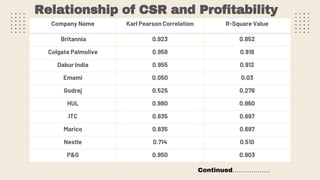
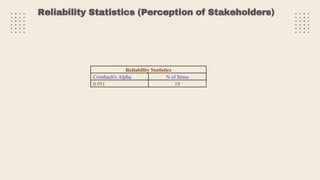
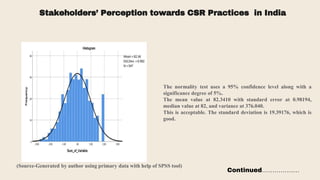
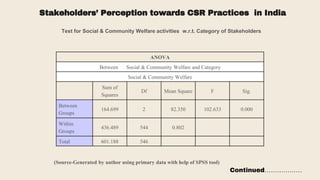
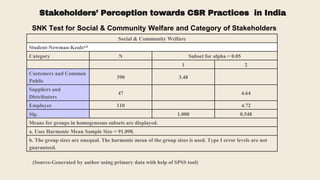
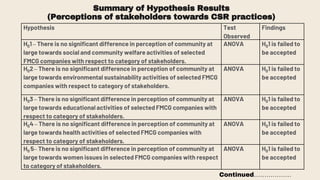
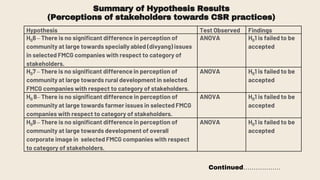
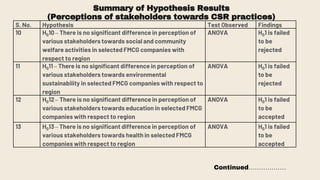
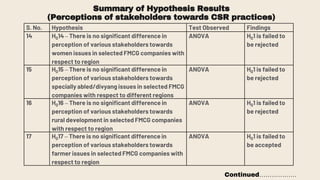
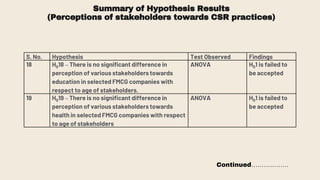
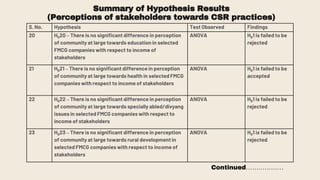
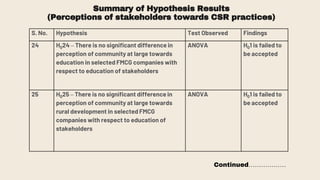
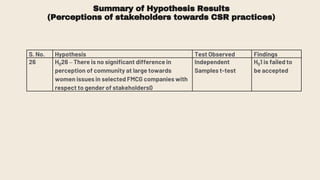
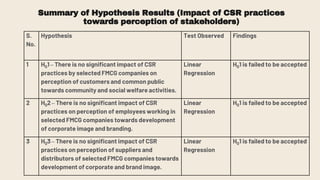
This document provides an overview of a research study on corporate social responsibility (CSR) practices of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) companies in India. The study aims to examine key CSR activities, trends in CSR spending, the relationship between CSR spending and profitability, and stakeholders' perceptions of CSR. It also seeks to identify new opportunities for CSR. The researcher conducted secondary data analysis of CSR reports and surveyed 547 stakeholders to understand perceptions. Statistical tools like index numbers, correlation tests, and reliability analysis were used to analyze the data.