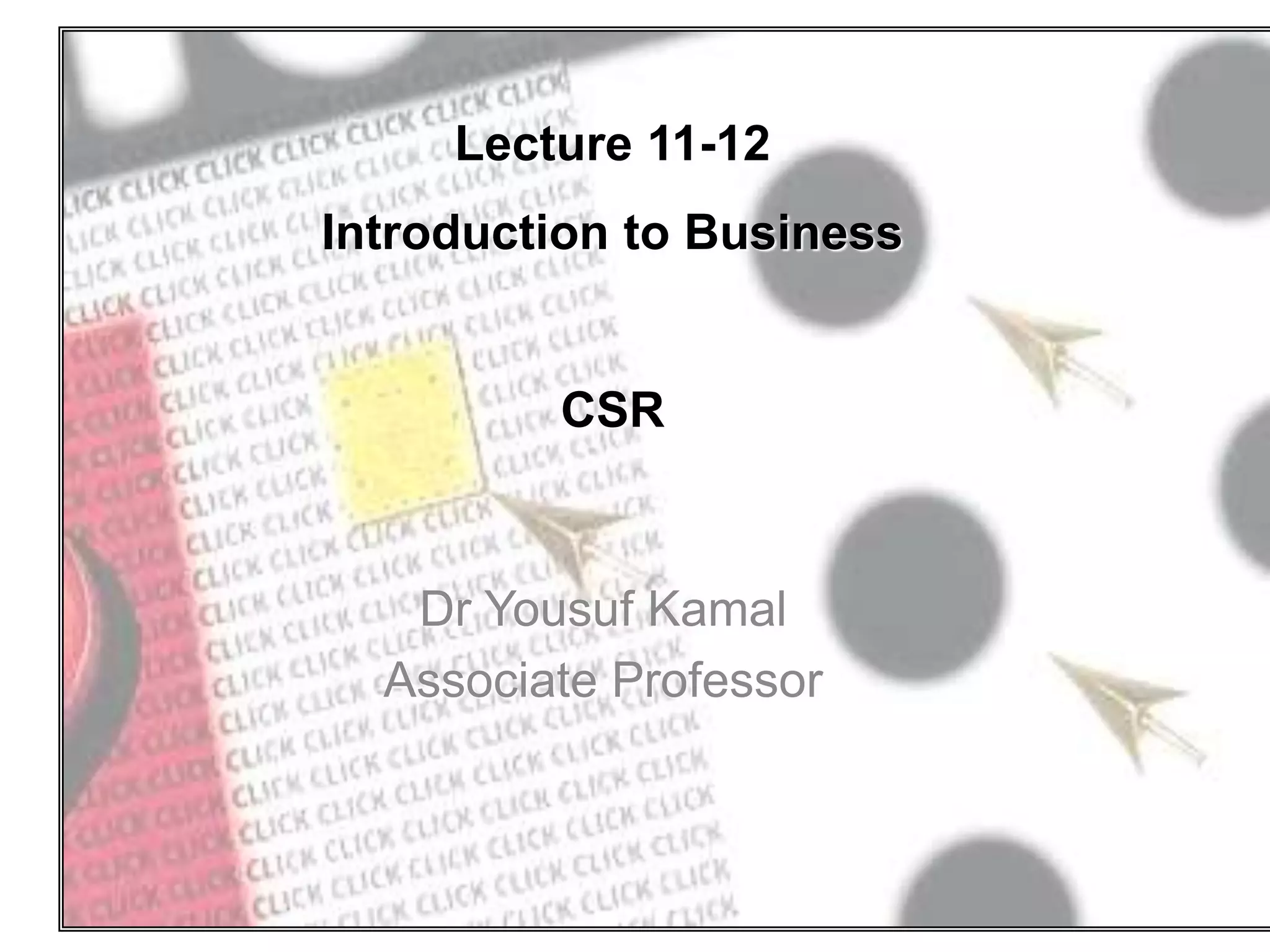
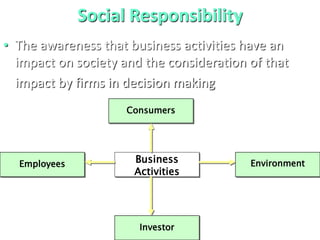
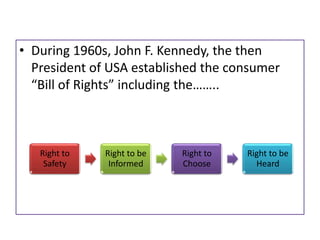
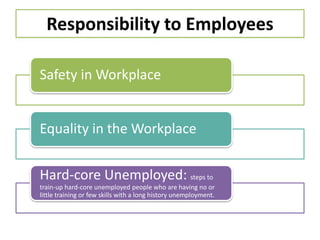
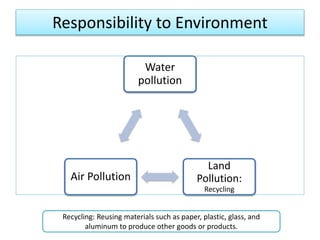
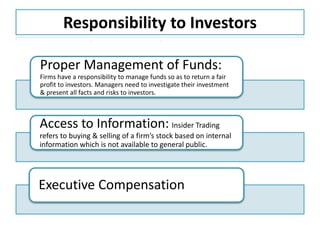
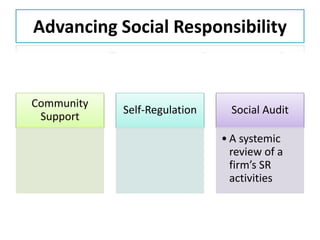
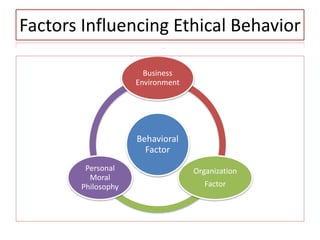
This document discusses the concepts of corporate social responsibility (CSR) and business ethics. It outlines the responsibilities that businesses have to various stakeholders like consumers, employees, the environment, and investors. Businesses must consider the impact of their activities on society. CSR involves voluntarily engaging in socially beneficial activities and reducing negative impacts. Firms that practice CSR gain benefits like positive publicity and customer loyalty. The document also discusses factors that influence ethical behavior in businesses.