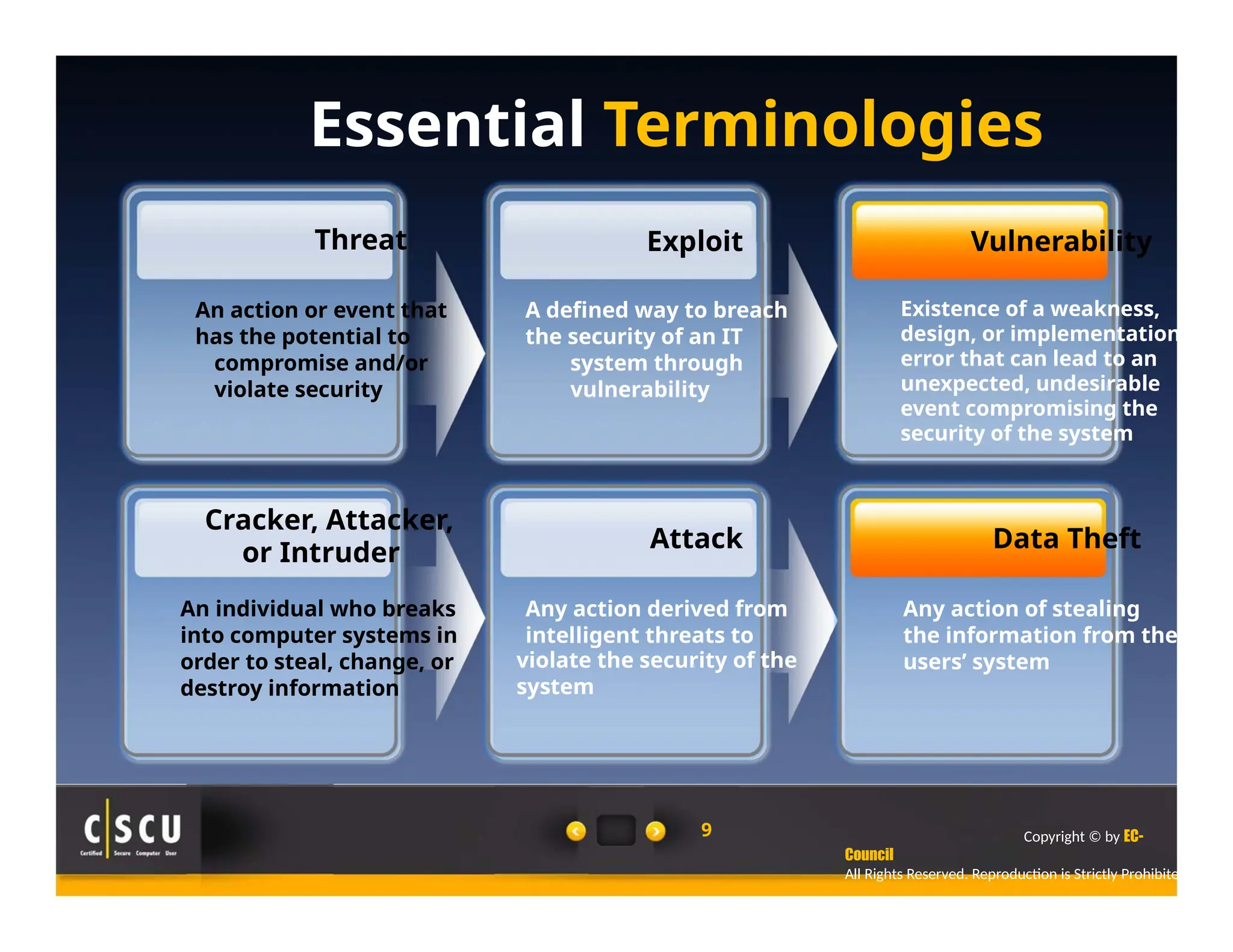
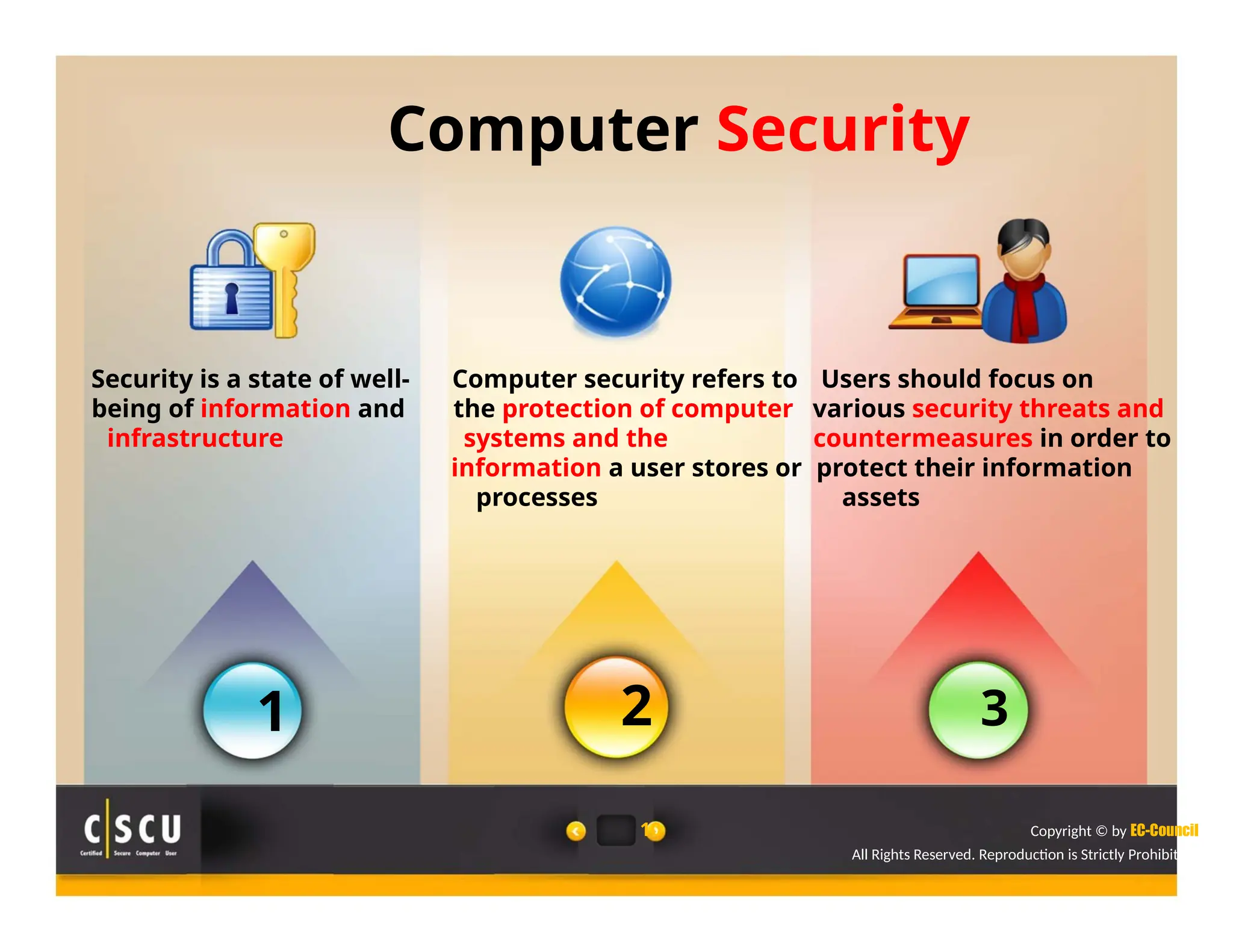
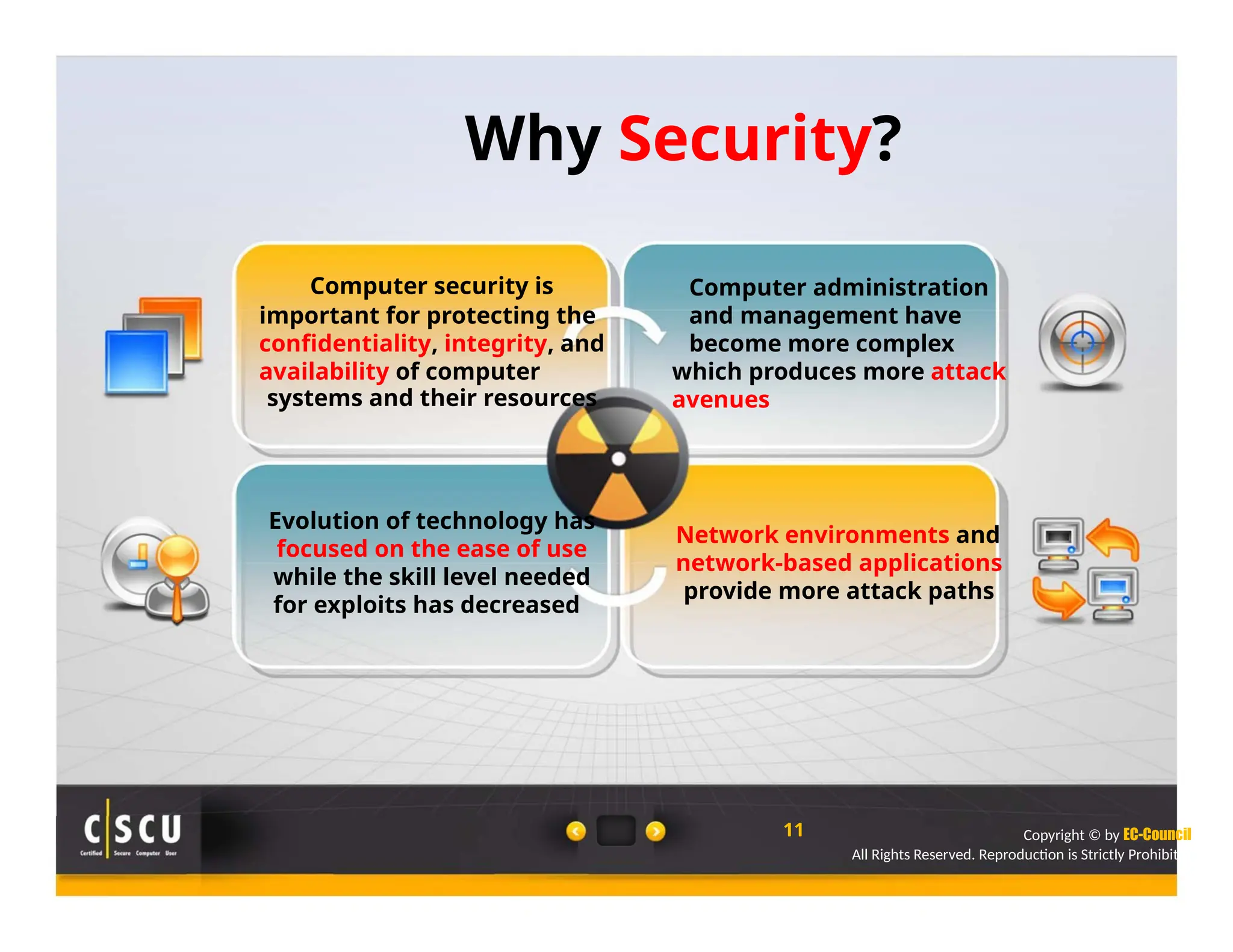
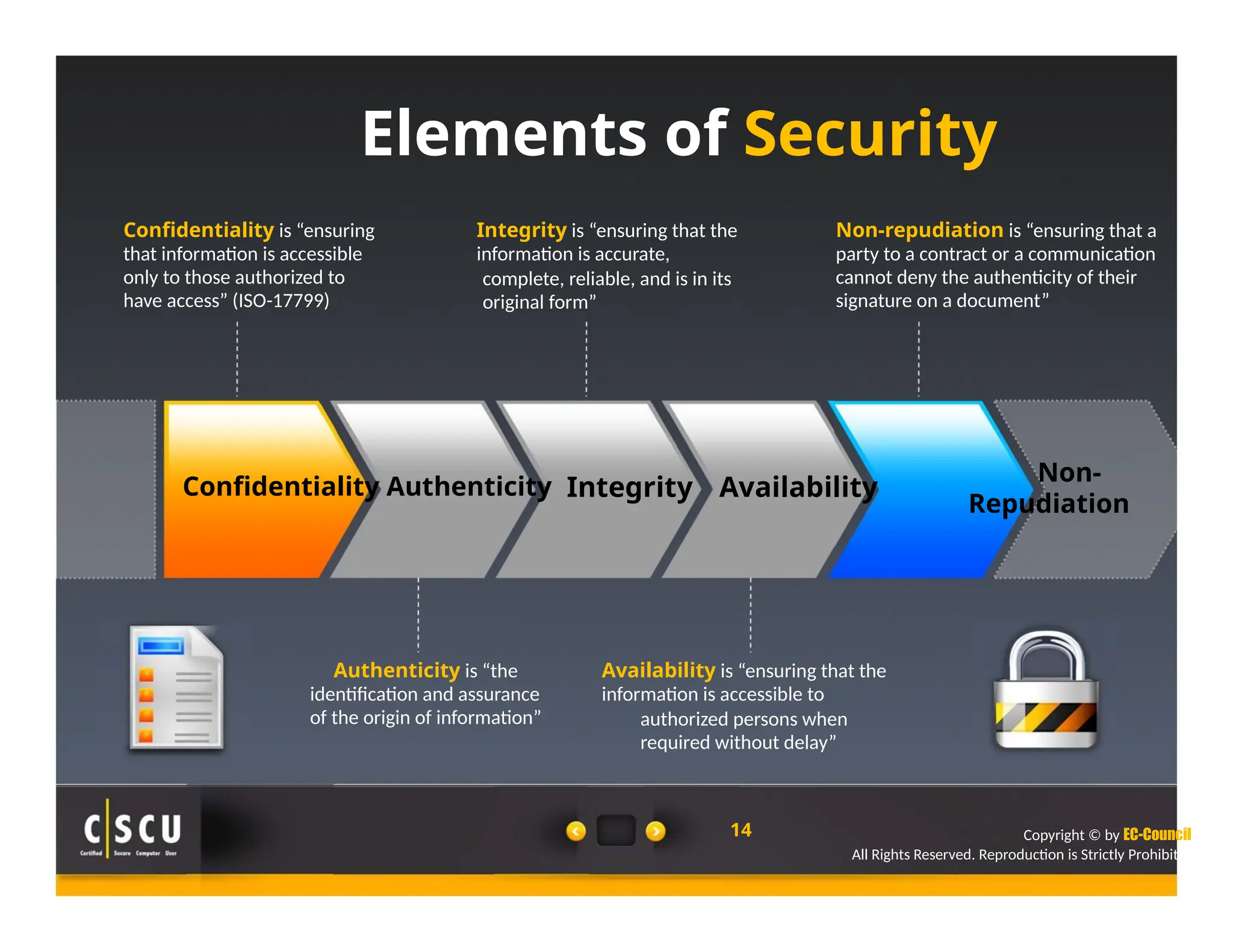
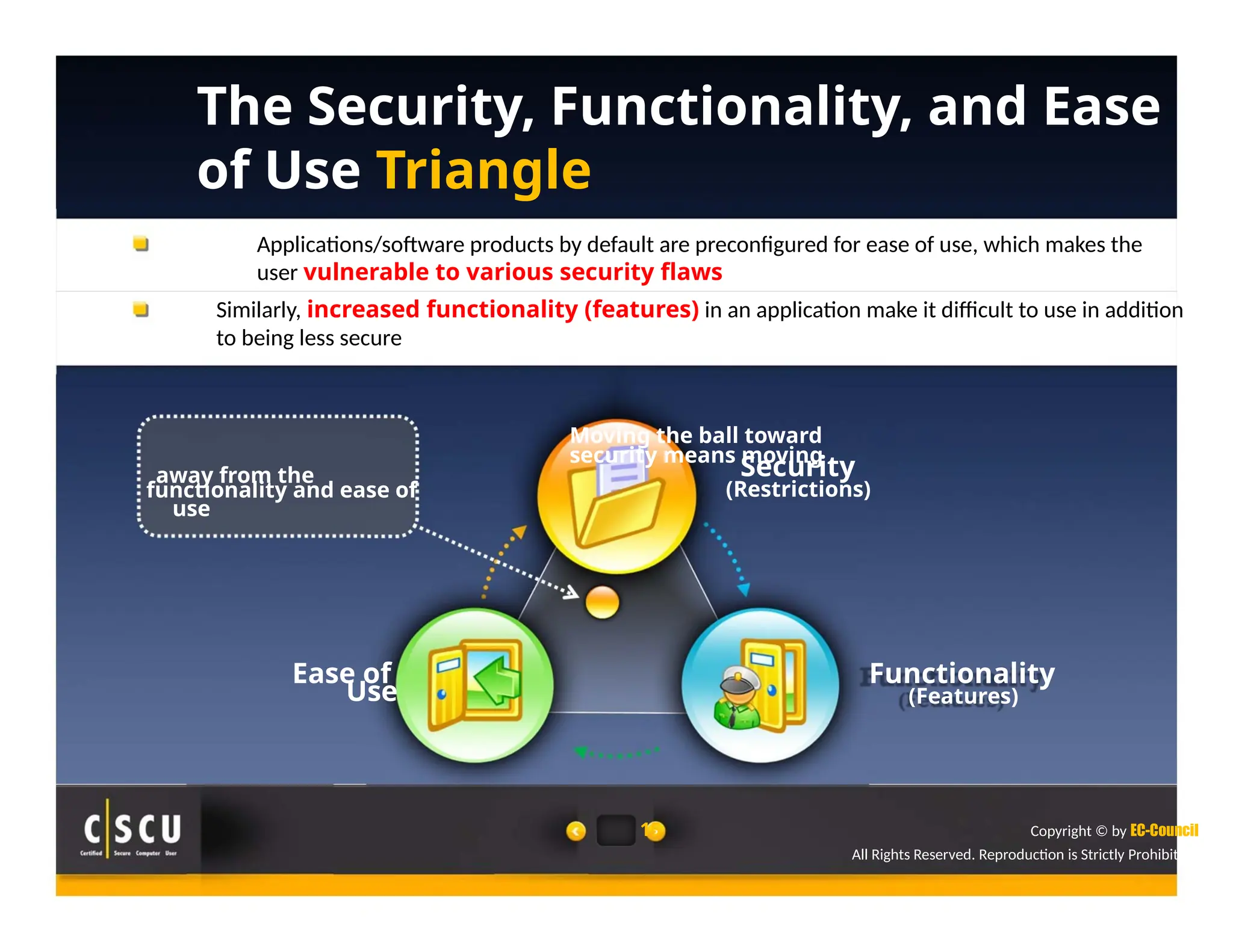
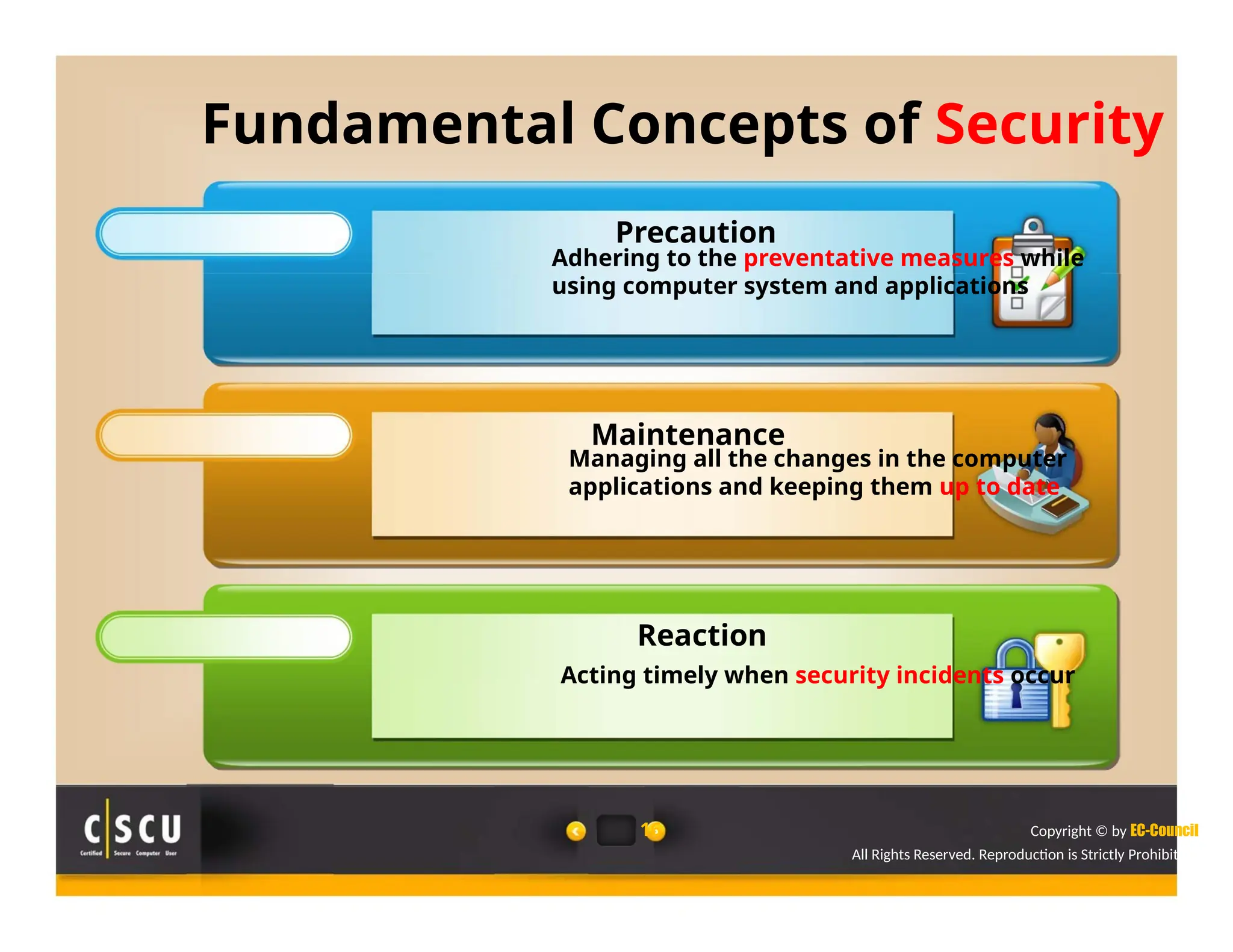
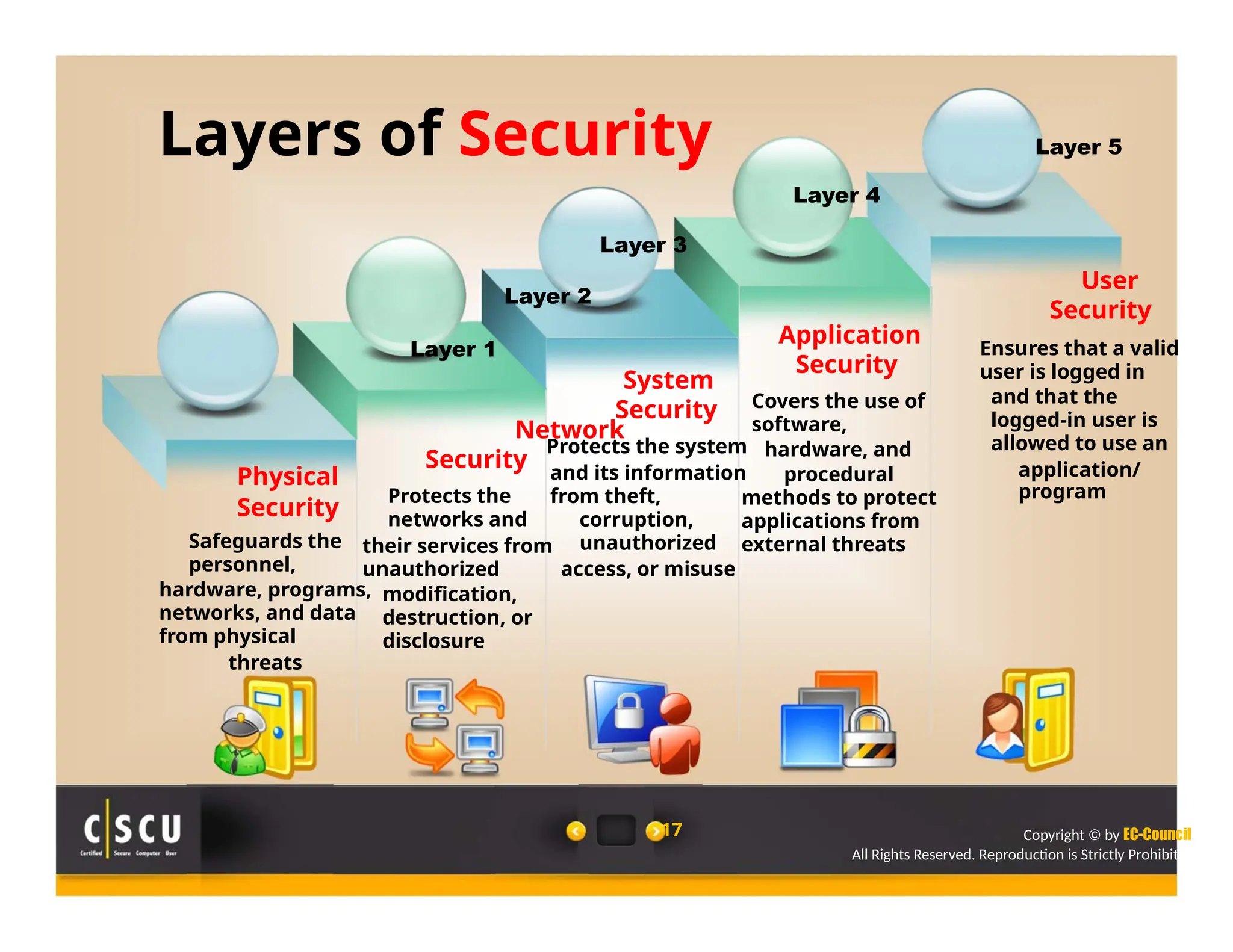
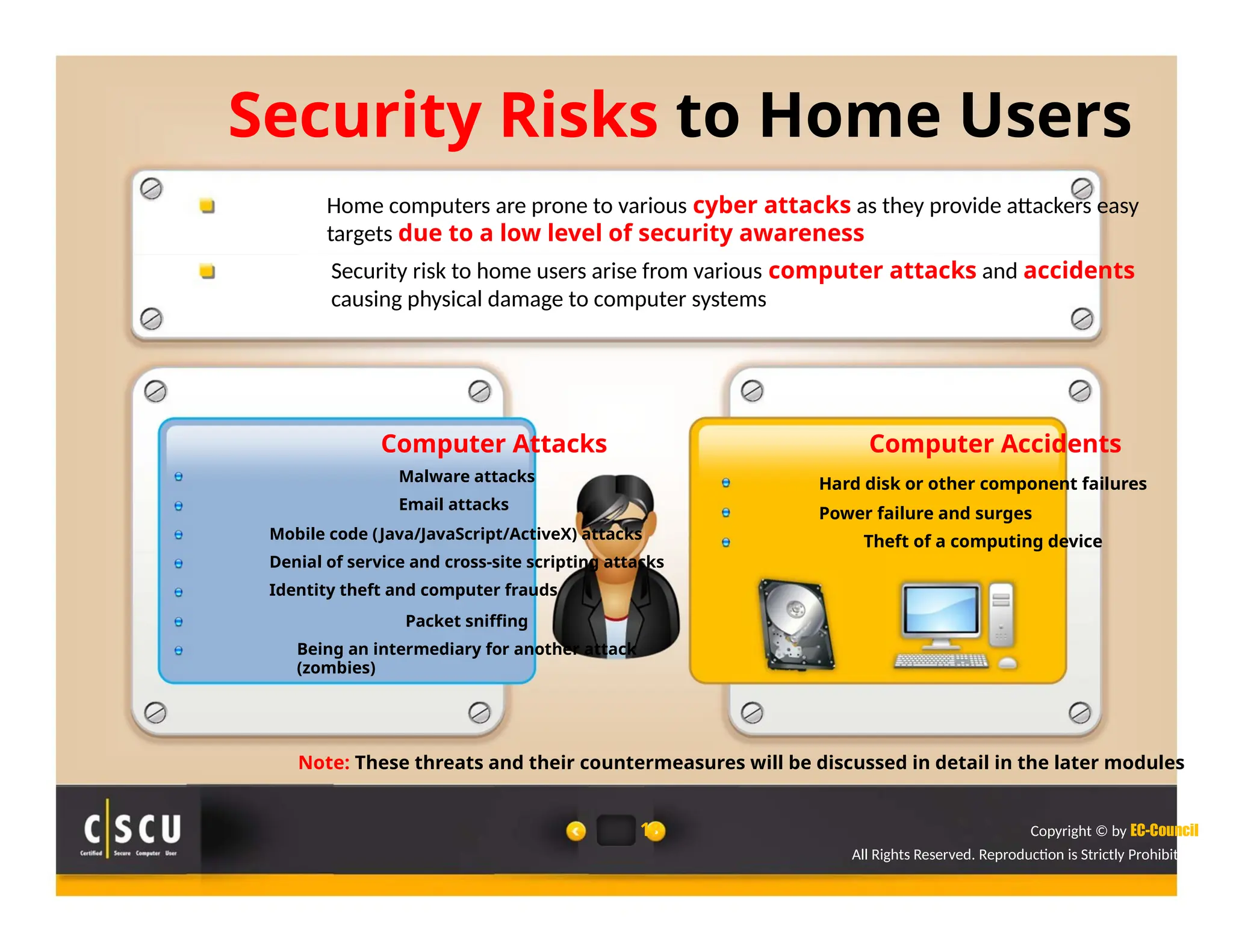
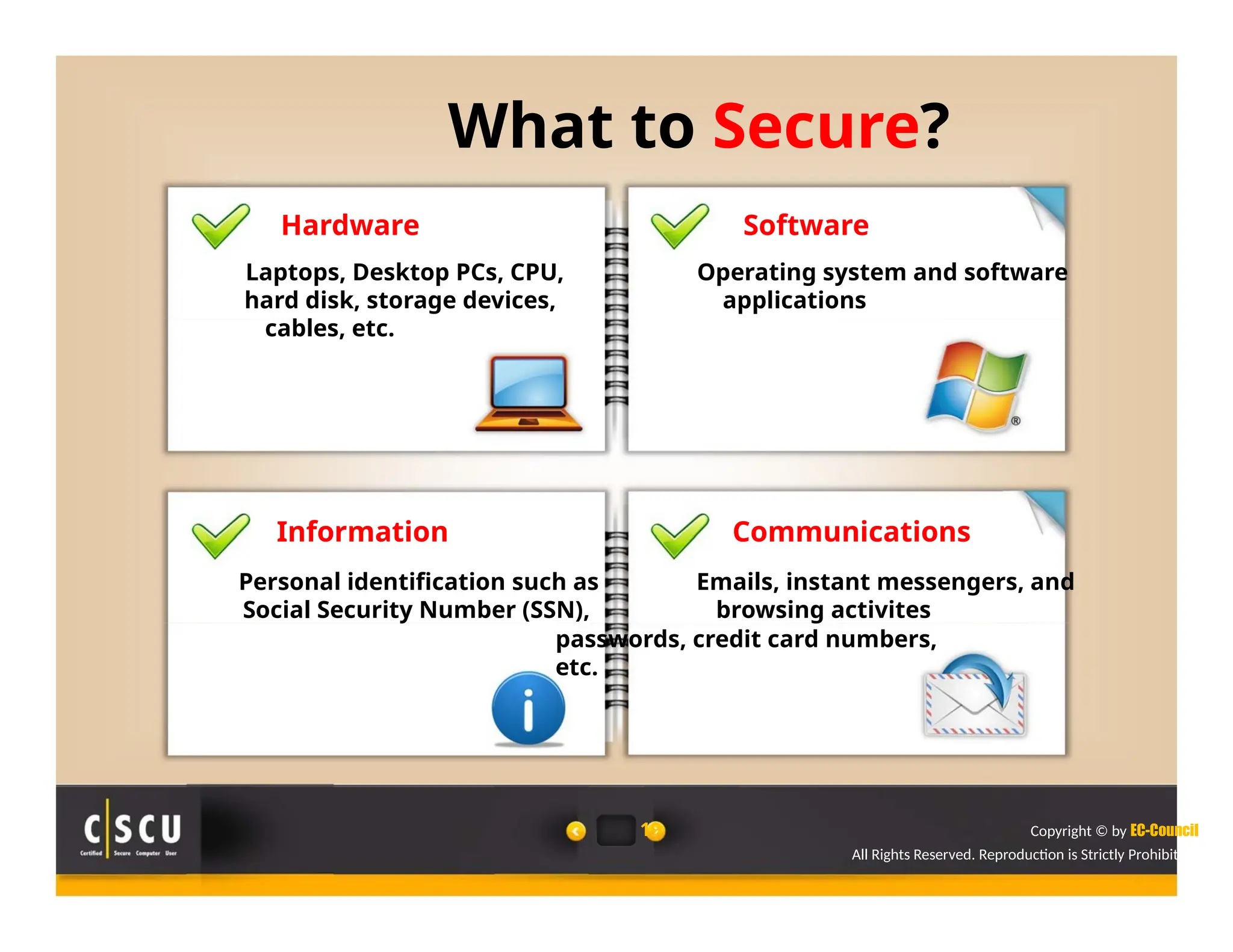
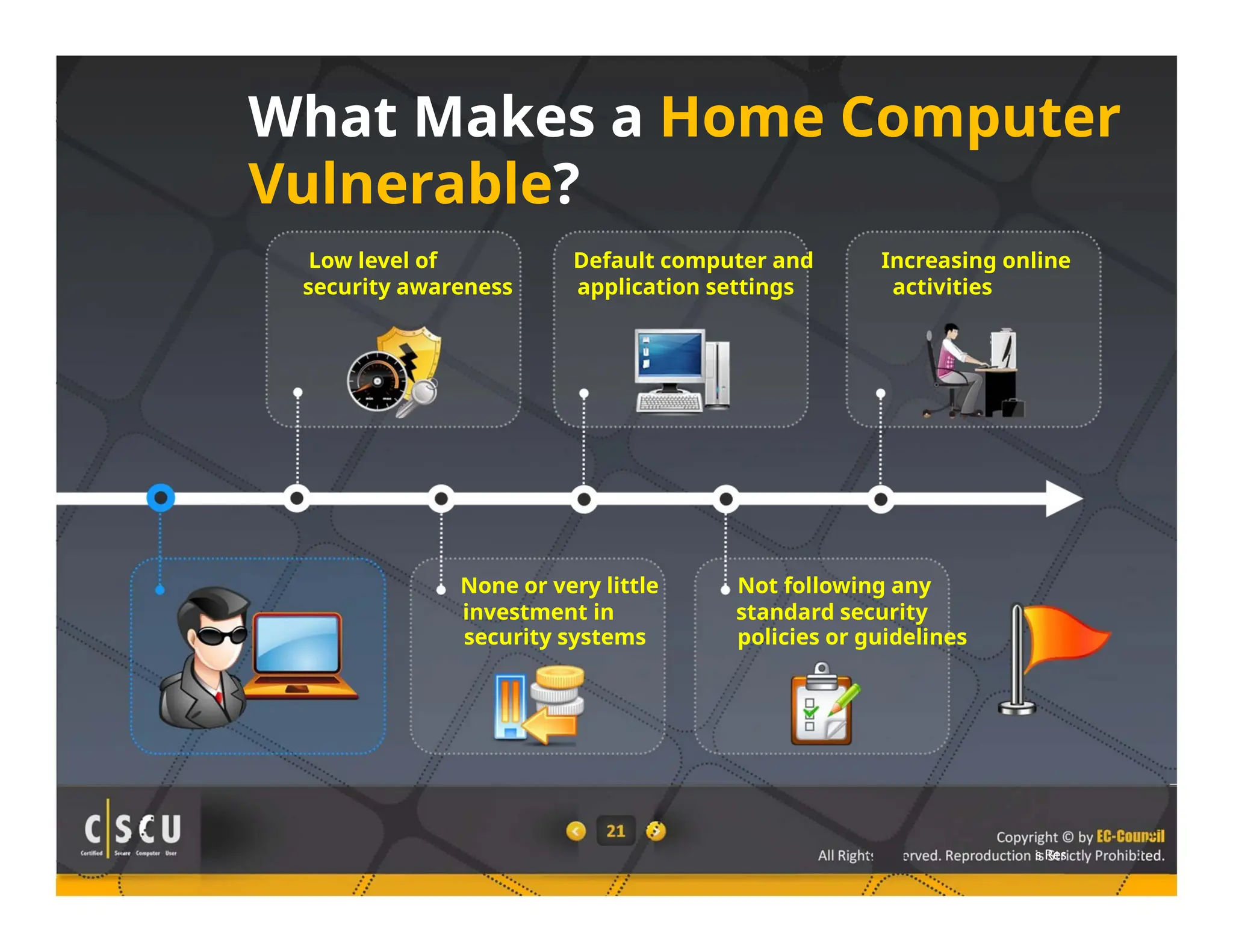
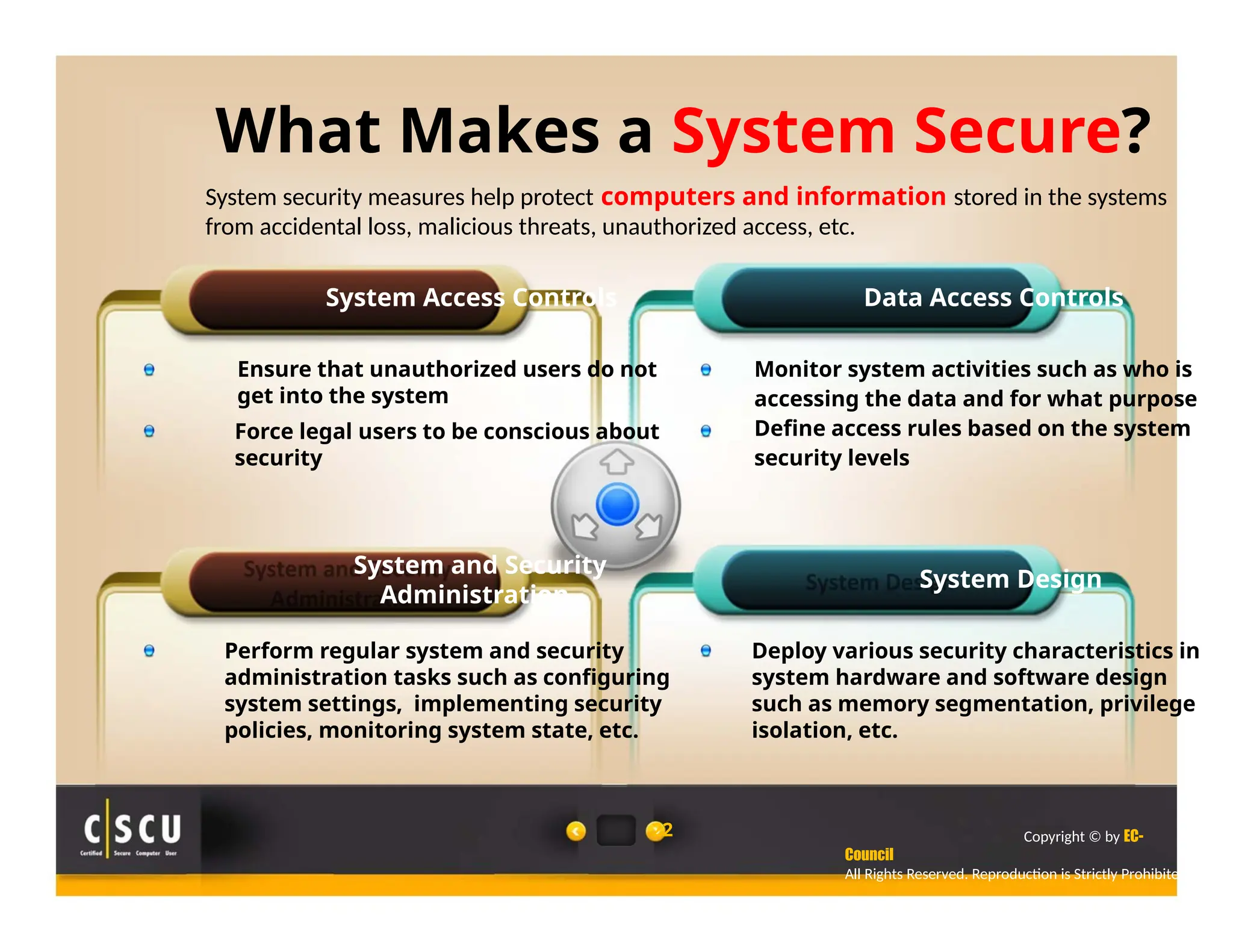
The document outlines the foundations of computer security, emphasizing the importance of protecting information and computer systems from security risks, particularly for home users. It covers essential terminologies, potential security threats, and fundamental security concepts like confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Additionally, it highlights the significance of computer security awareness and provides guidance on basic security measures to mitigate risks.