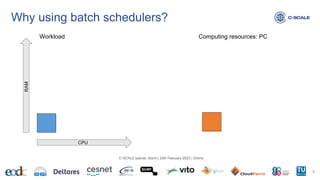
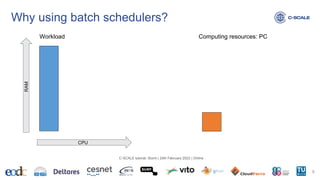
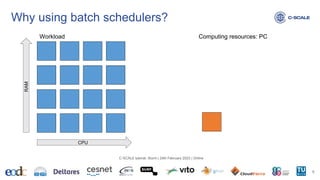
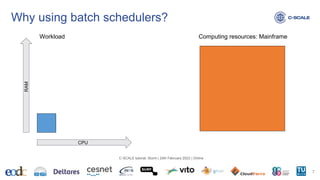
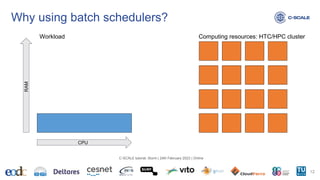
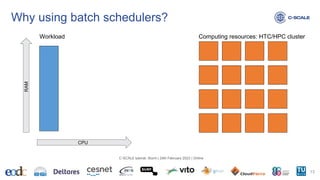
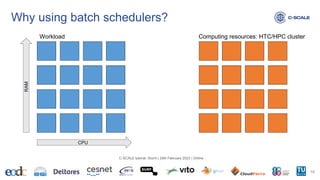
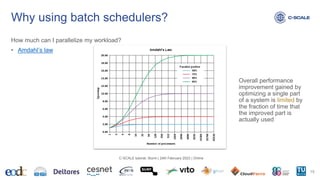
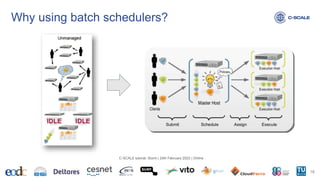
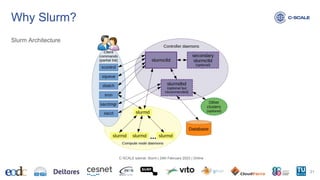
This document provides an introduction to using the Slurm workload manager on HPC clusters. It explains that batch schedulers like Slurm are useful for parallelizing jobs that require more resources than a single computer has. It then gives an overview of Slurm's architecture and goals before demonstrating how to profile jobs, learn about cluster resources, and submit jobs using sbatch.



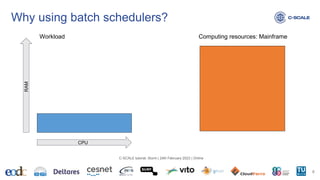
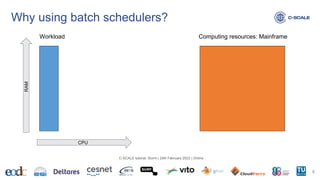
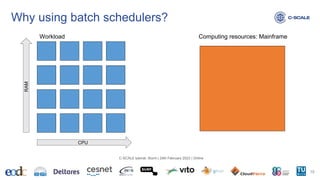
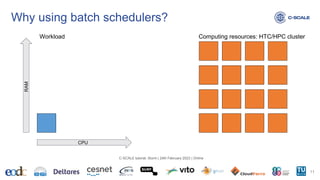







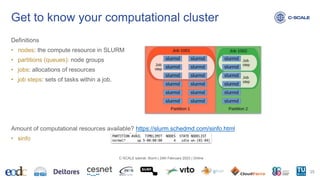





![Amount of resources available in a specific partition? https://slurm.schedmd.com/scontrol.html
• scontrol show node wn-01
• scontrol show node fat[41-44]
Get to know your computational cluster
31
C-SCALE tutorial: Slurm | 24th February 2023 | Online](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2023-02-24-c-scale-tutorial-slurm-230914100312-f7901d97/85/C-SCALE-Tutorial-Slurm-31-320.jpg)

![Is the cluster empty of busy? https://slurm.schedmd.com/squeue.html
• squeue
• squeue -u $USER
• squeue --partition=el7taskp
• squeue --nodelist=fat[41-44]
Get to know your computational cluster
33
C-SCALE tutorial: Slurm | 24th February 2023 | Online](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2023-02-24-c-scale-tutorial-slurm-230914100312-f7901d97/85/C-SCALE-Tutorial-Slurm-33-320.jpg)
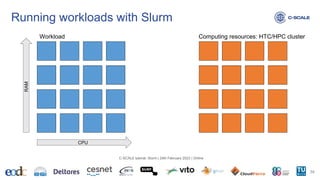

![Let’s submit jobs! https://slurm.schedmd.com/sbatch.html
• sbatch --ntasks=<number> # number of tasks
• sbatch --nodes=<number> # number of nodes requested
• sbatch --ntasks-per-node=<ntasks> # number of tasks per node
• sbatch --cpus-per-task=<number> # threads per task
• sbatch --mem=<size>[units] # amount of memory per node. Units: [K|M(default)|G|T]
Following examples based on: https://doc.aris.grnet.gr/run/job_submission/
• Check out example MPI and OpenMP jobs
Running workloads with Slurm
36
C-SCALE tutorial: Slurm | 24th February 2023 | Online](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2023-02-24-c-scale-tutorial-slurm-230914100312-f7901d97/85/C-SCALE-Tutorial-Slurm-36-320.jpg)






