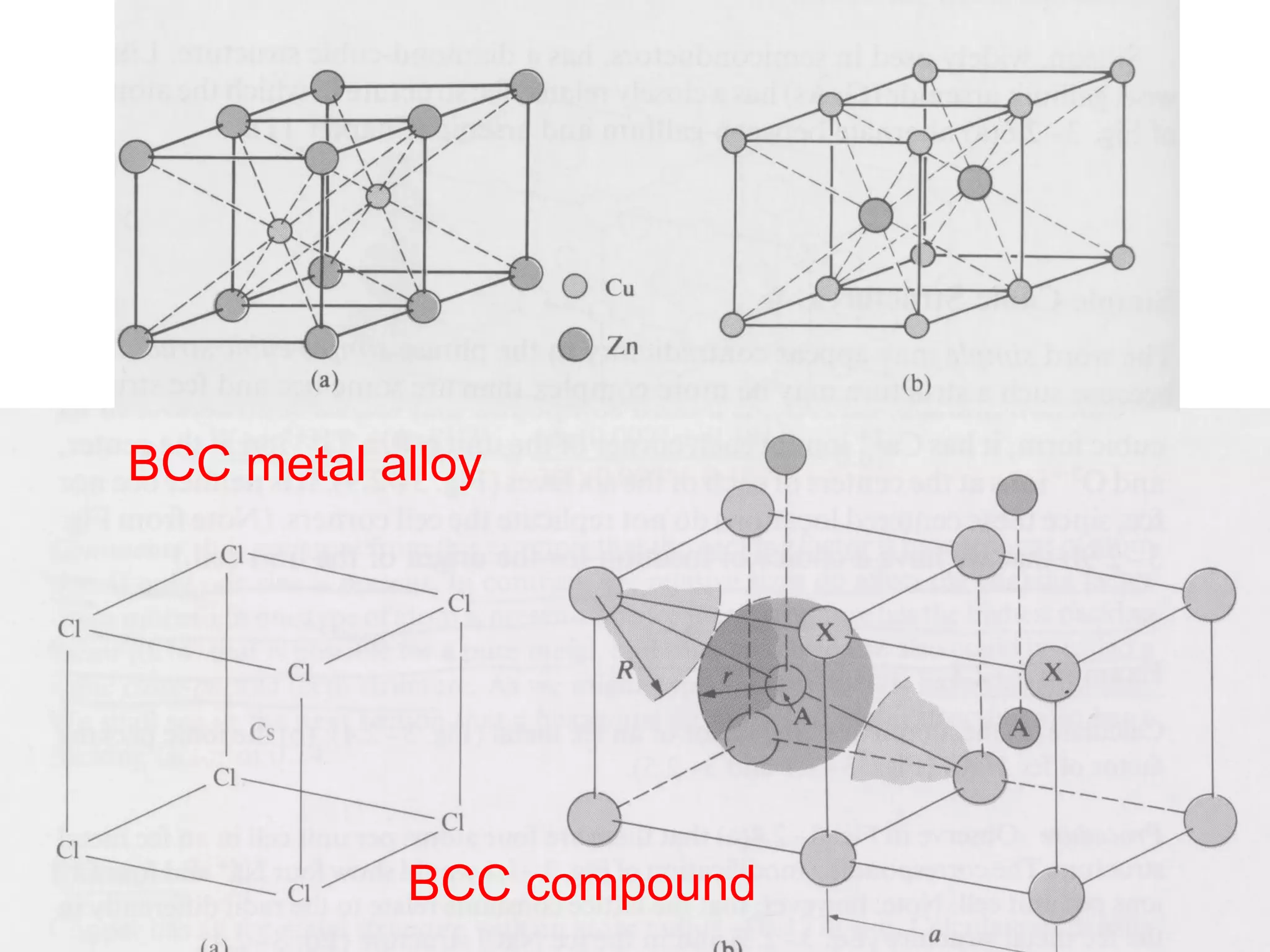
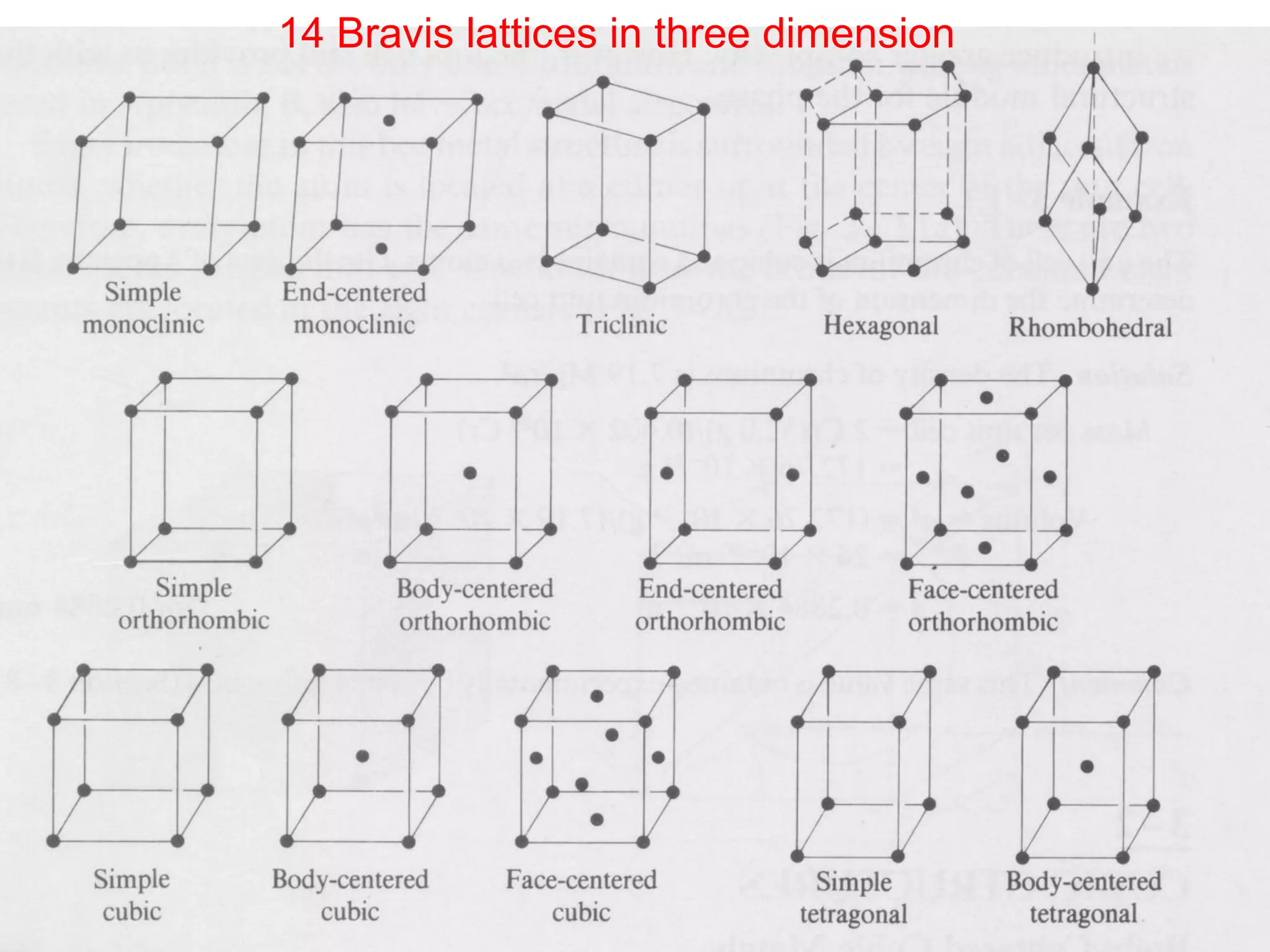
This document provides an introduction to crystal structure, including key discoveries and scientists in the field. It describes common crystal structures like body centered cubic (BCC), face centered cubic (FCC), and hexagonal close packed (HCP). It also discusses properties of unit cells, lattice points, primitive vectors, and Miller indices for crystal planes.










![FCC metal
金屬鍵沒方向性
4R=√(2) a Volume of one atom=4πR3/3
Packing fraction=[8x(1/8)+6x(1/2)] x4πR3/3/(volume of one unit cell)=0.74](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crystalstructuresweek2-230130061926-1cbbb428/75/crystal-structures-week-2-pdf-12-2048.jpg)