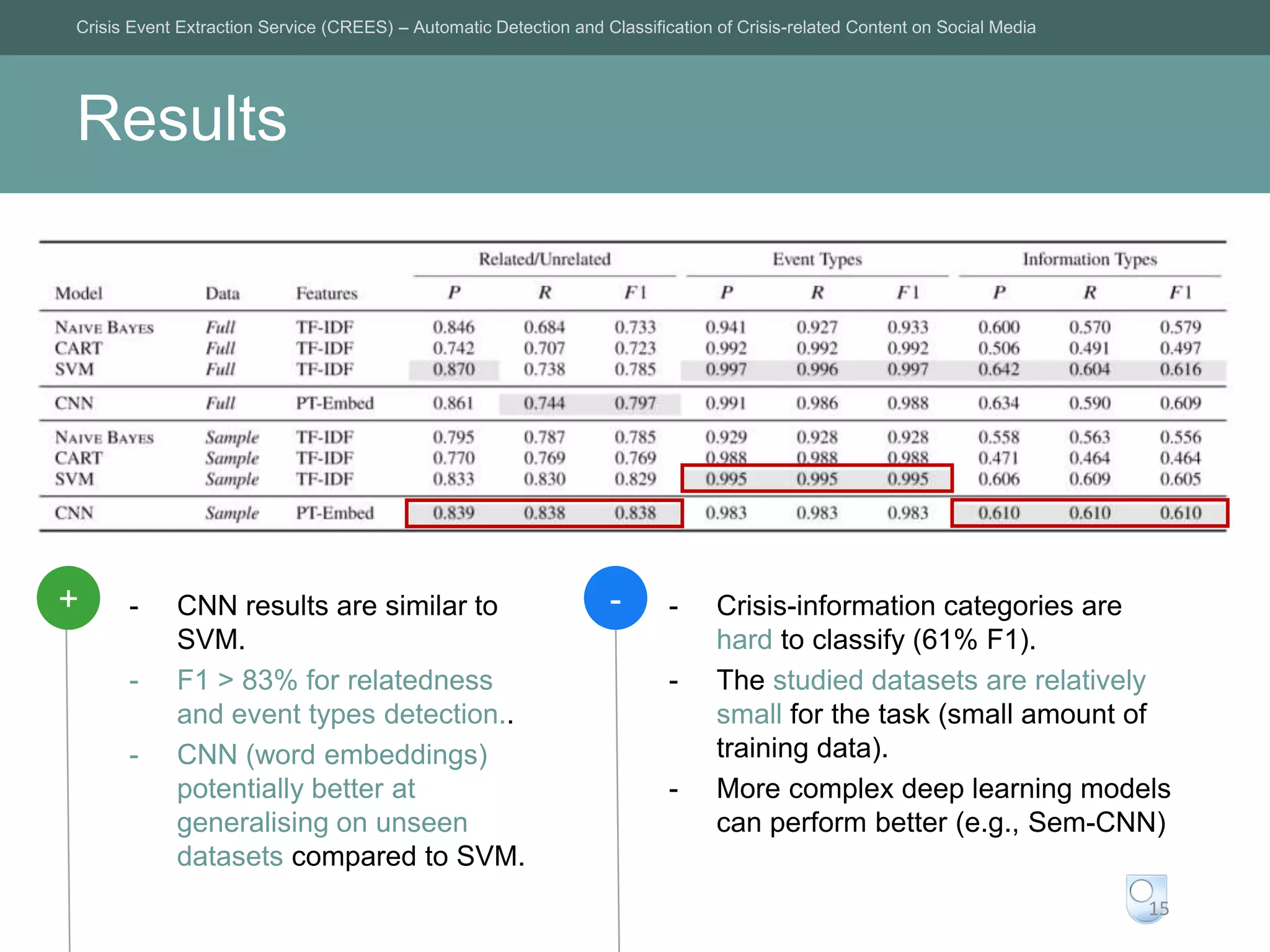
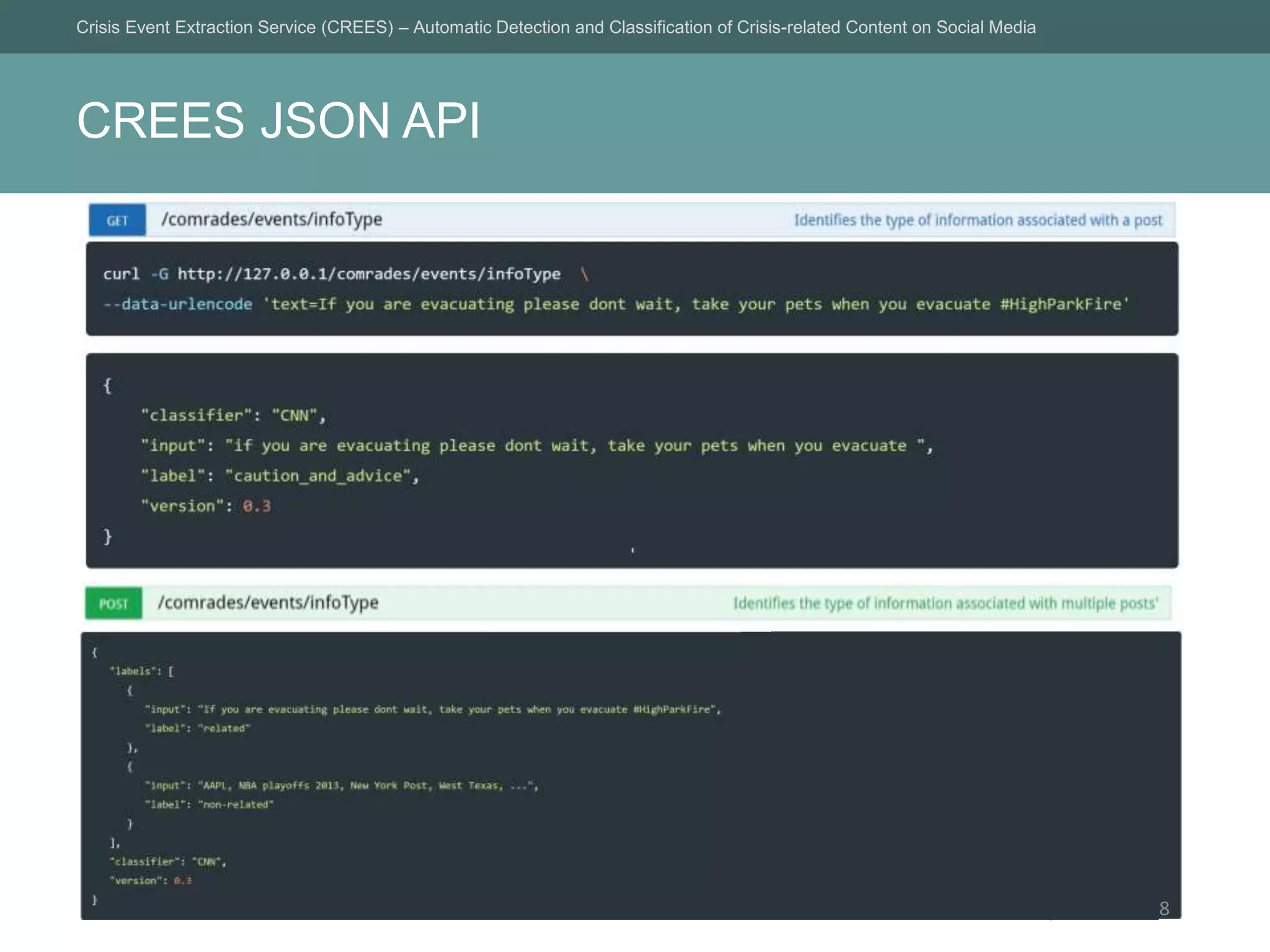
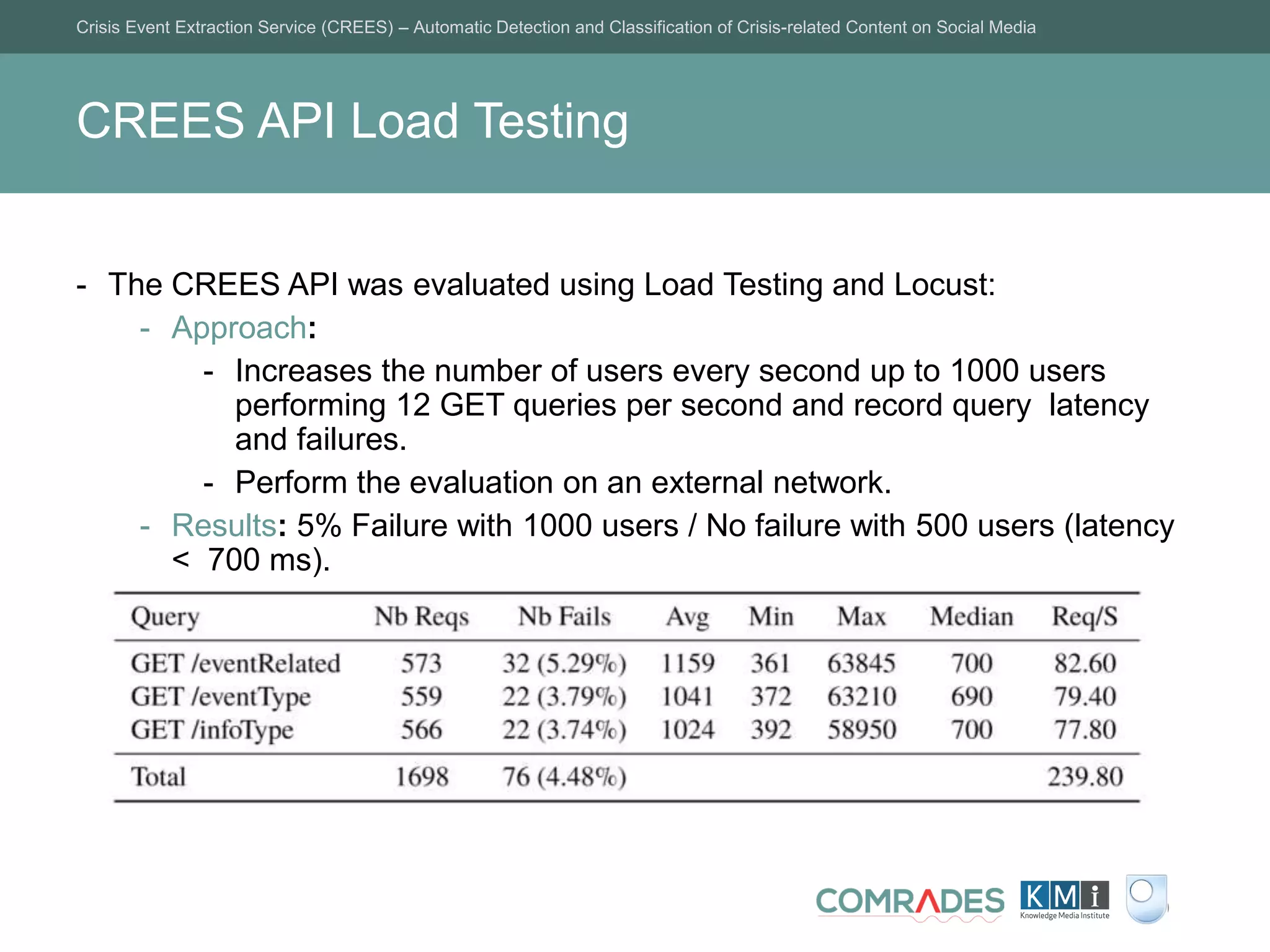
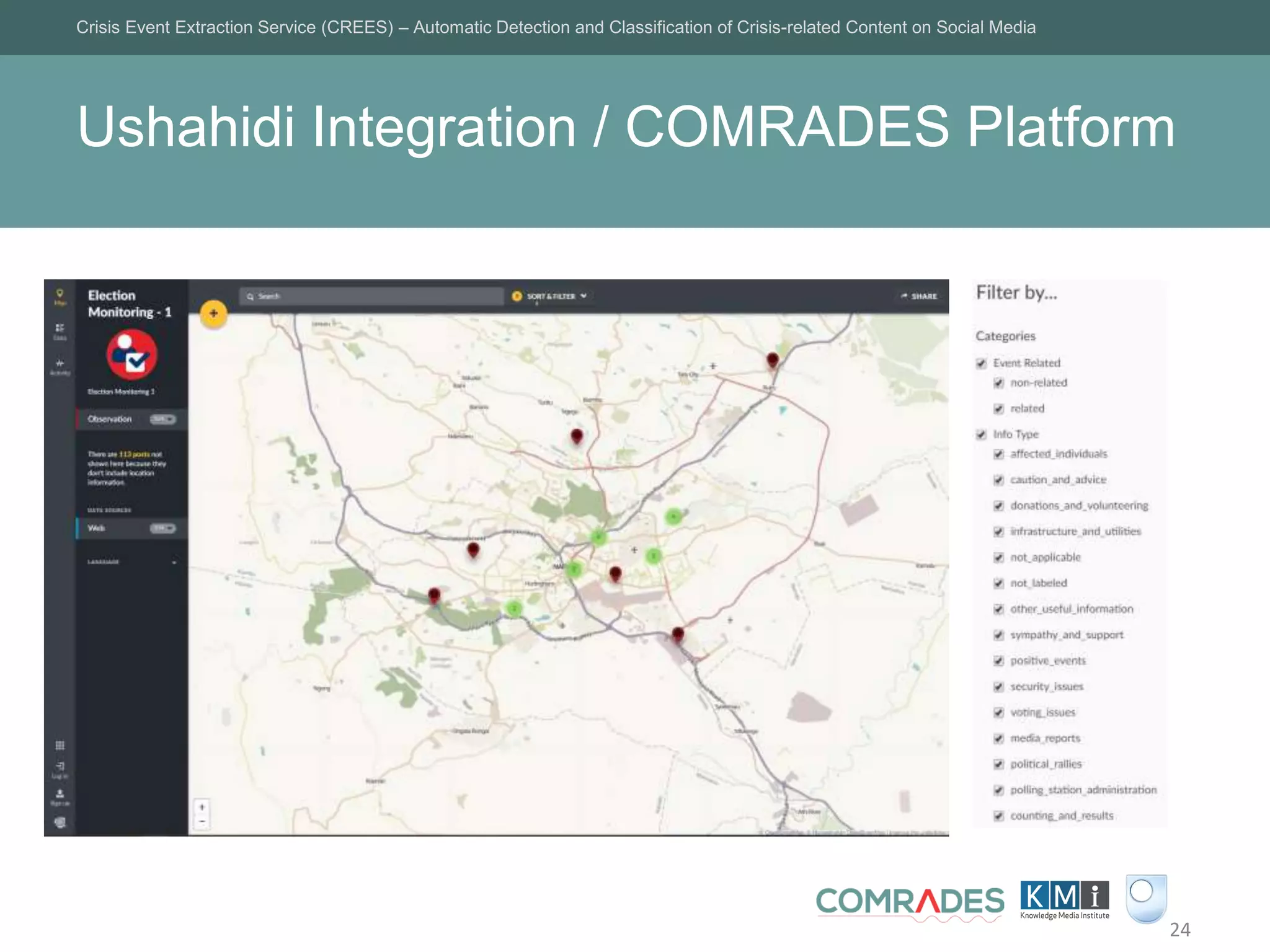
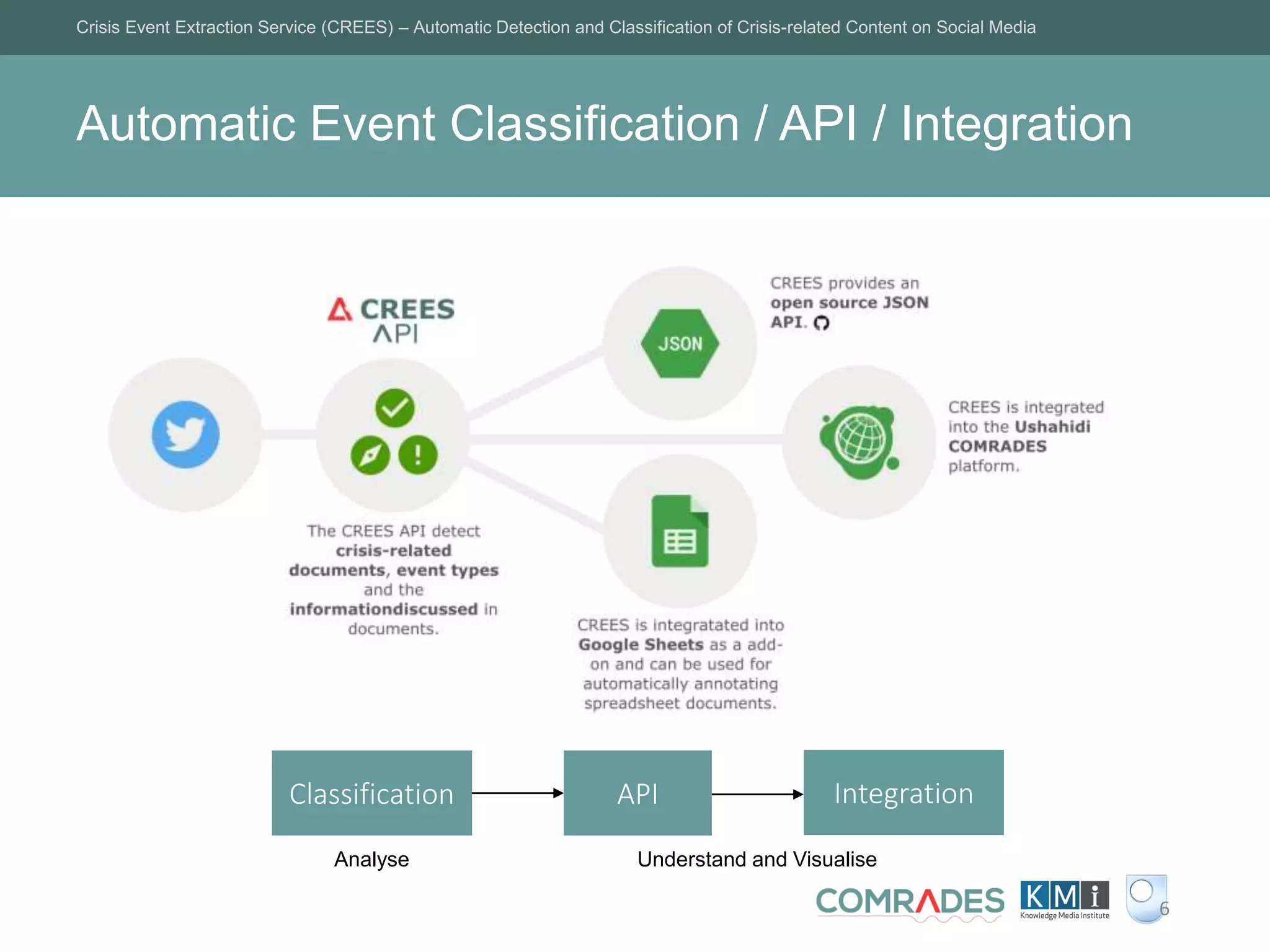
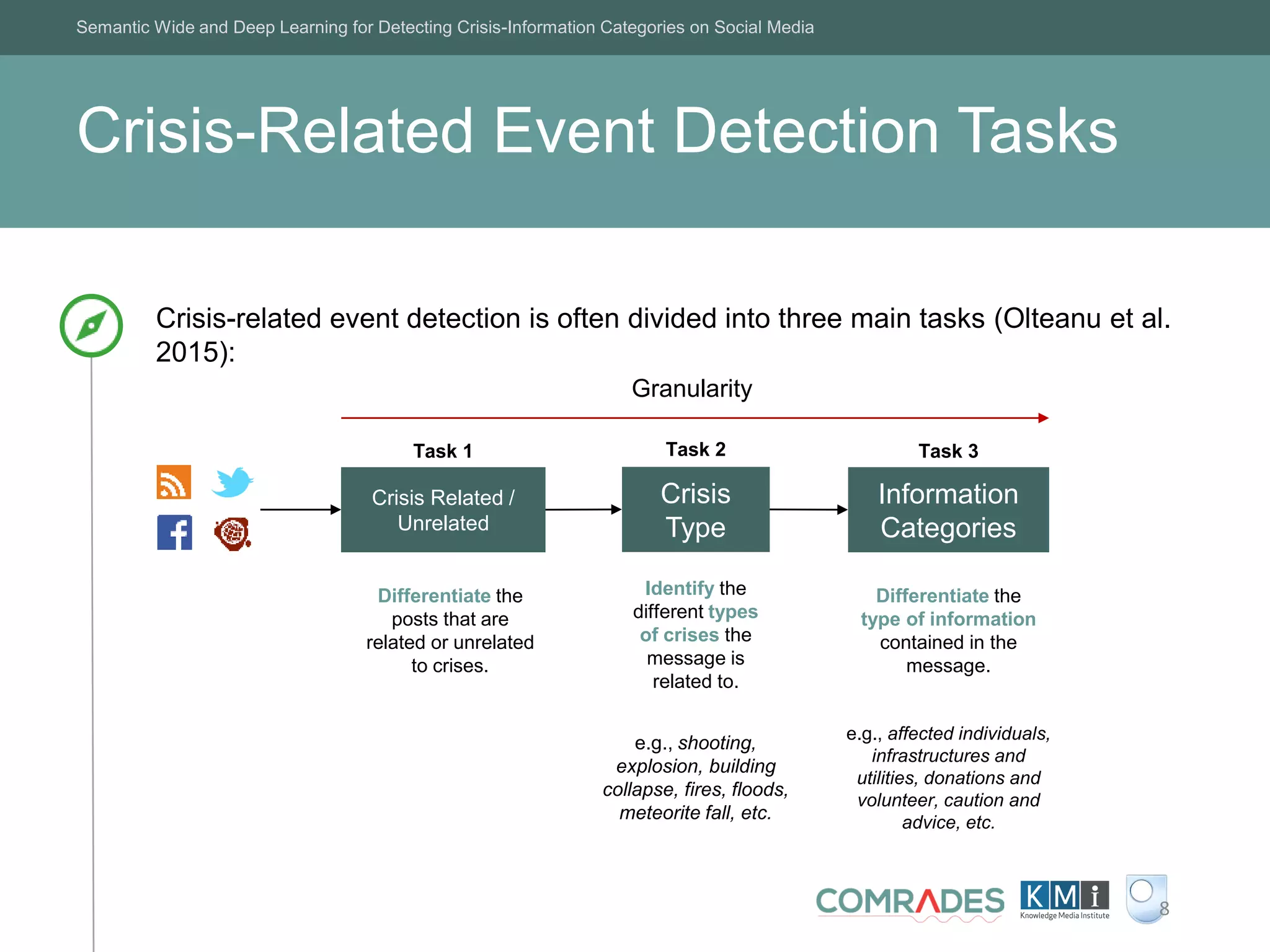
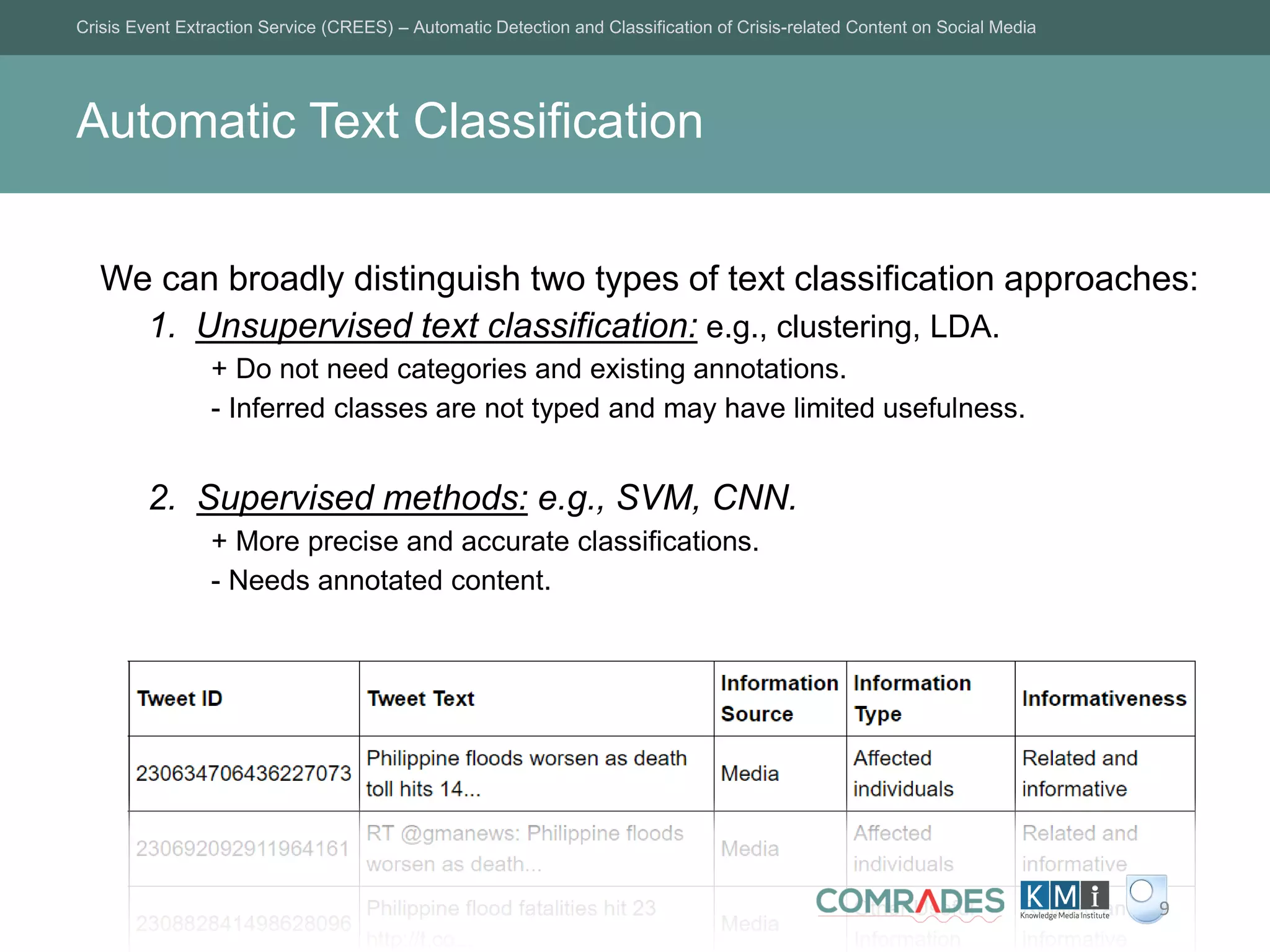
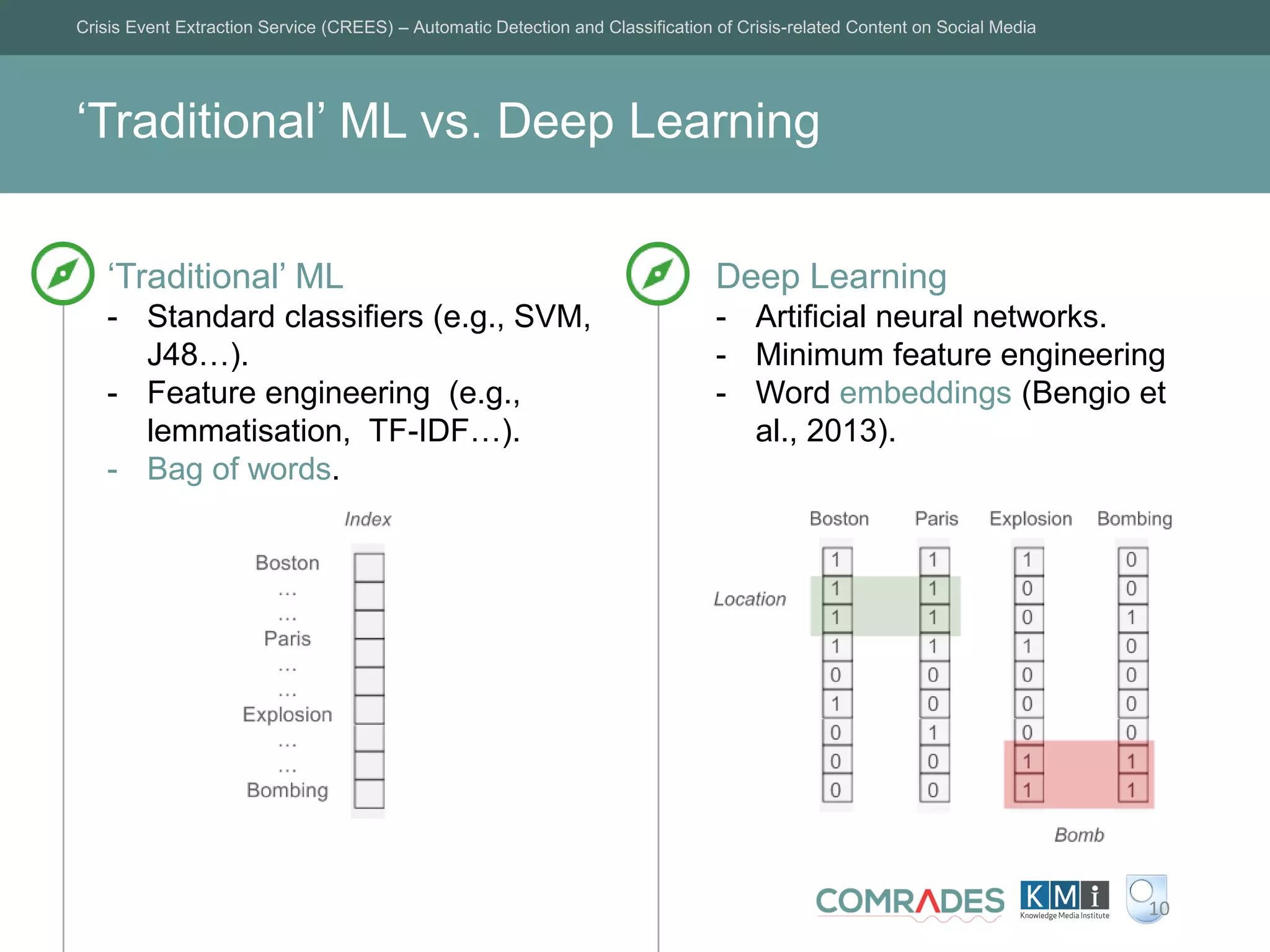
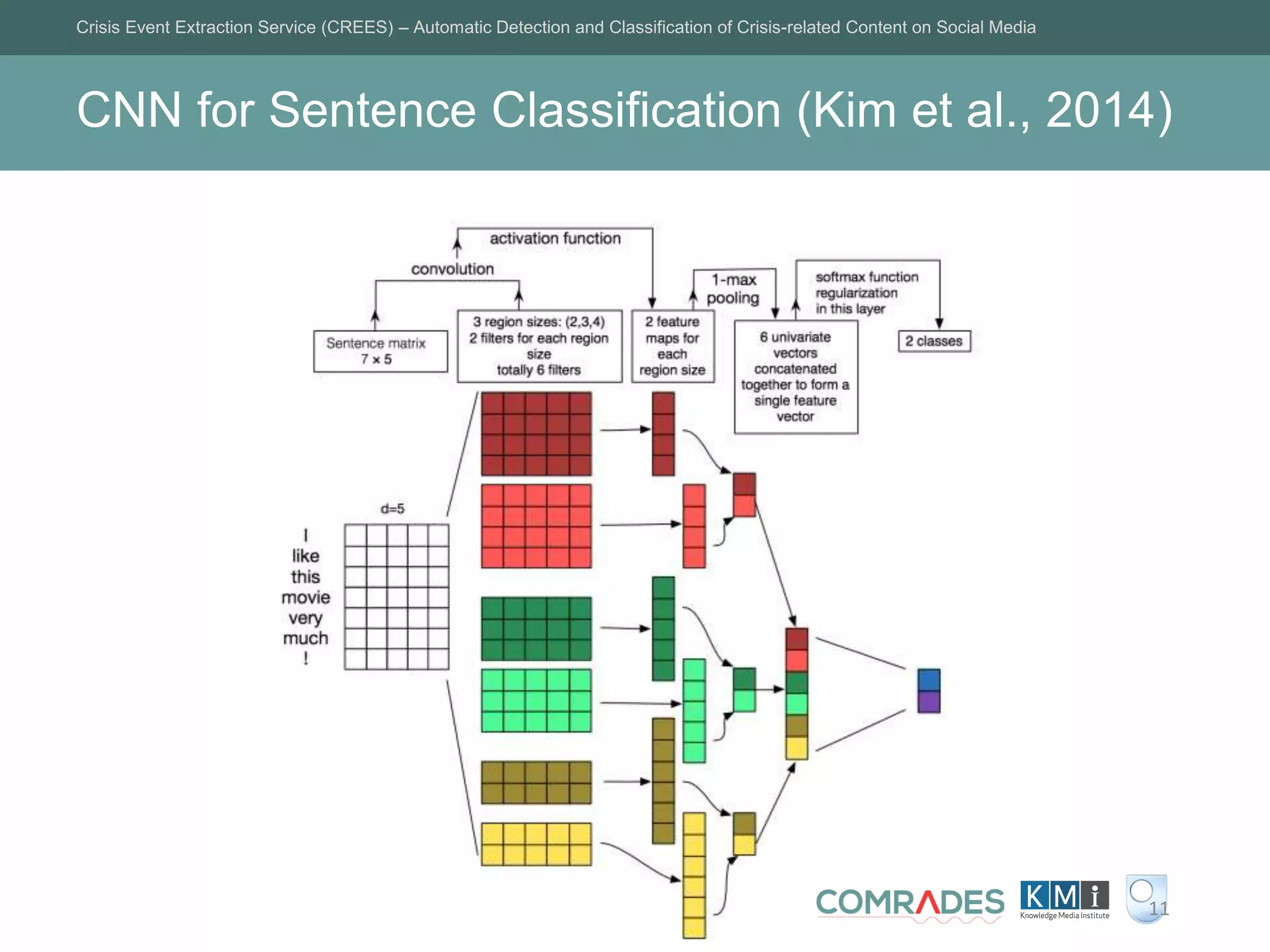
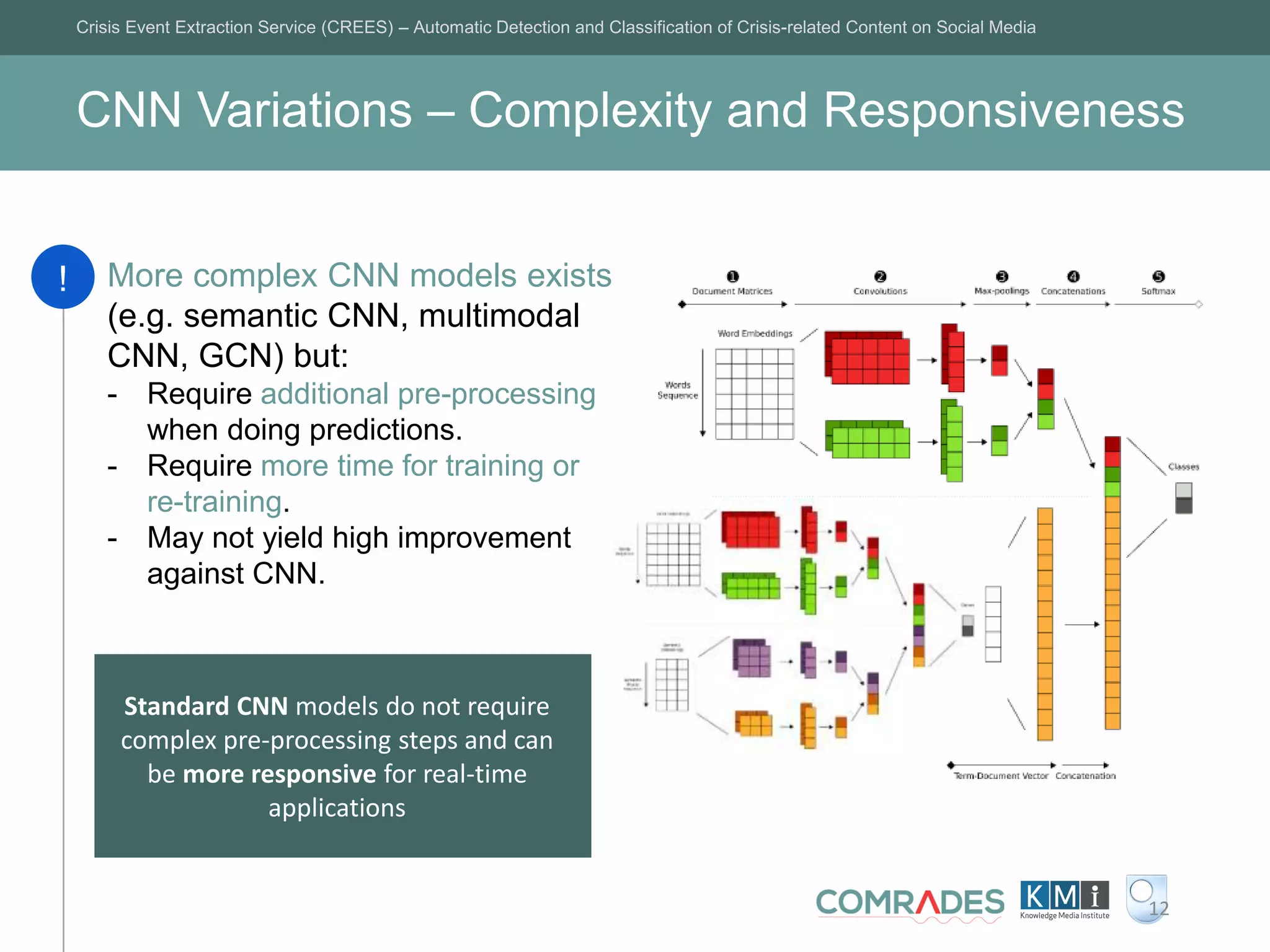
The Crisis Event Extraction Service (CREES) is an automatic system designed to detect and classify crisis-related content on social media using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). It processes data from platforms like Twitter to enhance situational awareness during crises, although challenges remain in reliably classifying information categories. The service is open-source, integrates with tools like Google Sheets, and aims for precise event identification with an F-measure above 83%.



![CNN Classification – Experimental Setup
Crisis Event Extraction Service (CREES) – Automatic Detection and Classification of Crisis-related Content on Social Media
14
Dataset versions
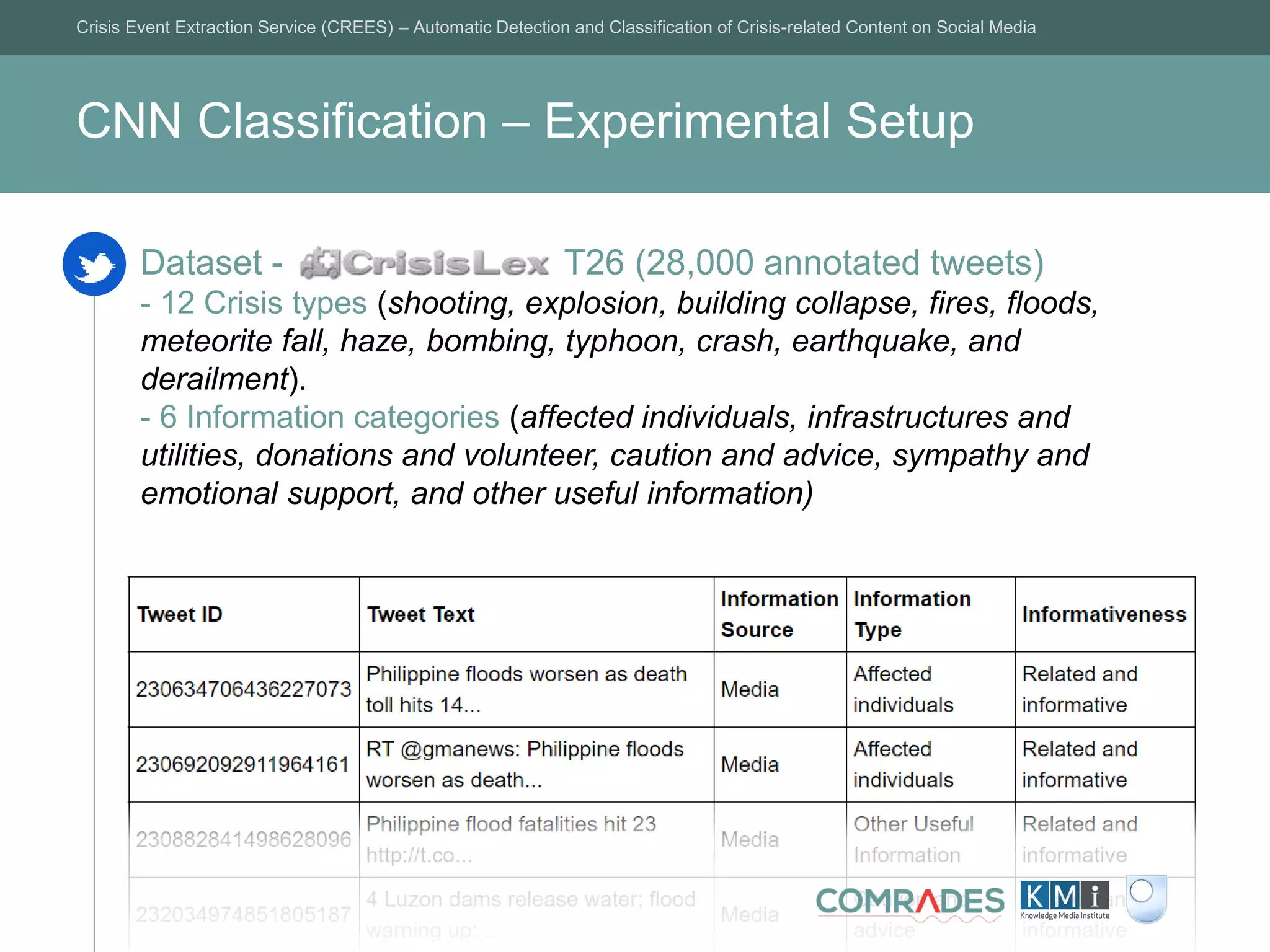
- Full Dataset: 28,000 tweets.
- Balanced Datasets: 6703 tweets (24%) / 12 997 tweets (46.5%) / 9 105
tweets (32.6%).
Baselines
- Naïve Bayes / CART / SVM: Classical ML models using the words’ TF-
IDF vectors extracted from our dataset.
Evaluation
- 5-folds cross validation.
- CNN: 300-dim embeddings, Fn = 128 convolutional filter of sizes Fs =
[3,4,5], 0.5 dropout and ADAM.
- Evaluation Measures: P, R and F1.
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iscram18light-180522190911/75/Crisis-Event-Extraction-Service-CREES-Automatic-Detection-and-Classification-of-Crisis-related-Content-on-Social-Media-14-2048.jpg)