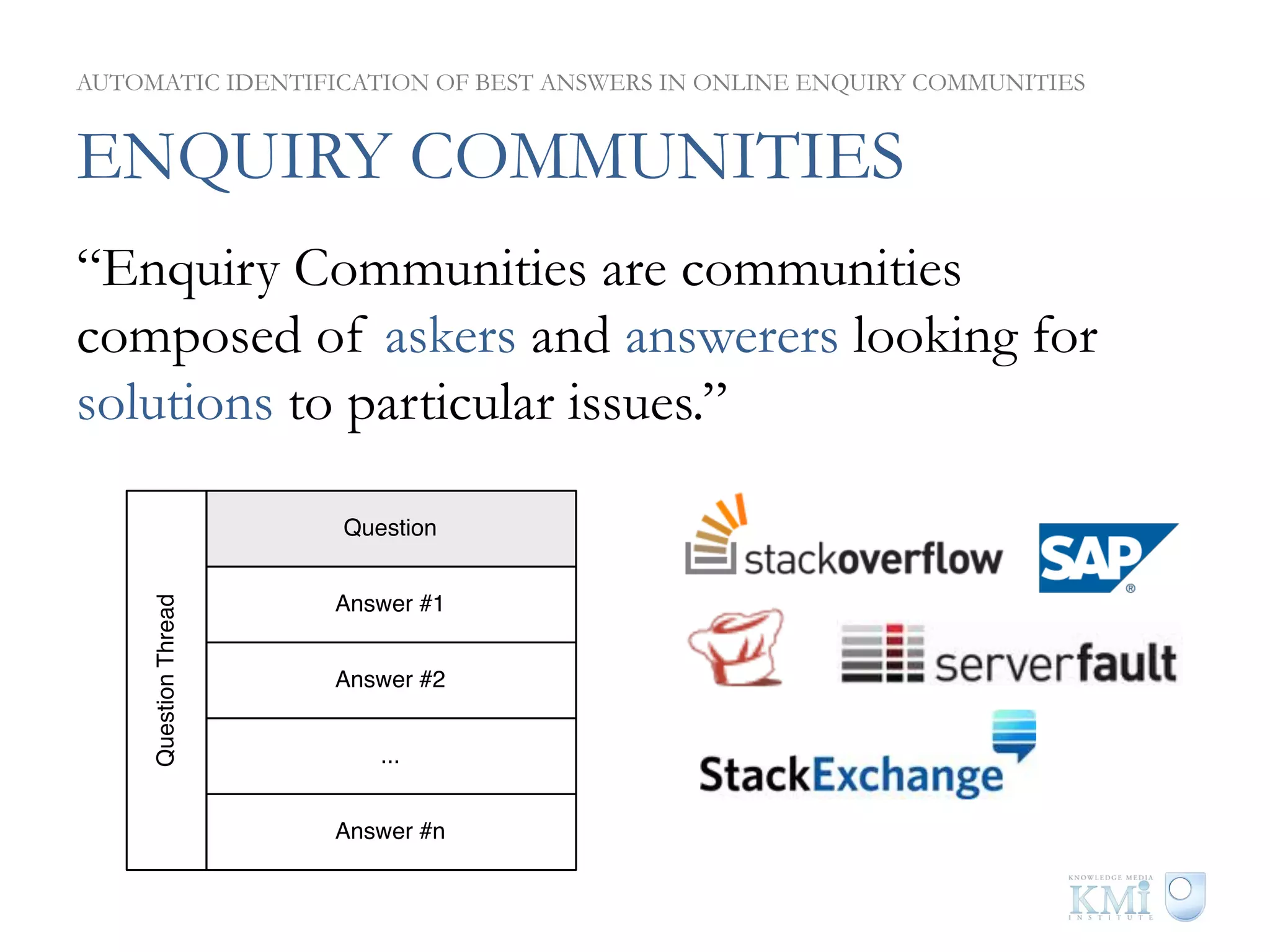
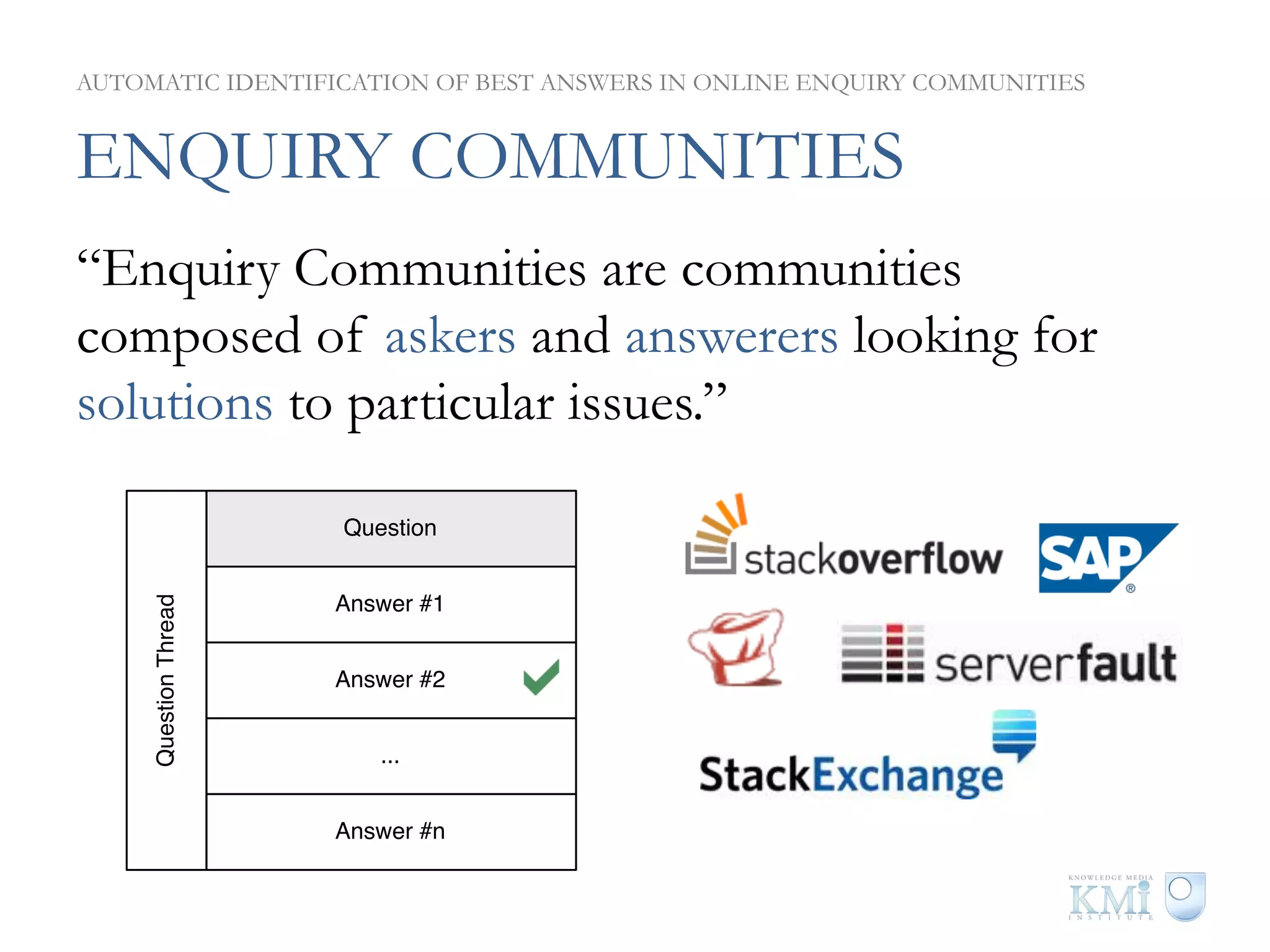
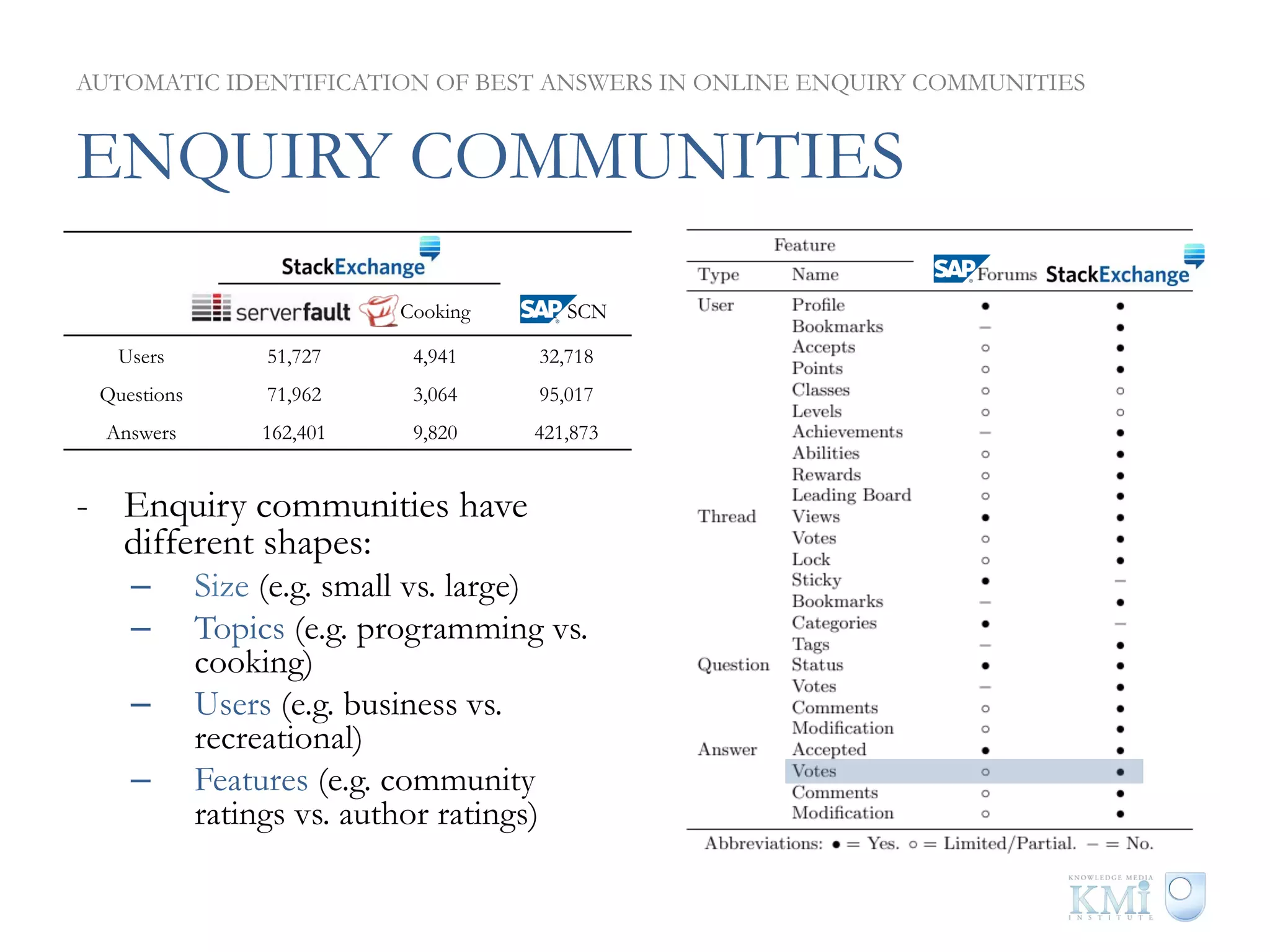
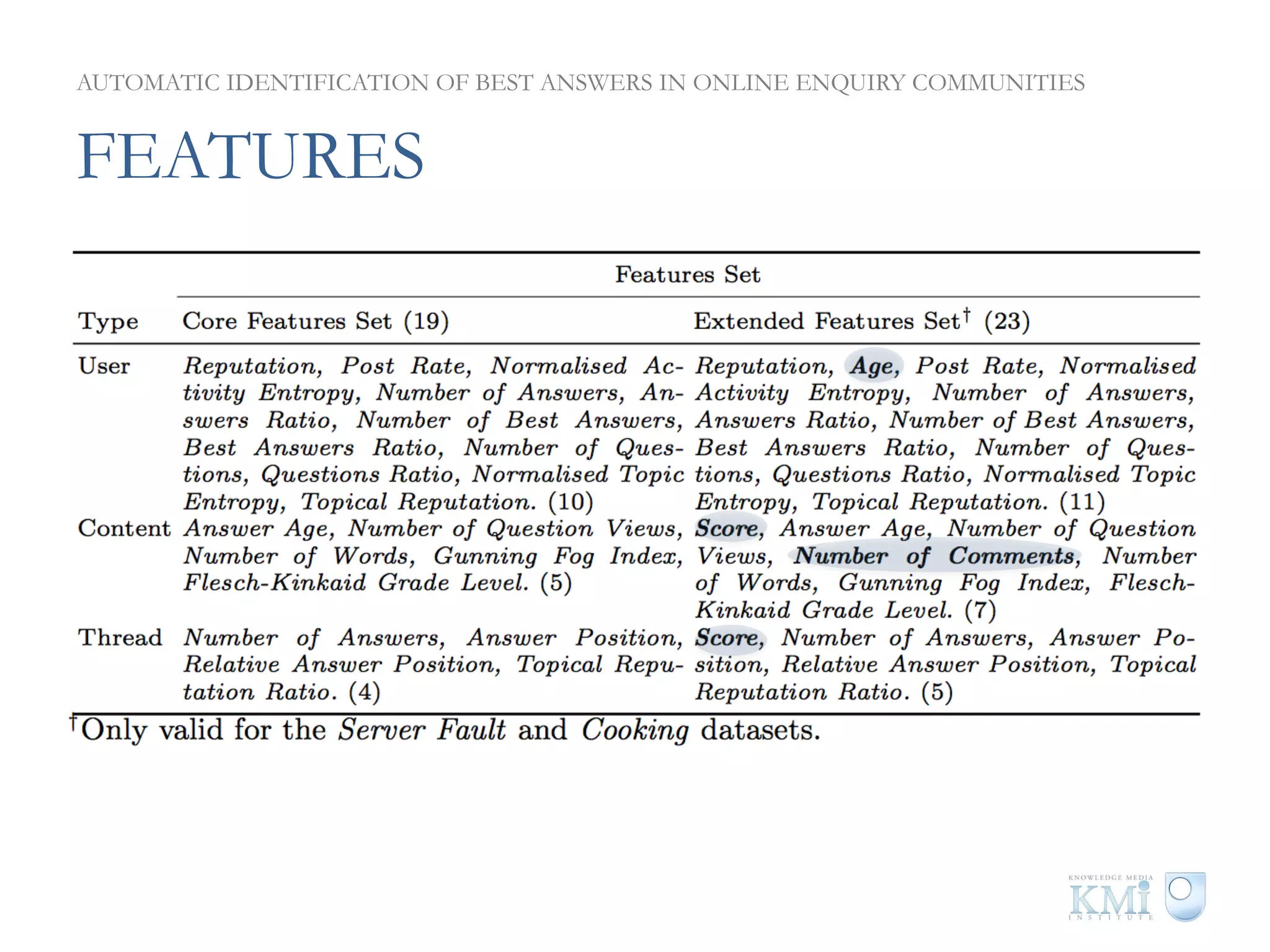
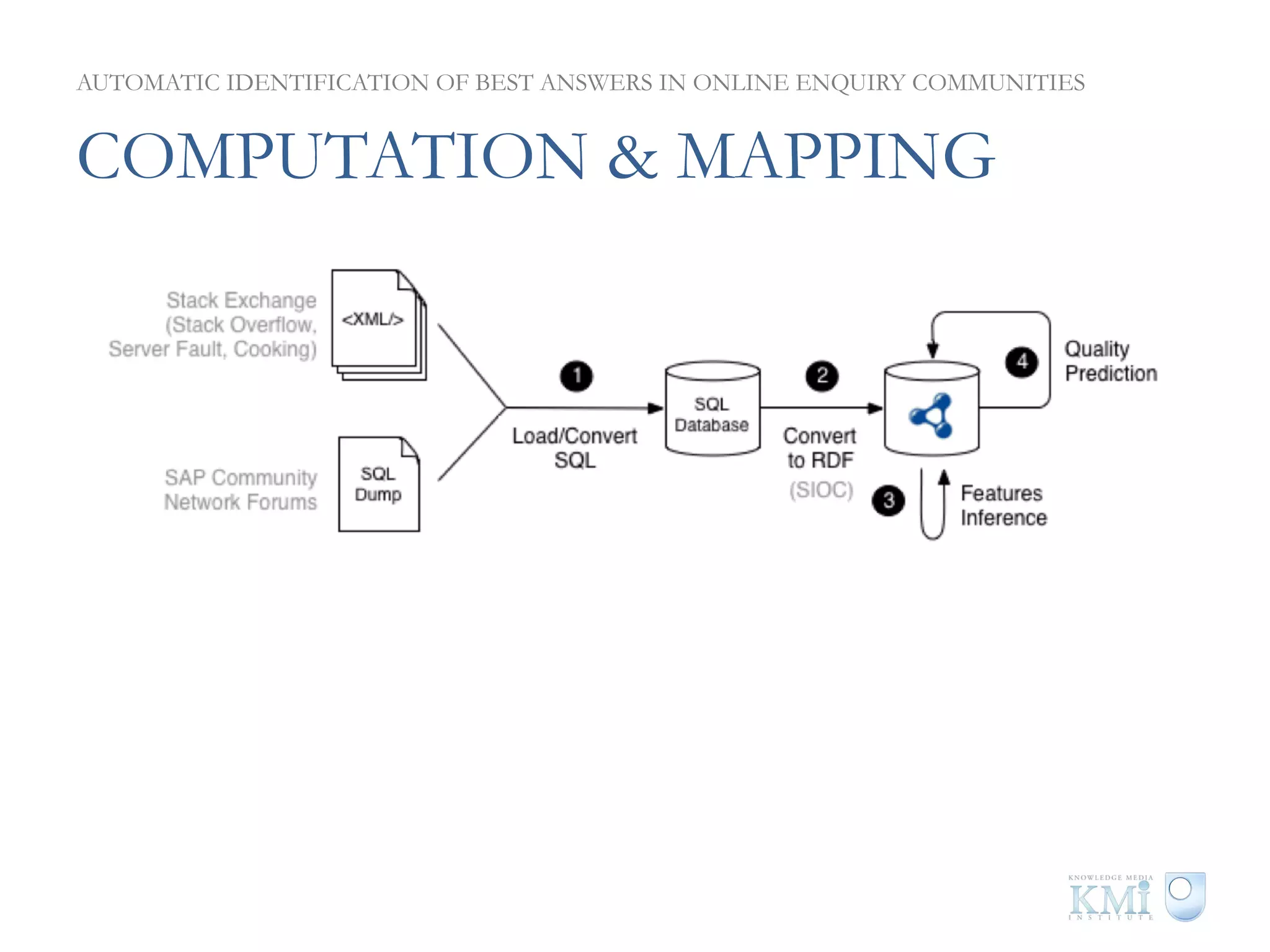
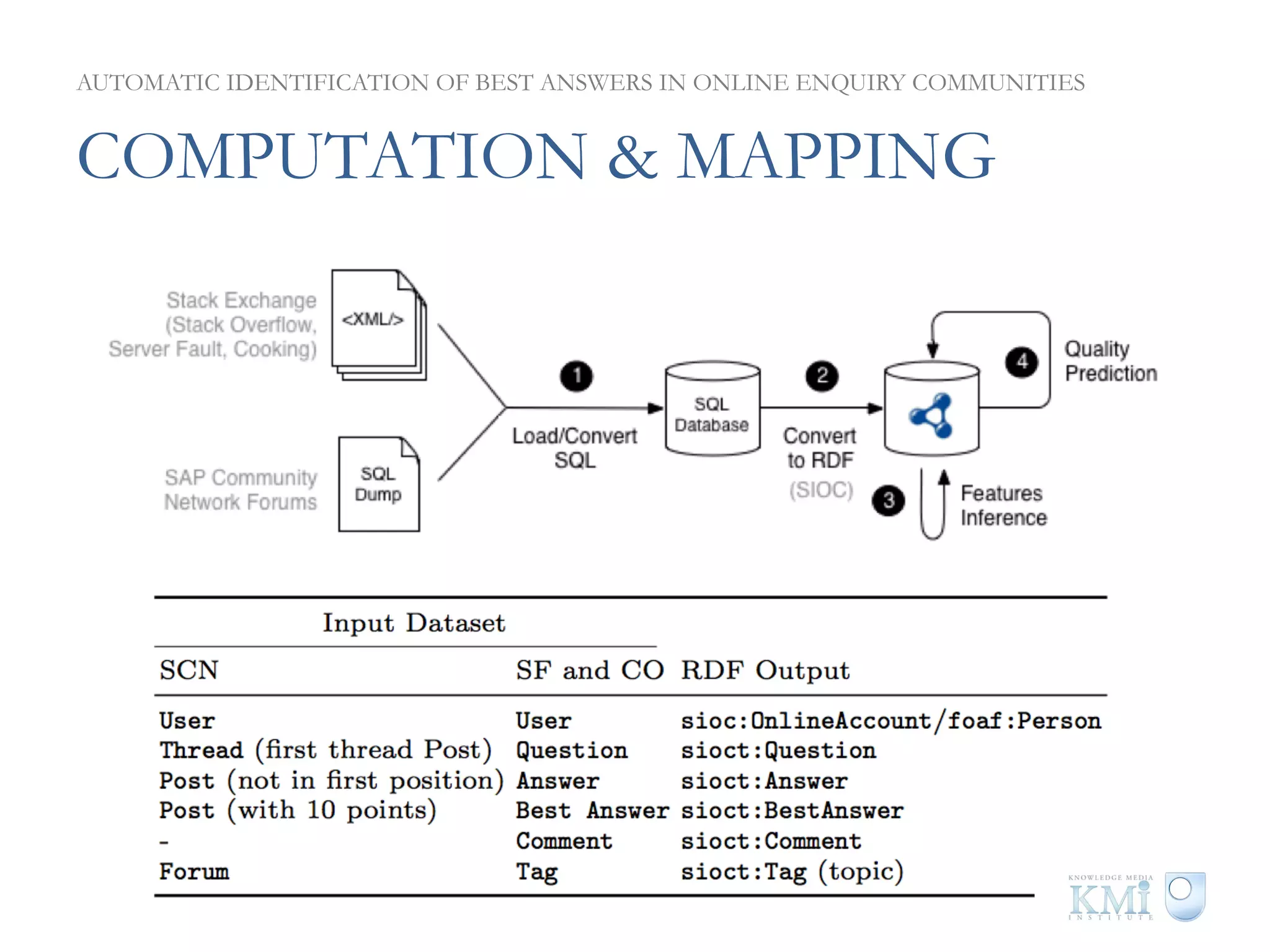
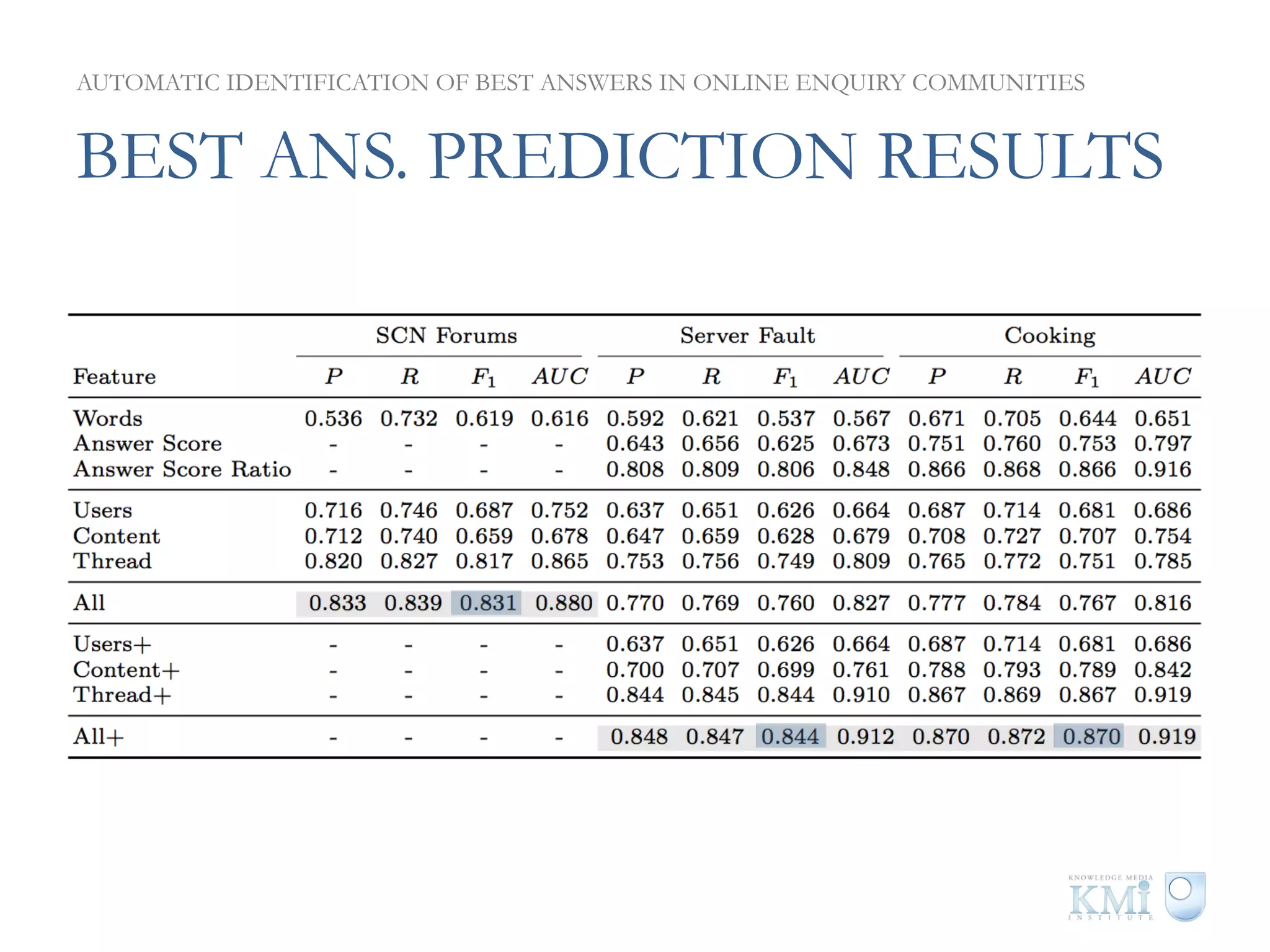
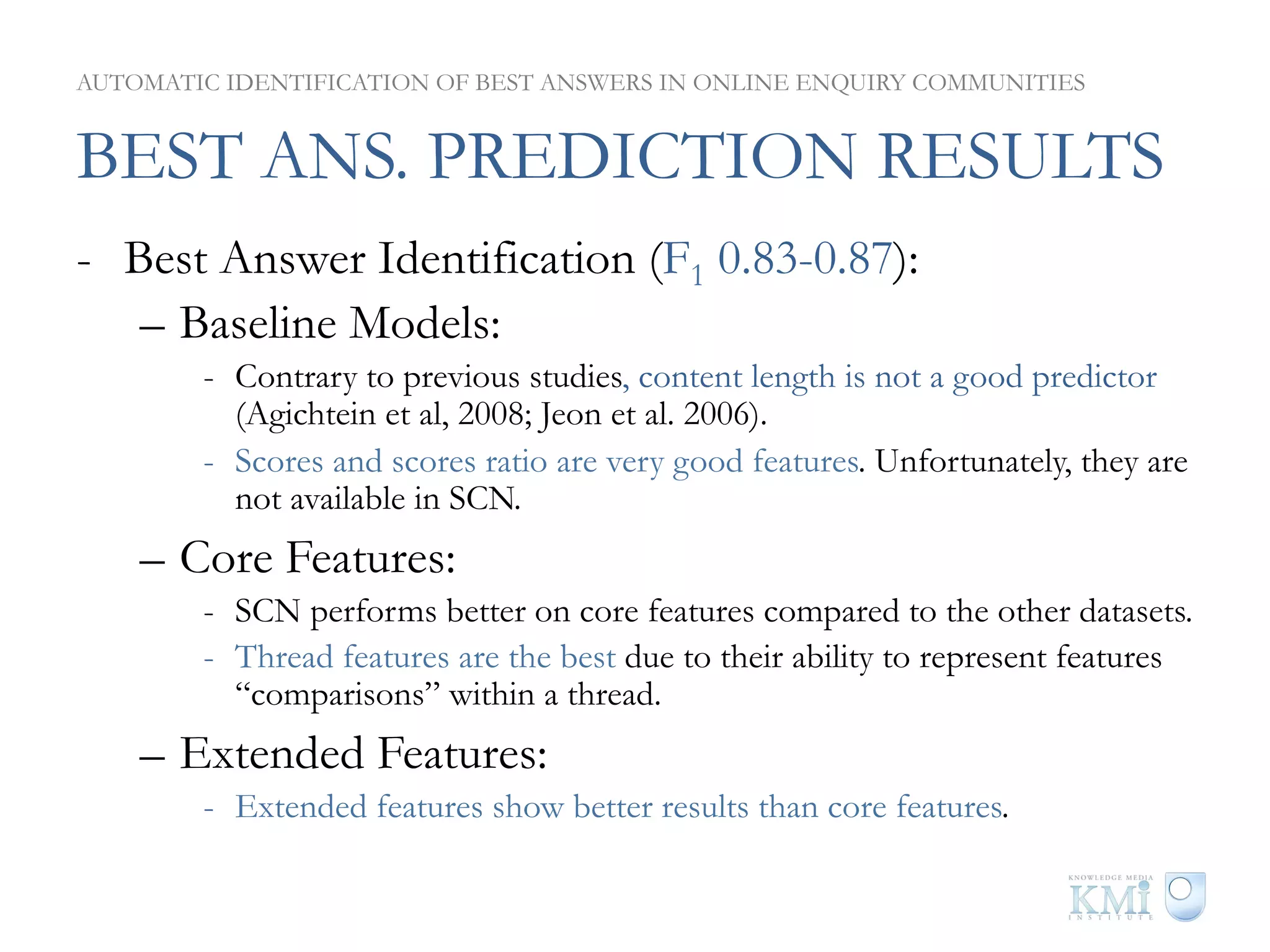
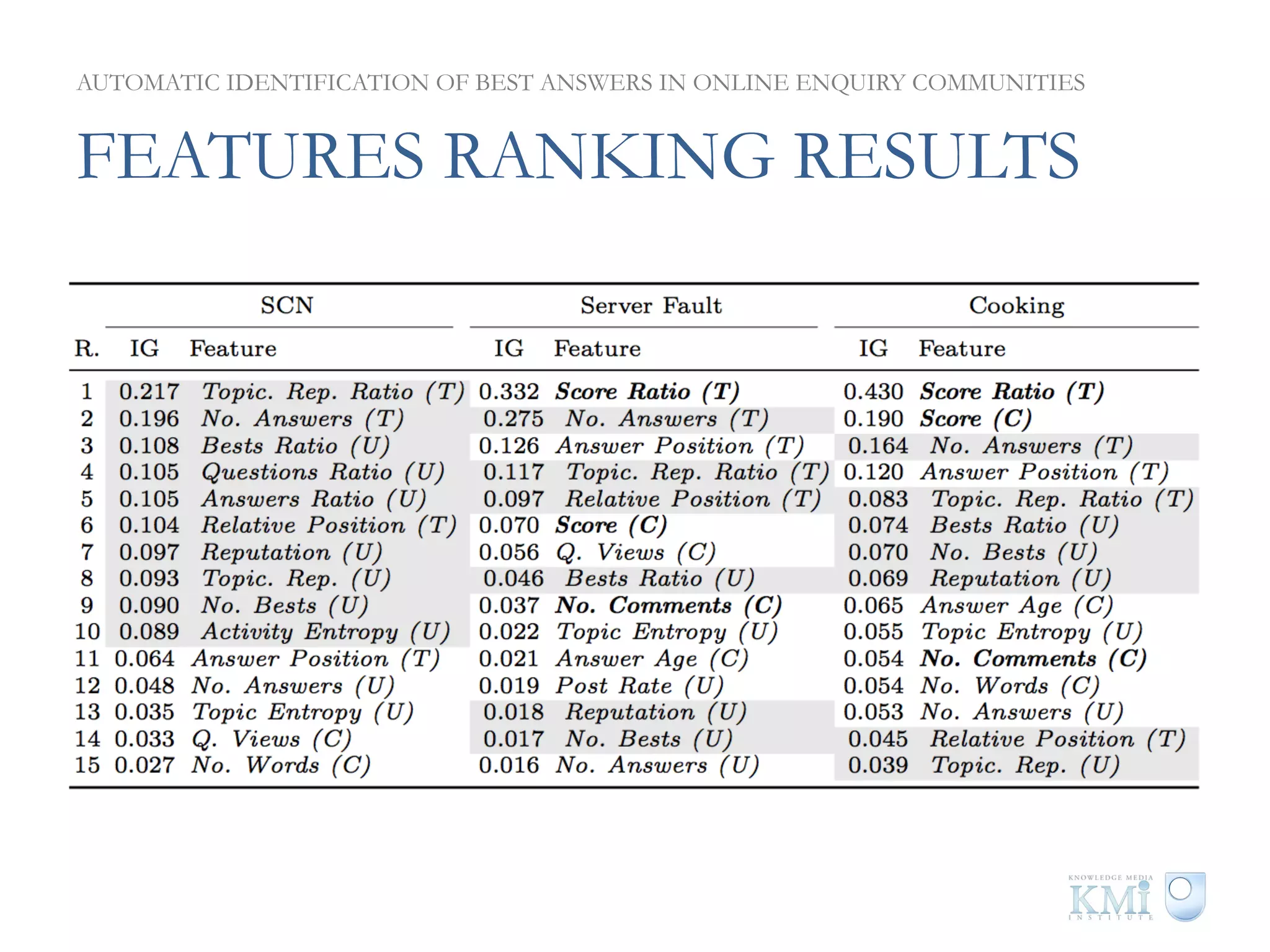
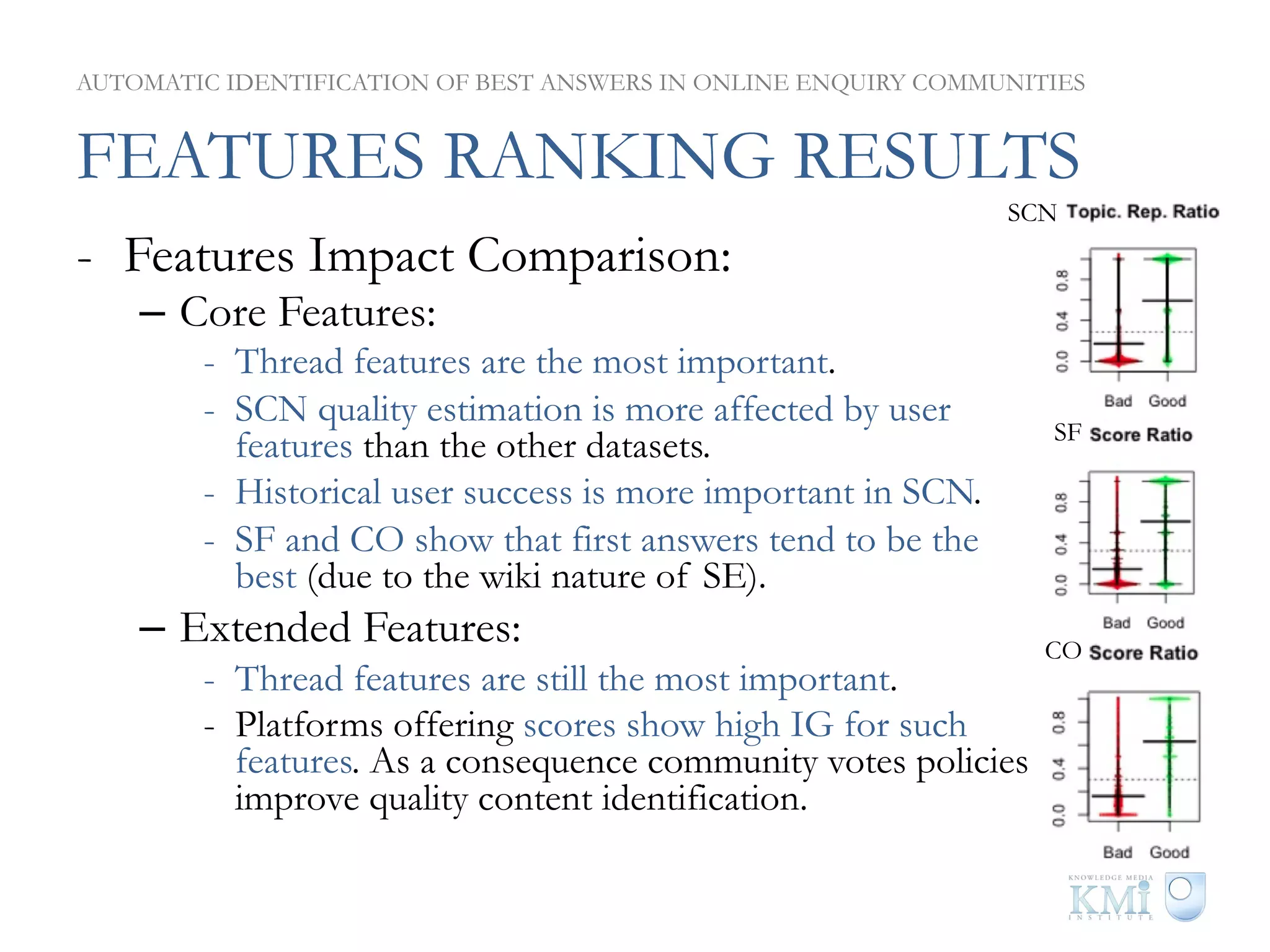
The document discusses the automatic identification of best answers in online enquiry communities, emphasizing the structure, needs, and motivations of these communities. It analyzes user, content, and thread features that influence the identification of quality answers, along with the prediction results and feature ranking across different platforms. The findings indicate that while community characteristics affect content quality, accurate identification of best answers can be achieved with high precision using specific features.