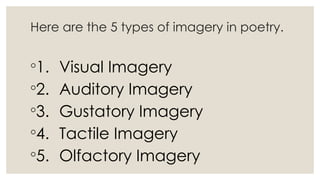
Imagery in creative writing refers to the sensory 'pictures' that readers experience through poetic language, encompassing five types: visual, auditory, gustatory, tactile, and olfactory. Each type engages different senses, with visual imagery describing sight, auditory imagery focusing on sound, and gustatory imagery invoking taste. Examples illustrate how poets create vivid sensory experiences to immerse readers in the poem's world.