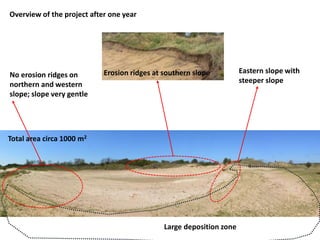
The document discusses creating and managing blowouts in dune systems to restore habitat diversity. It provides examples from the PWN dunes of the Netherlands. Statistics show most natural blowouts form within 1000 meters of the beach and are 10-100 square meters in size. Both small and large blowouts can be reactivated. The size and goals of projects influence blowout size. Care must be taken when rejuvenating old blowouts that provide refuge. Erosion ridges are important habitat features that can be artificially created to manage blowouts. Overall the document explores considerations for intentionally creating blowouts through management and restoration efforts.