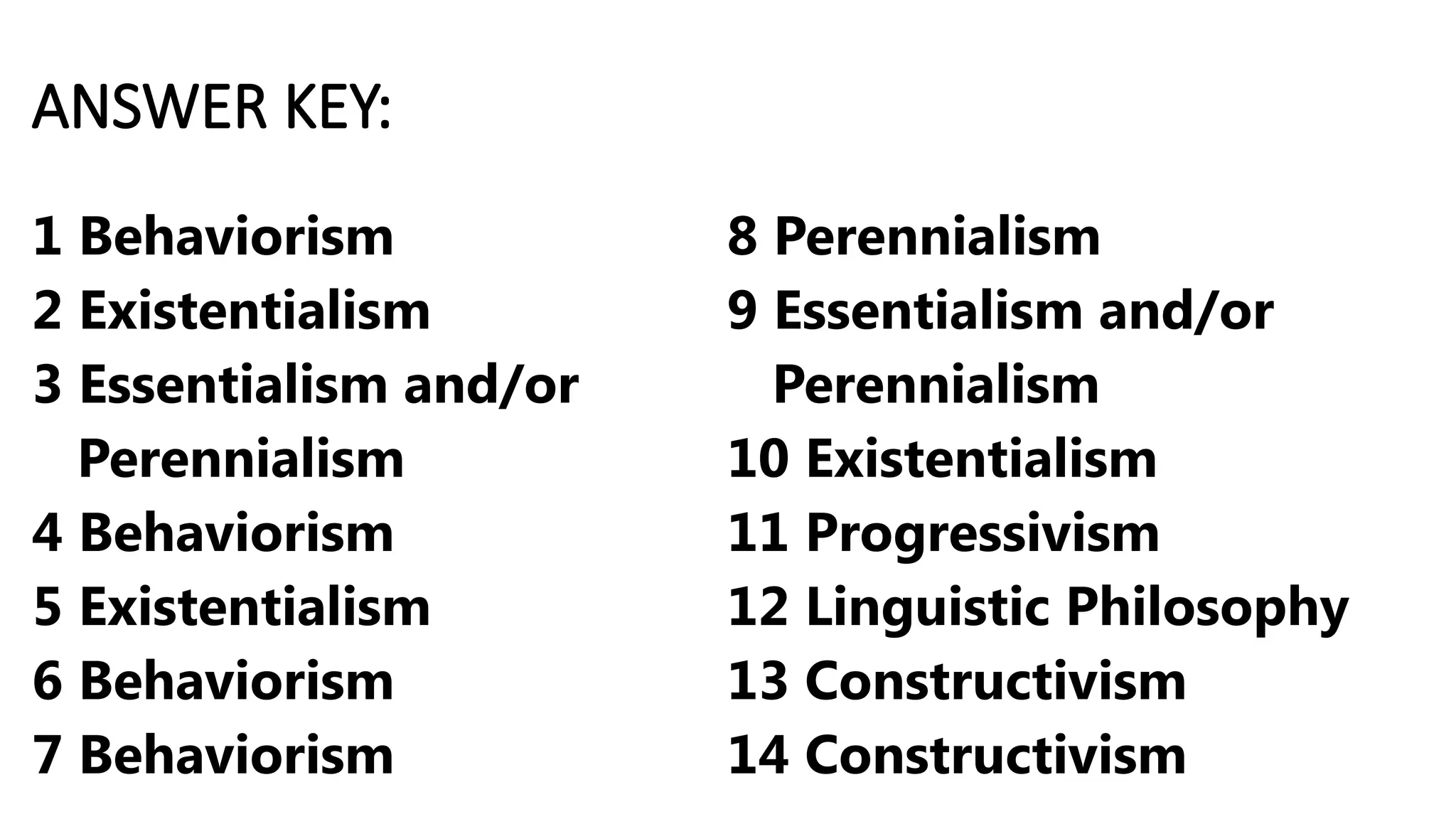
The document outlines various educational philosophies, including essentialism, progressivism, perennialism, behaviorism, linguistic philosophy, and constructivism, evaluating their core tenets through a series of yes/no questions. It highlights key distinctions, such as the emphasis on societal reconstruction in essentialism versus student interests in progressivism. Additionally, it categorizes various theories of man according to these philosophies, providing an 'answer key' for clarity.