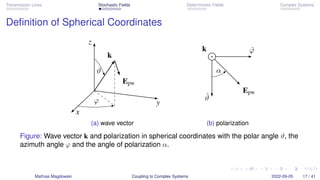
The workshop presented by Dr.-Ing. Mathias Magdowski at EMC Europe 2022 discusses the coupling of transmission lines to complex systems, focusing on stochastic and deterministic fields. It includes various theoretical aspects, results regarding coupling effects, and resonances caused by load mismatches. The presentation also compares analytical results with measurements, highlighting different coupling scenarios and their implications in electromagnetic compatibility.