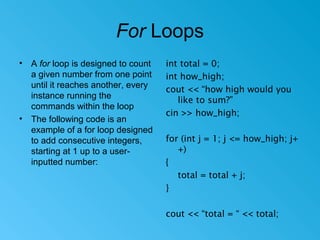
This document provides an introduction to counting and looping in C++ programming. It explains that for loops are commonly used for counting, and are designed to repeat a block of code a specific number of times. The document then provides a detailed step-by-step example of a for loop that adds consecutive integers from 1 to a user-input number. It breaks down each step of the for loop execution. The document also introduces while loops and provides a brief example of how the same integer addition could be done using a while loop instead of a for loop.