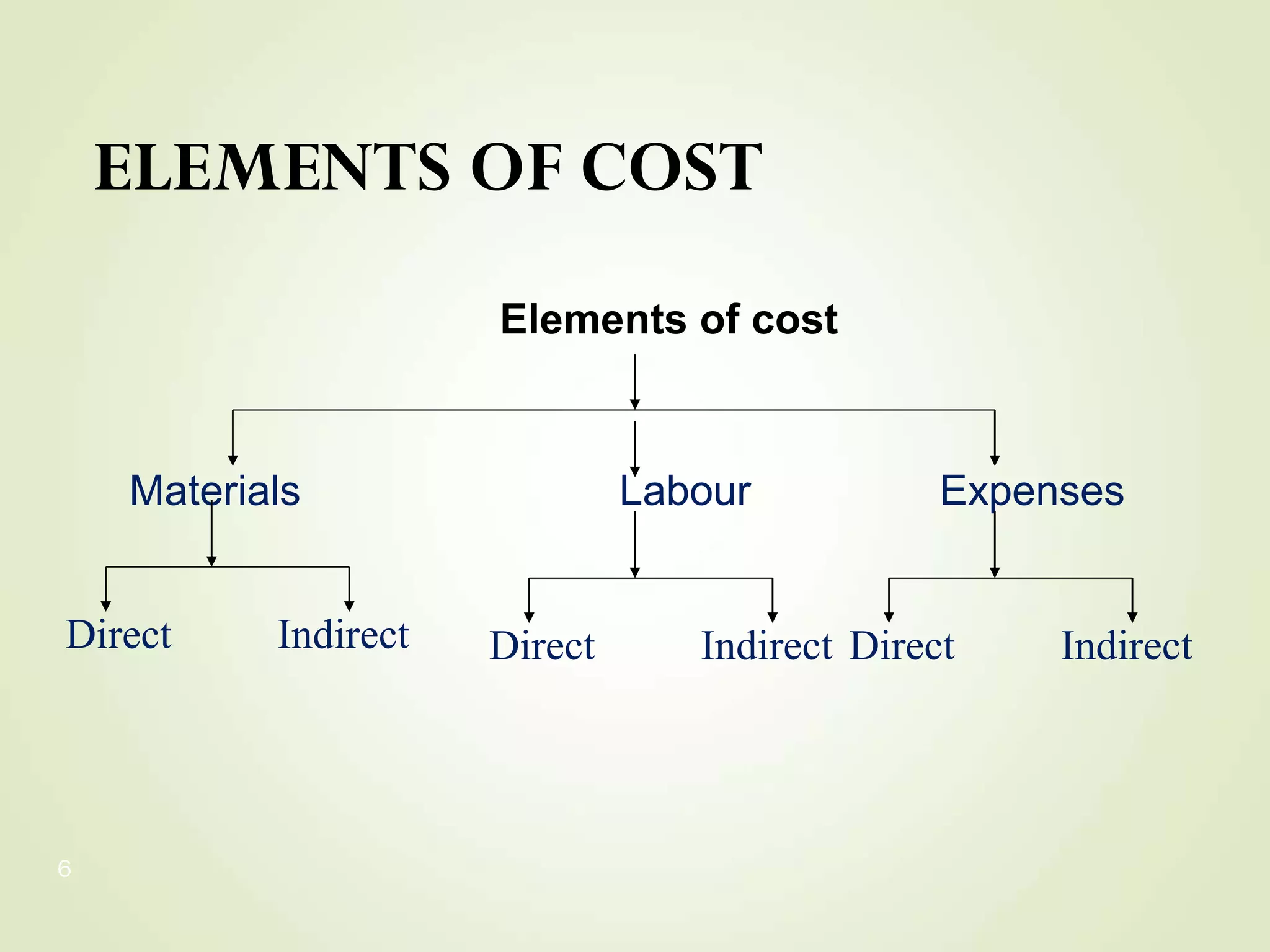
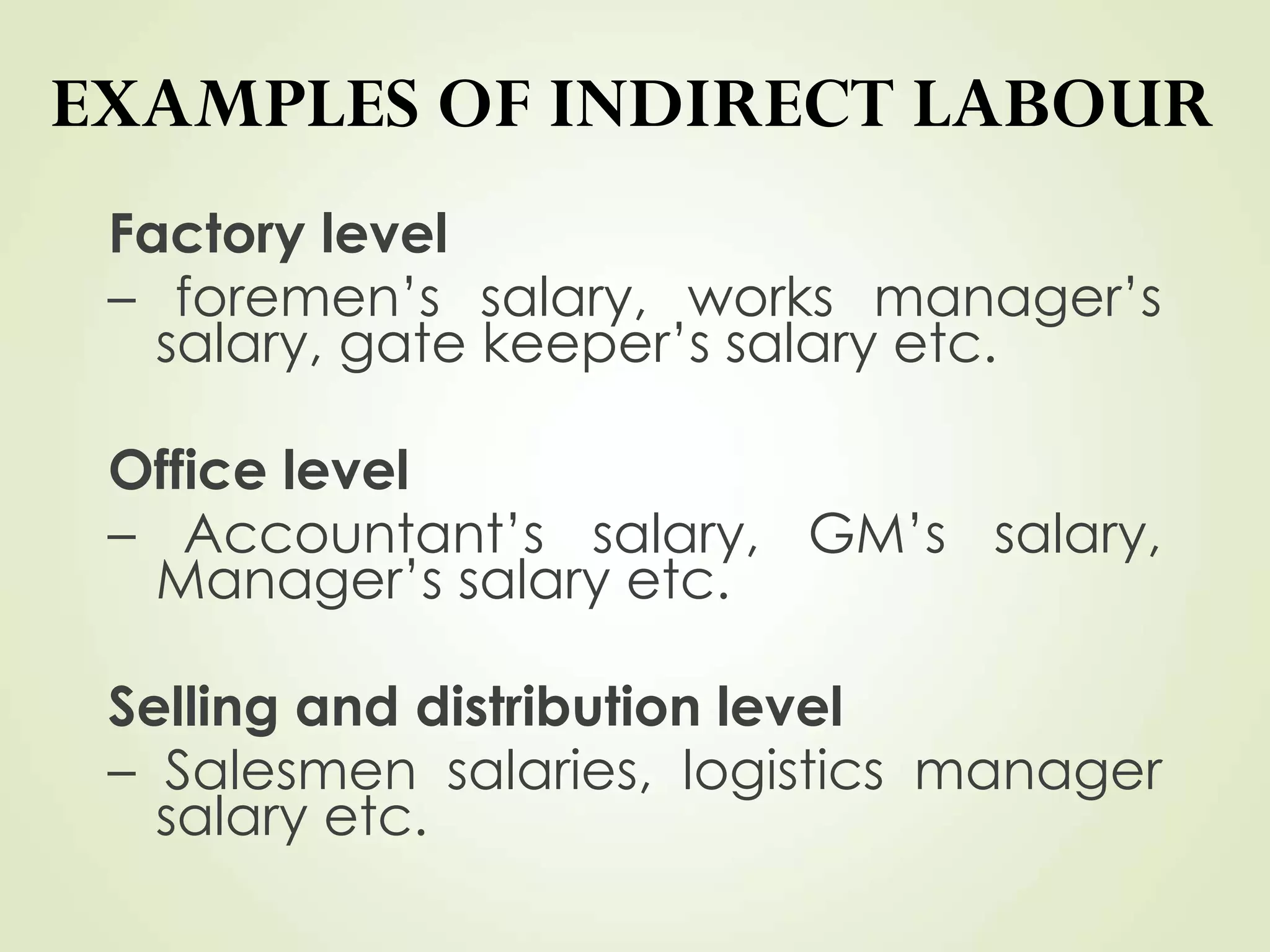
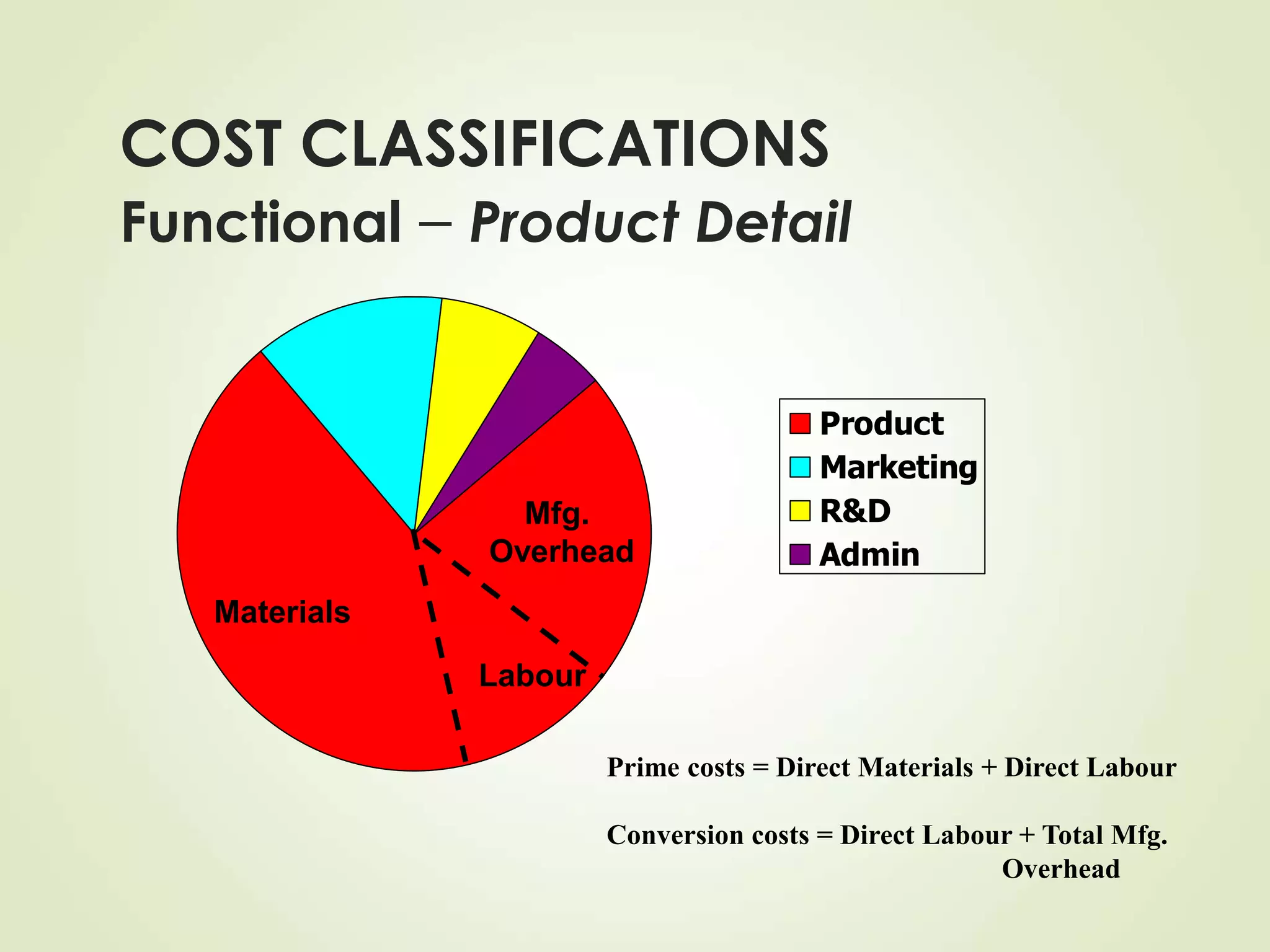
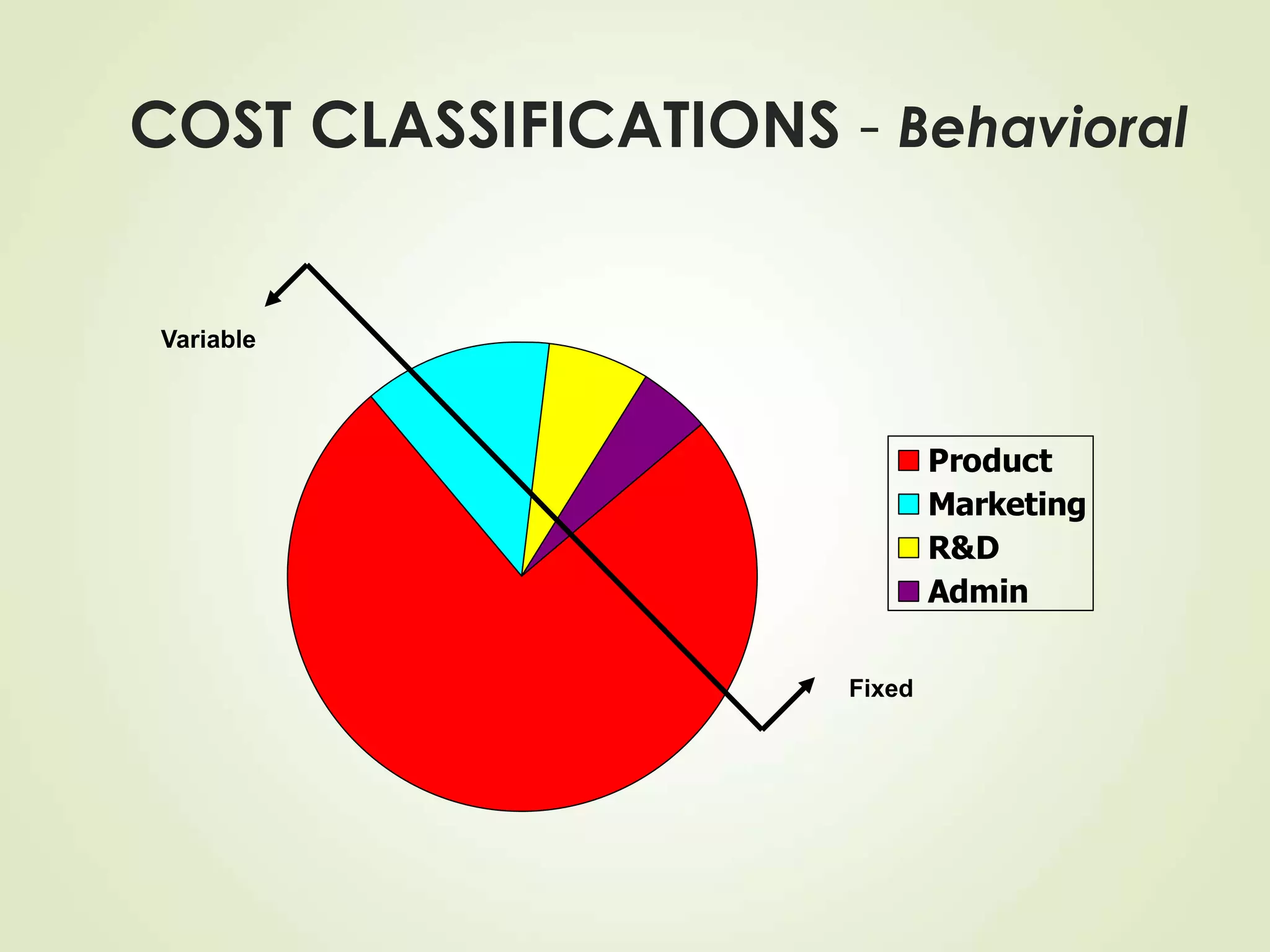
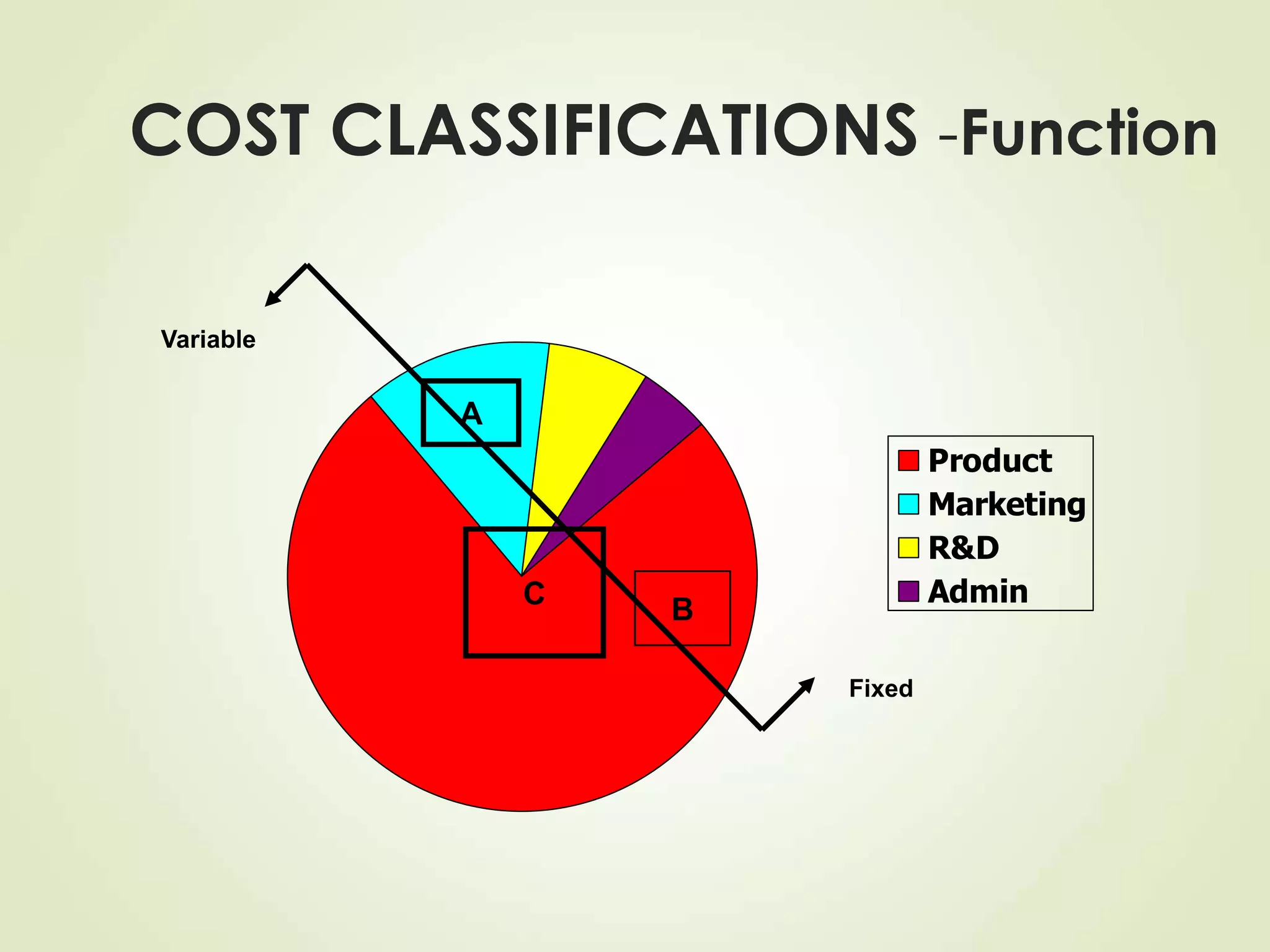
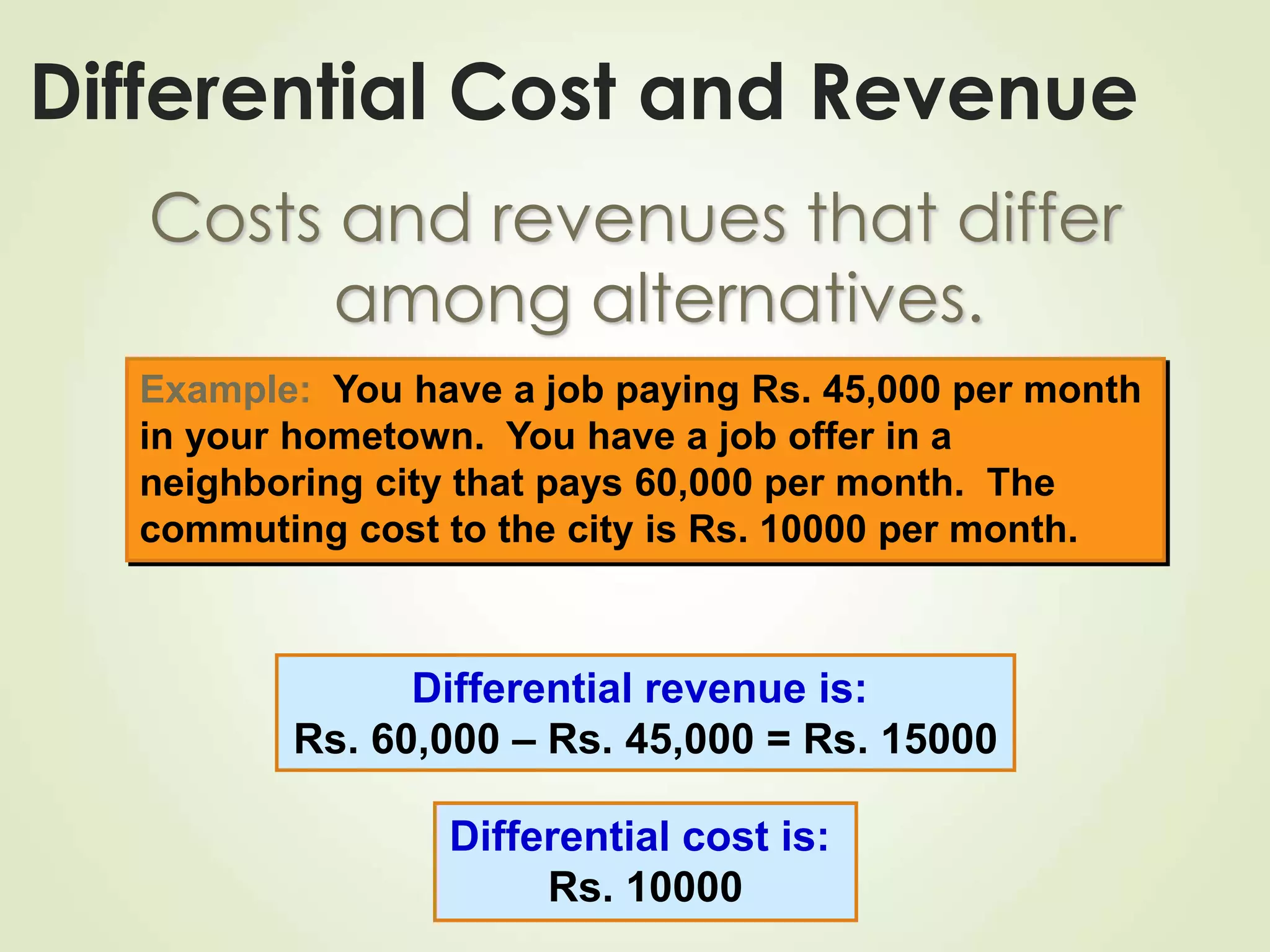
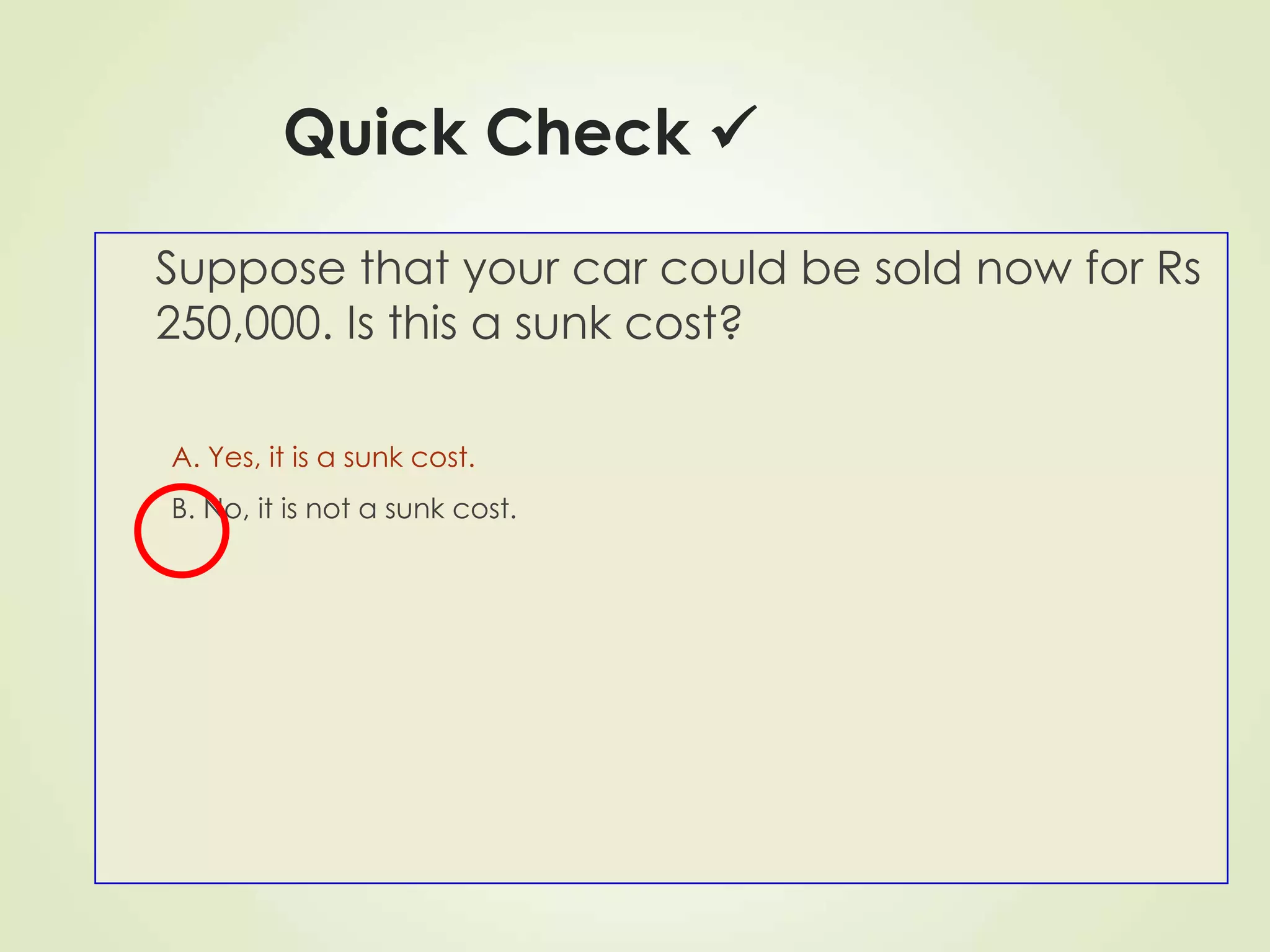
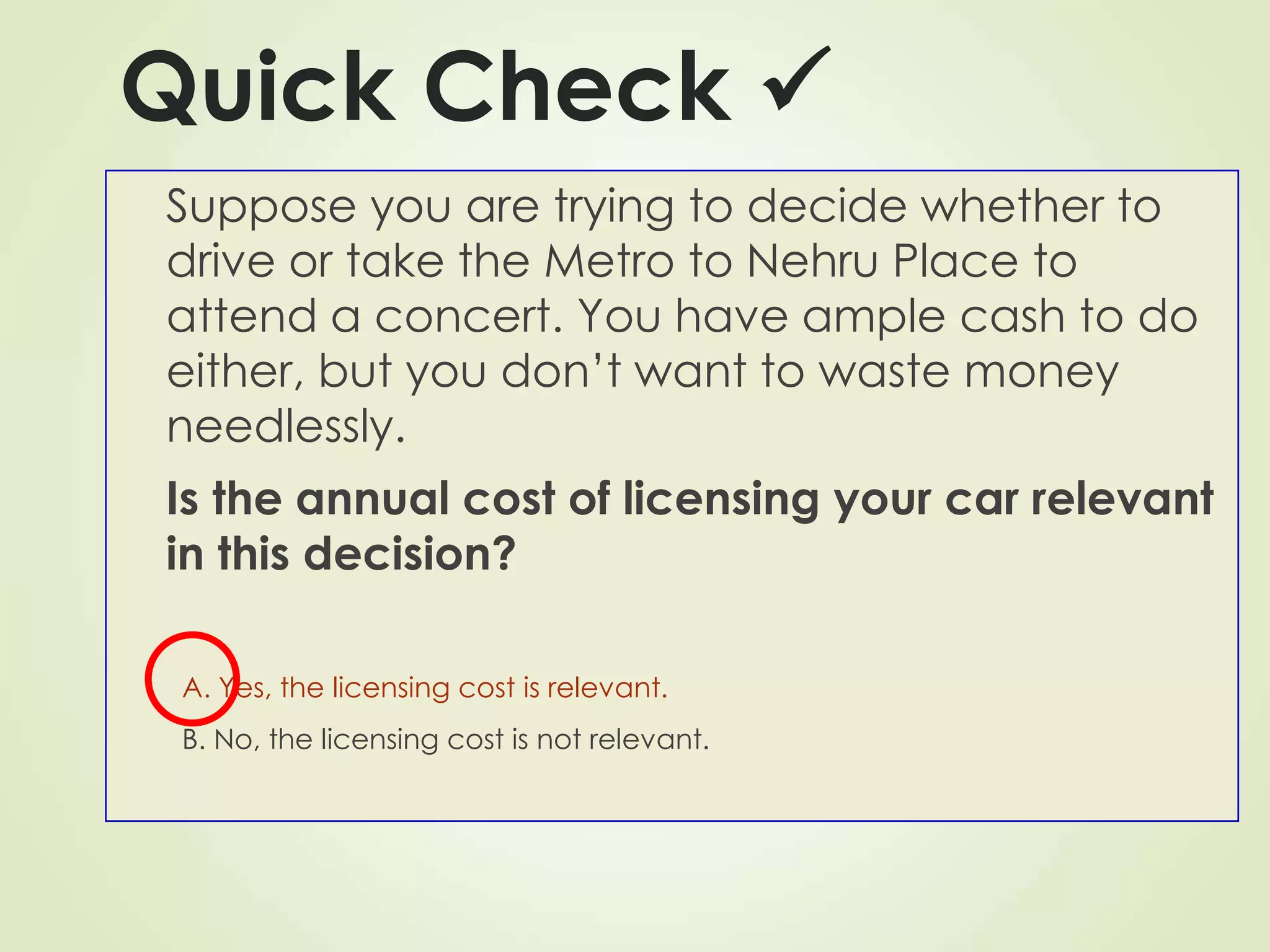
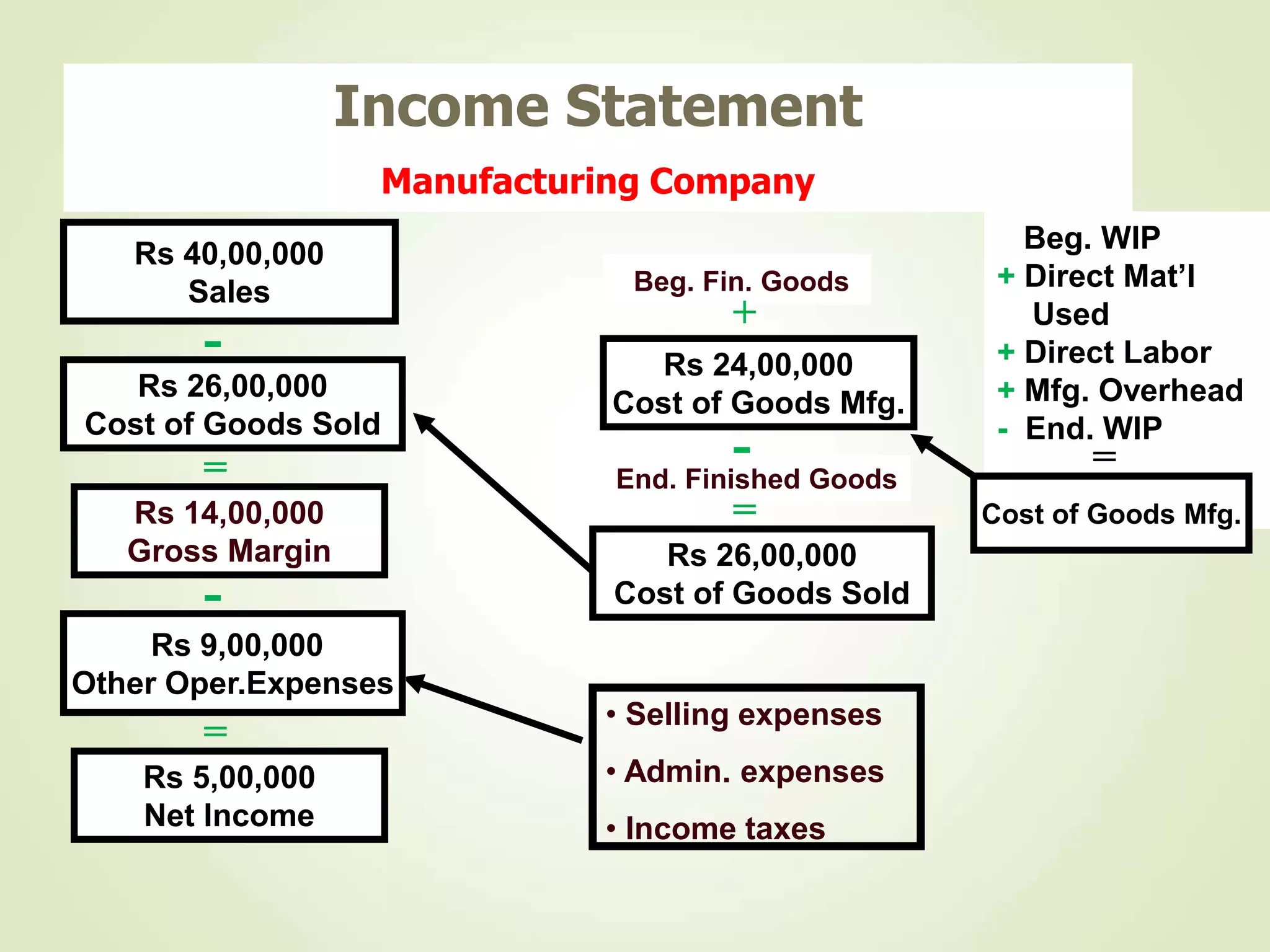
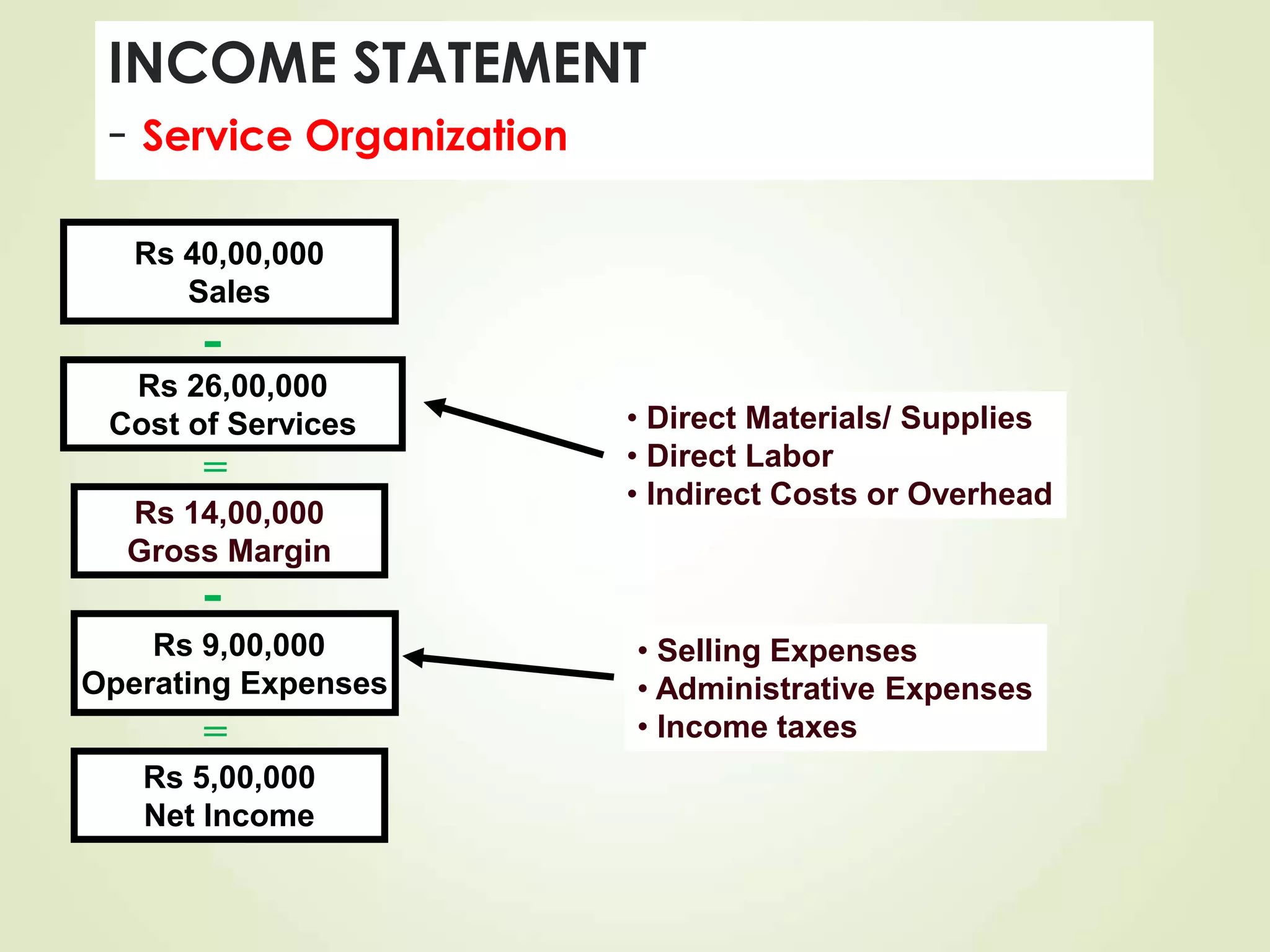
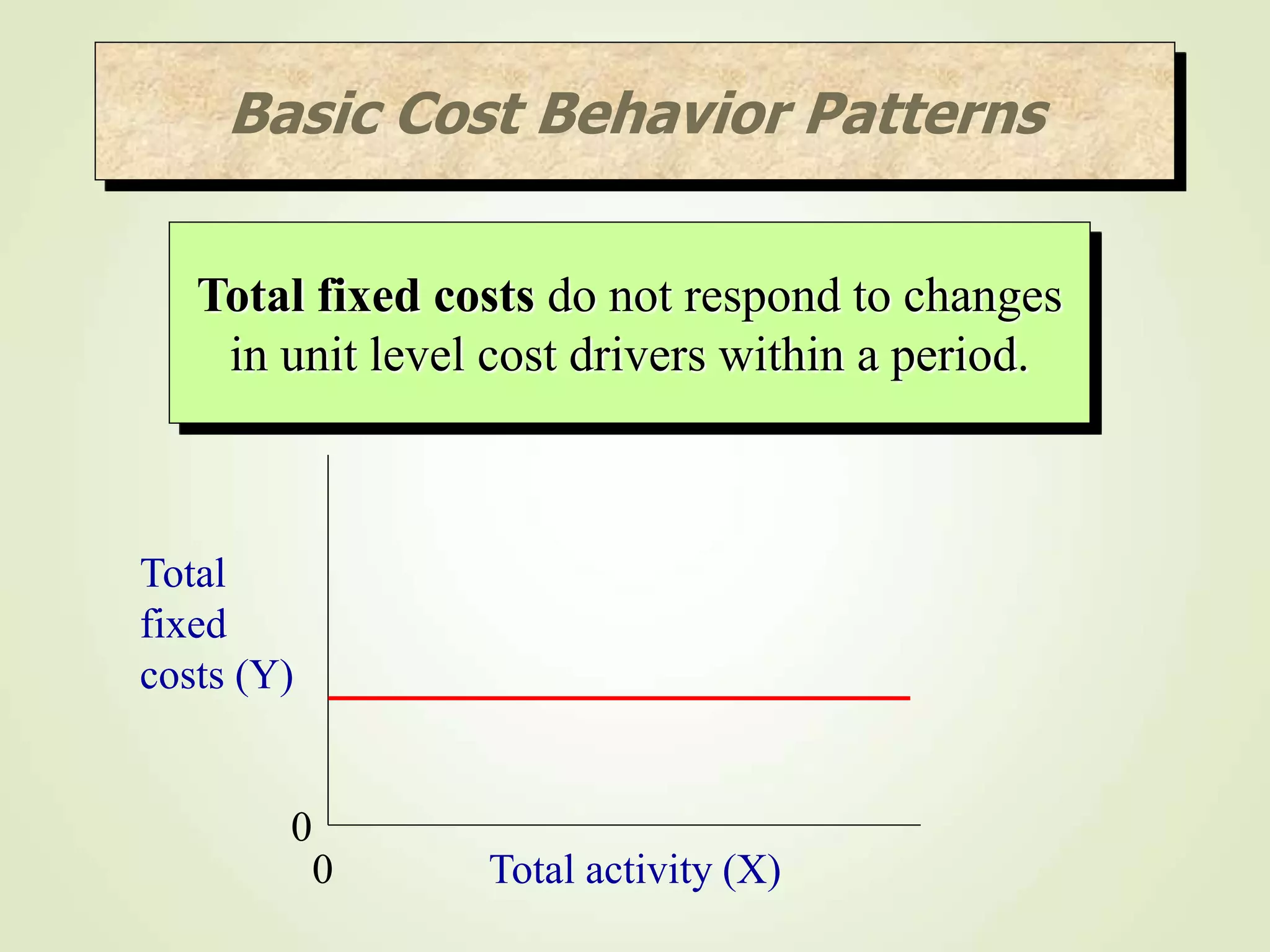
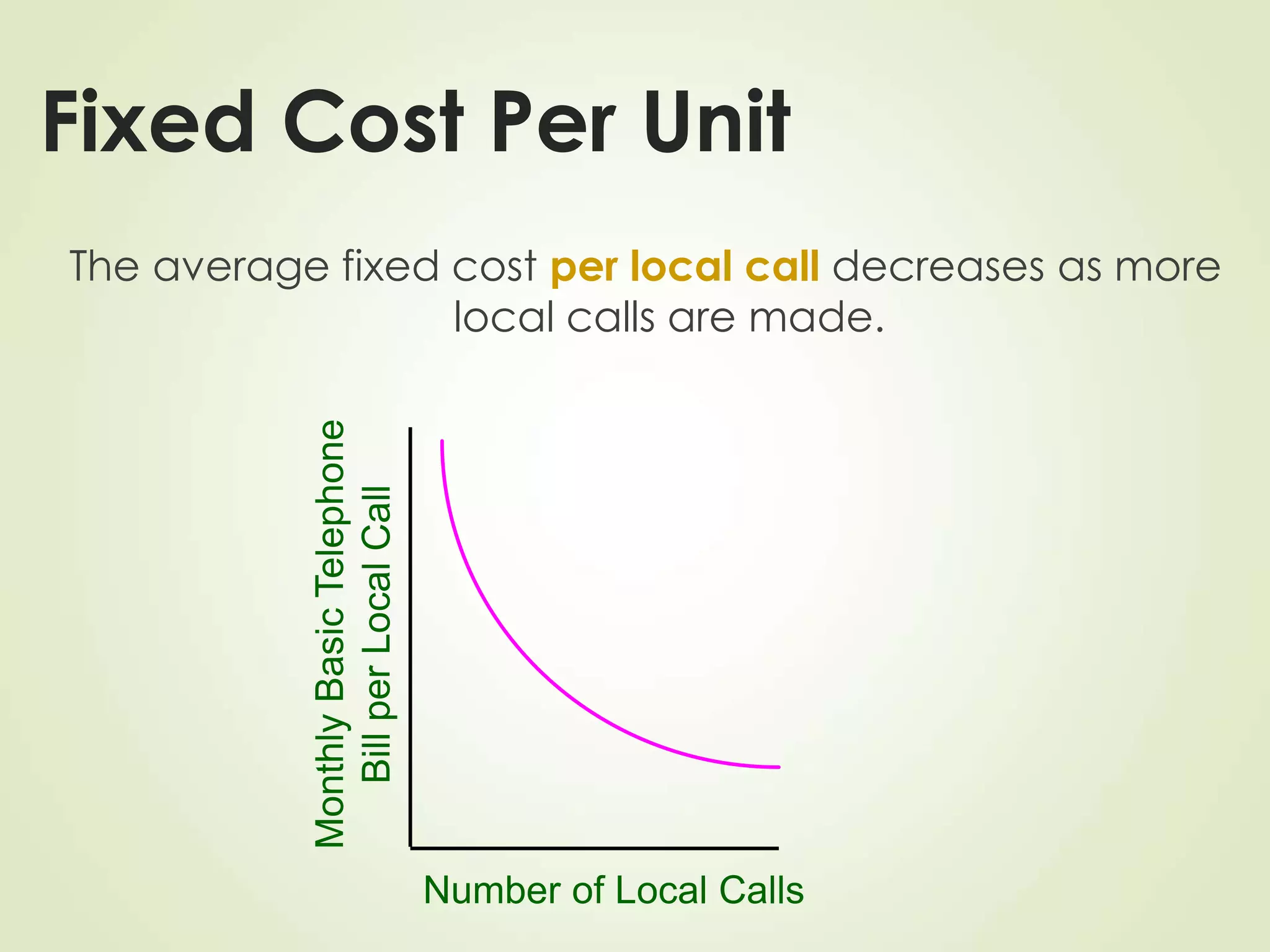
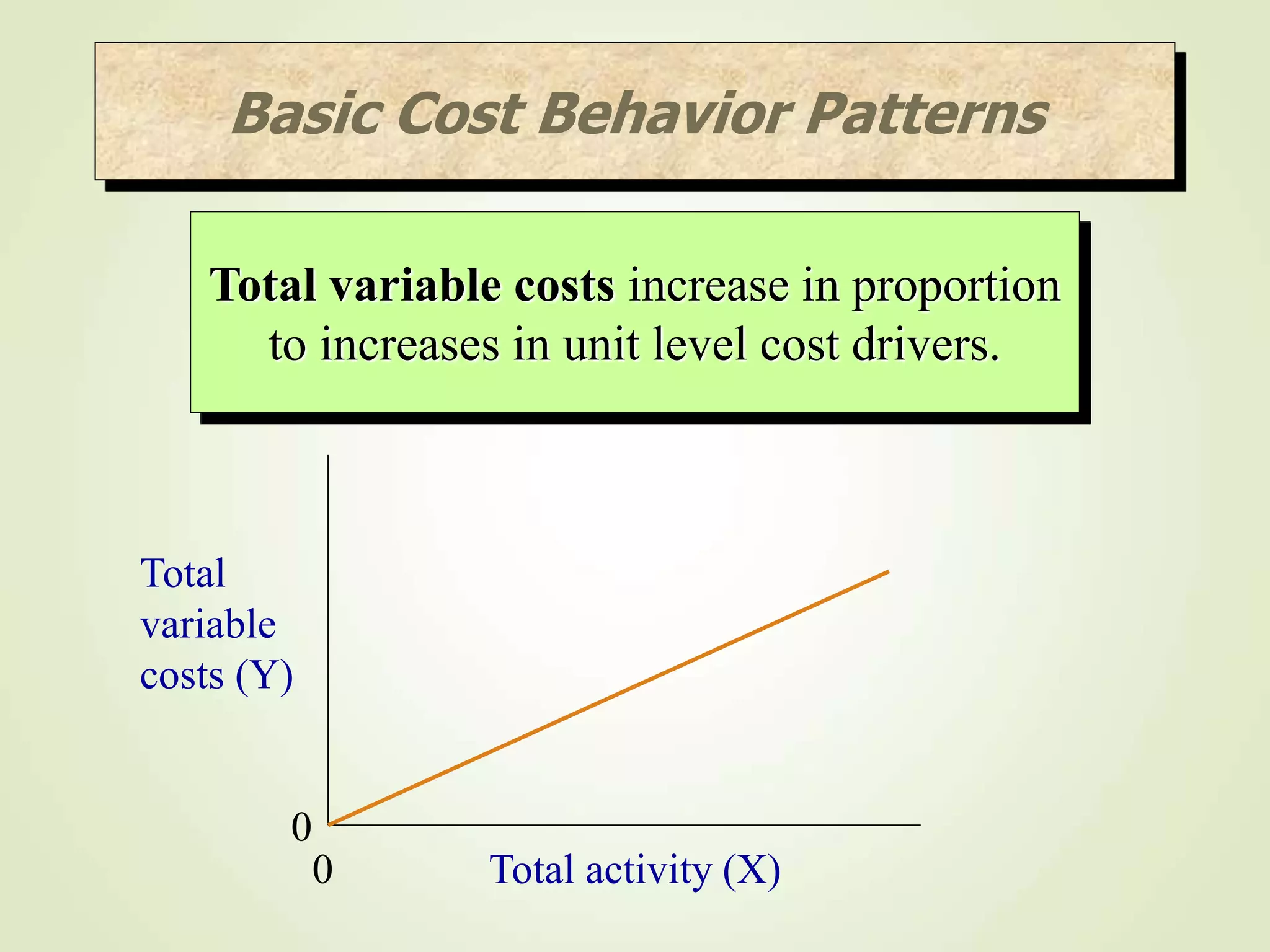
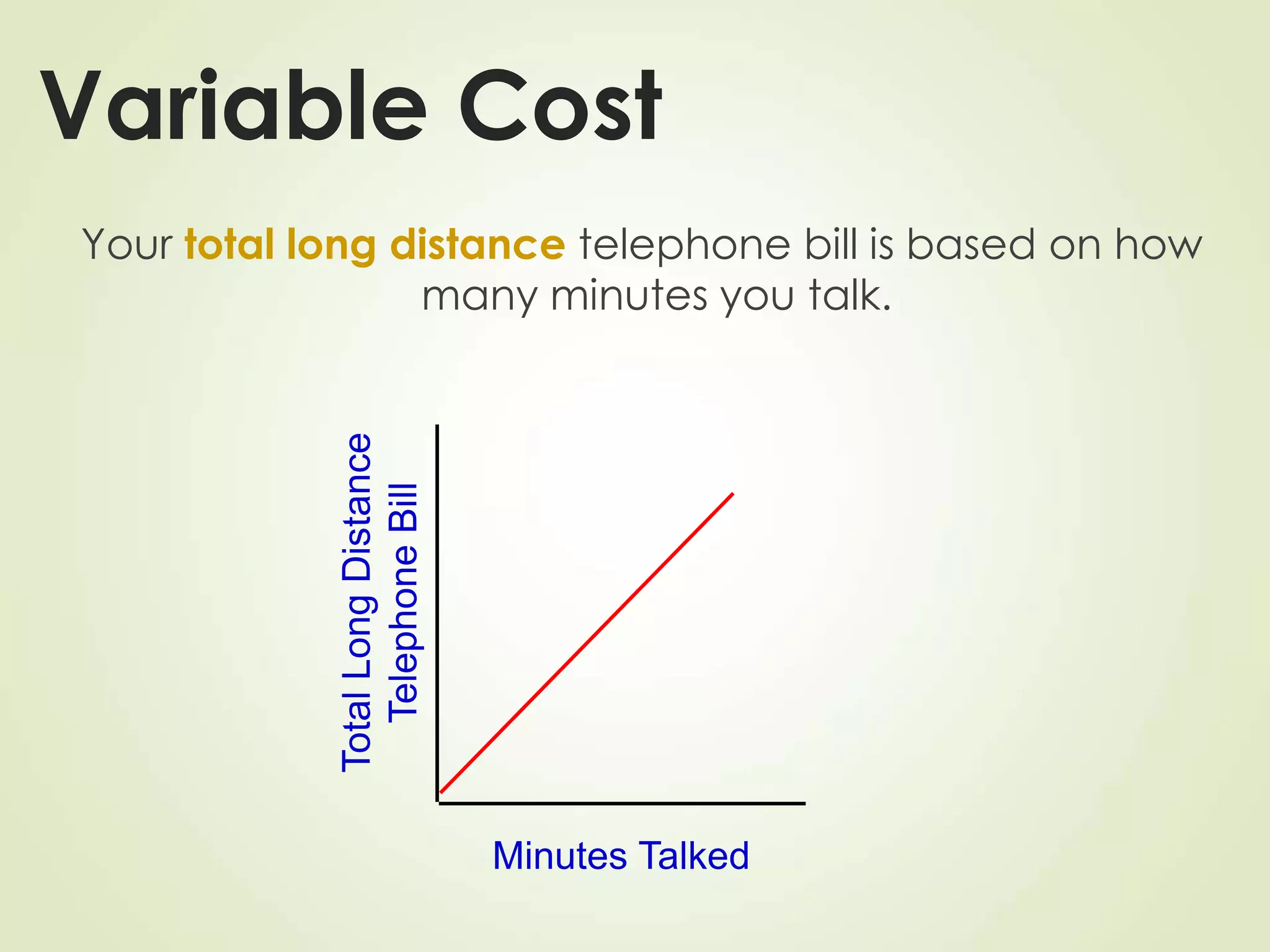
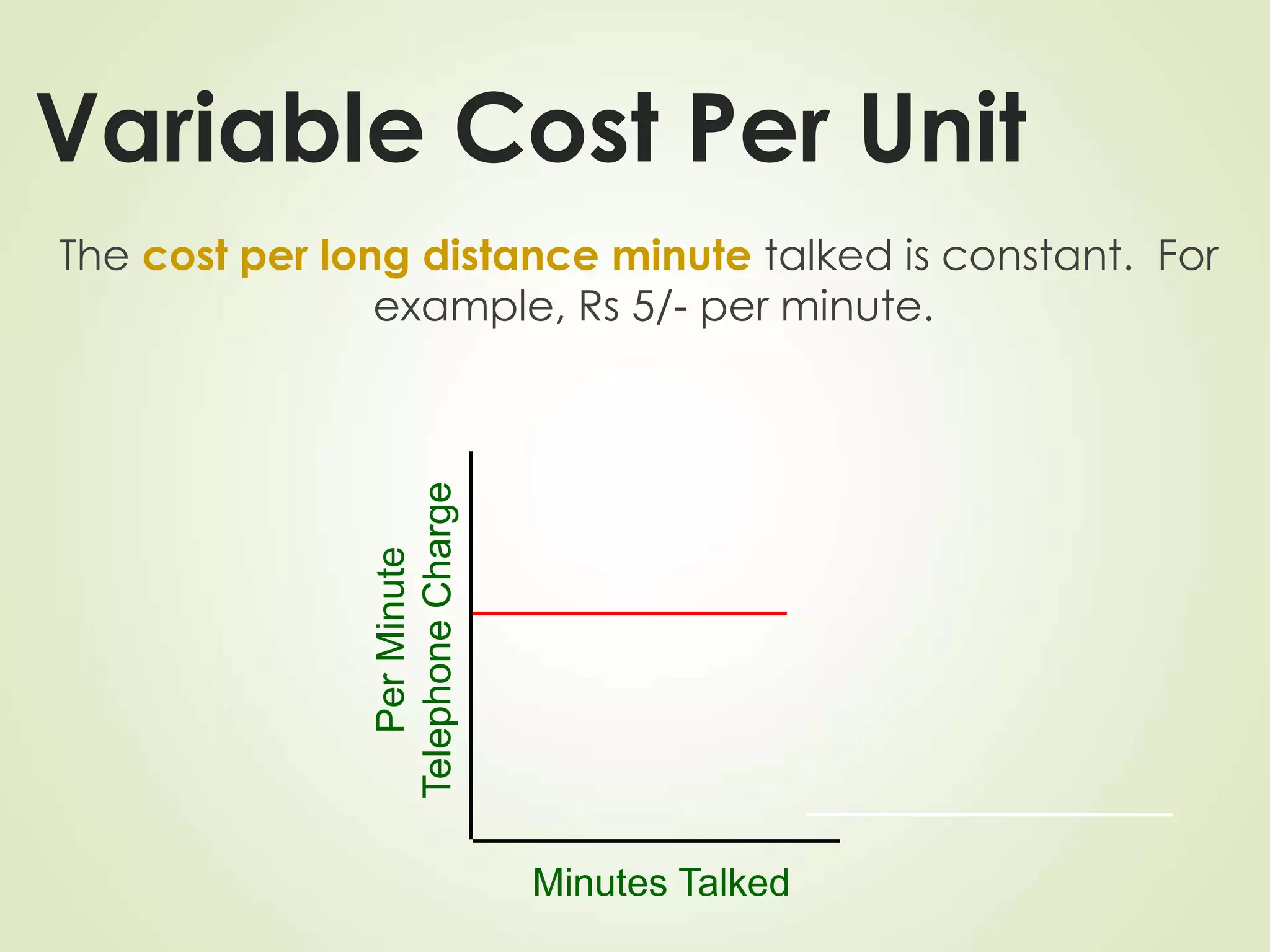
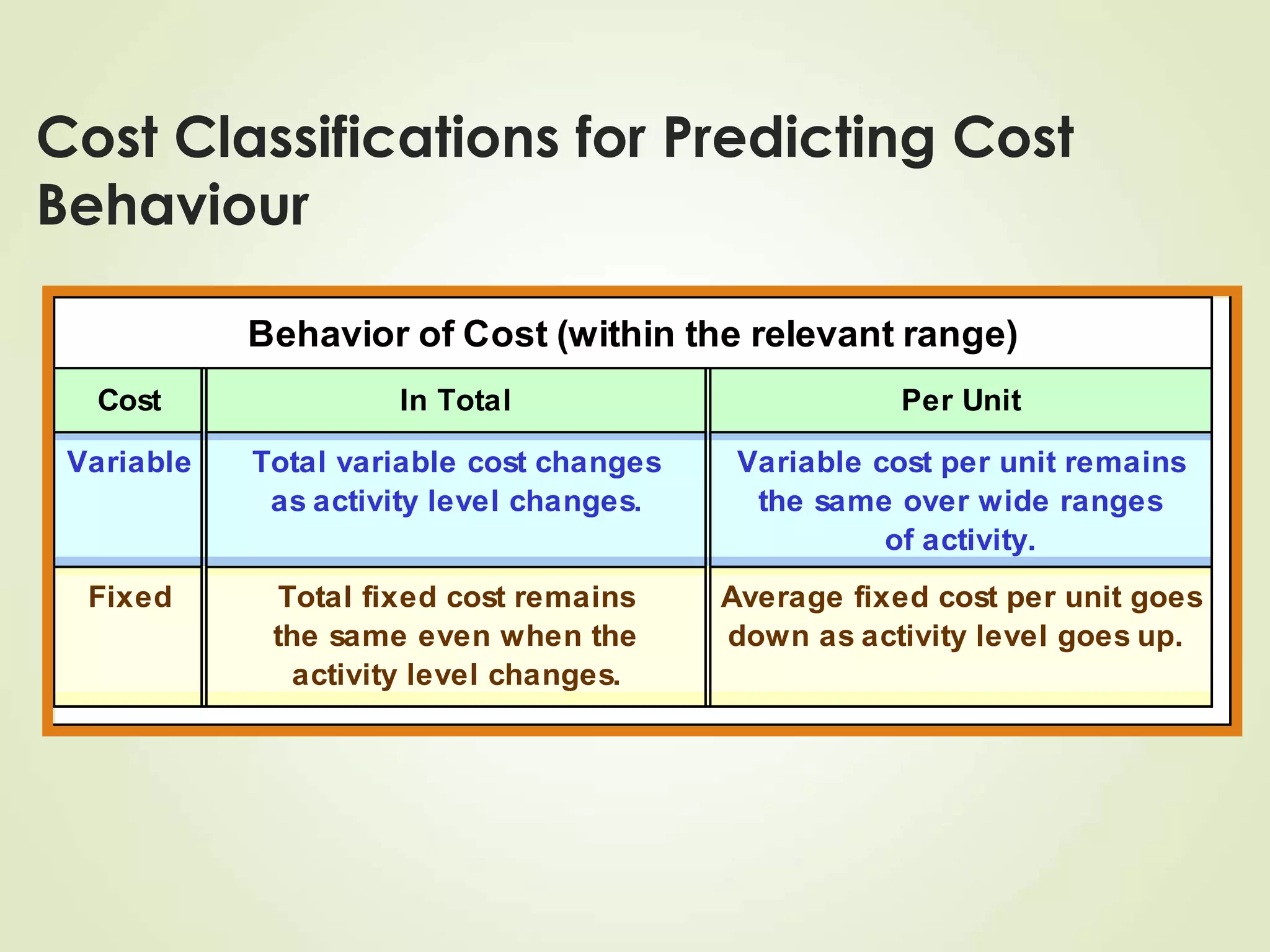
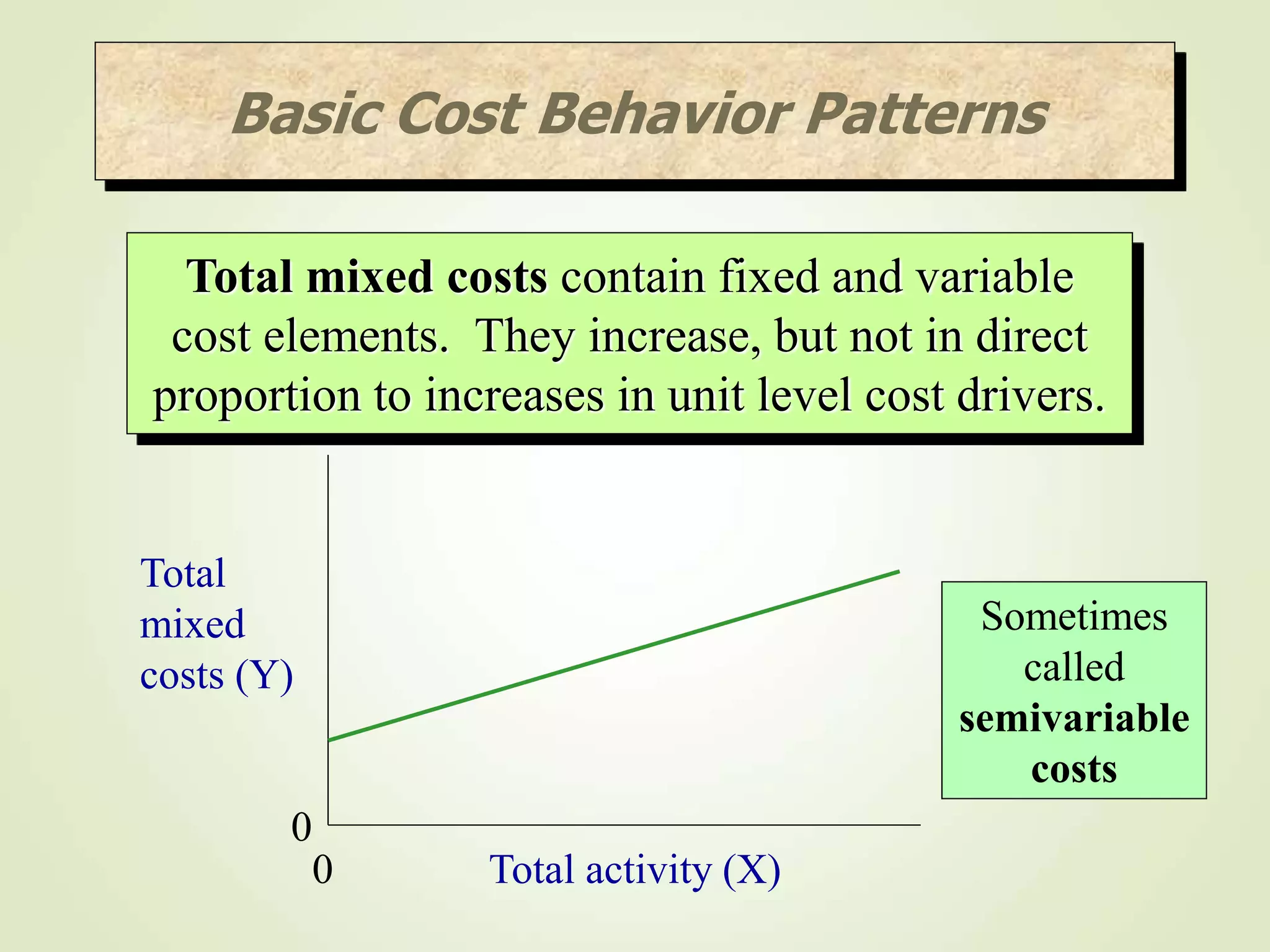
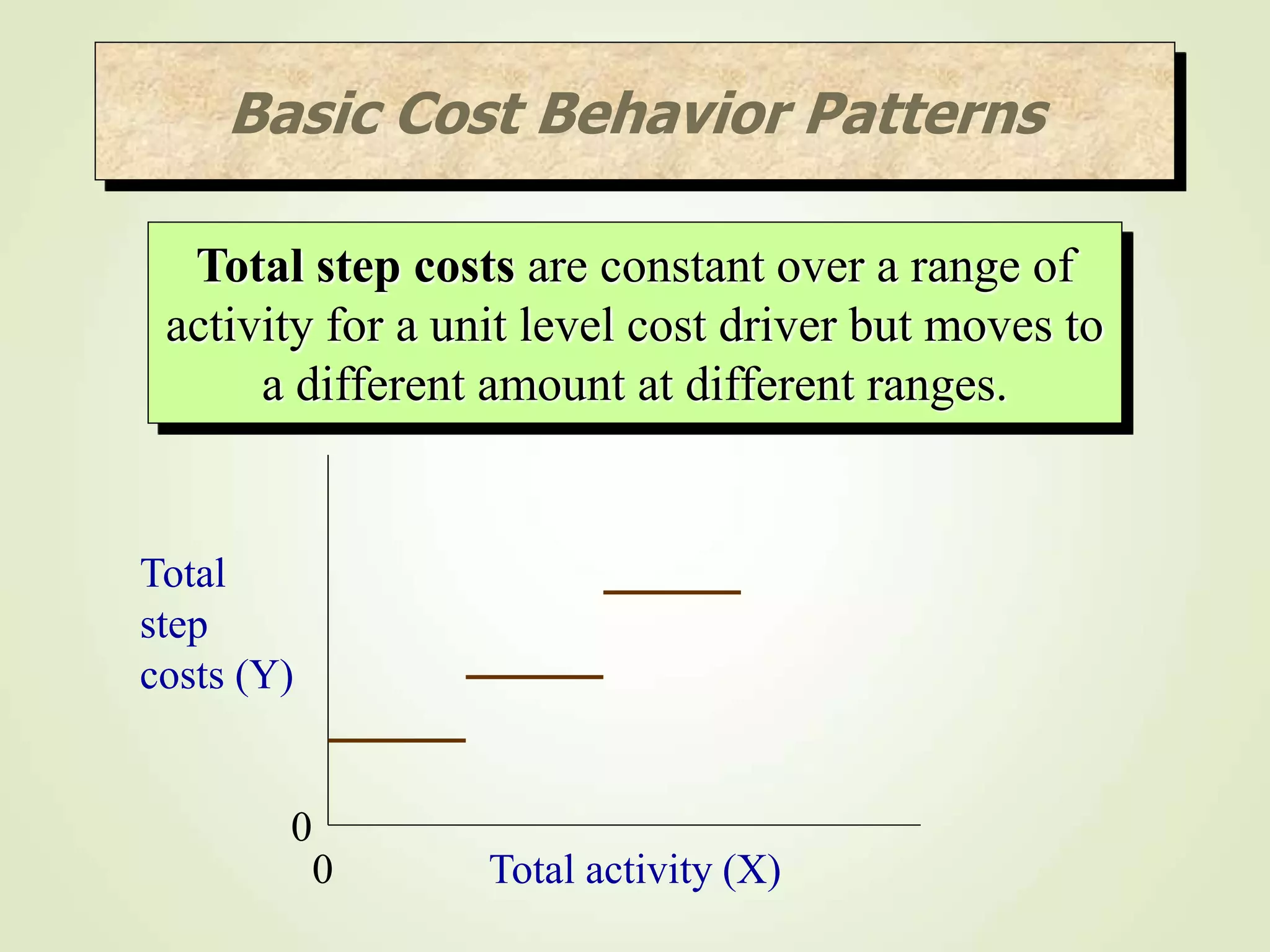
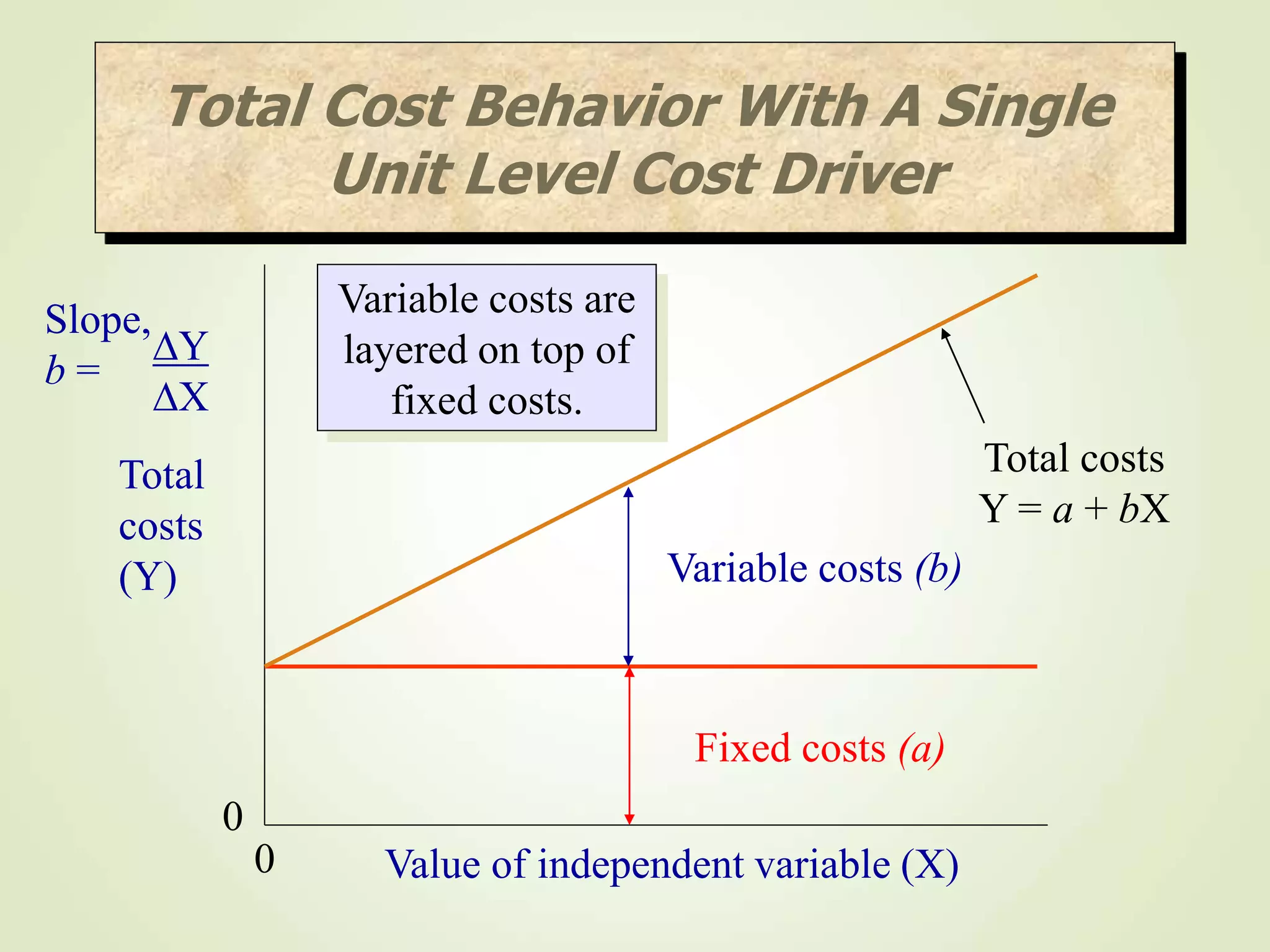
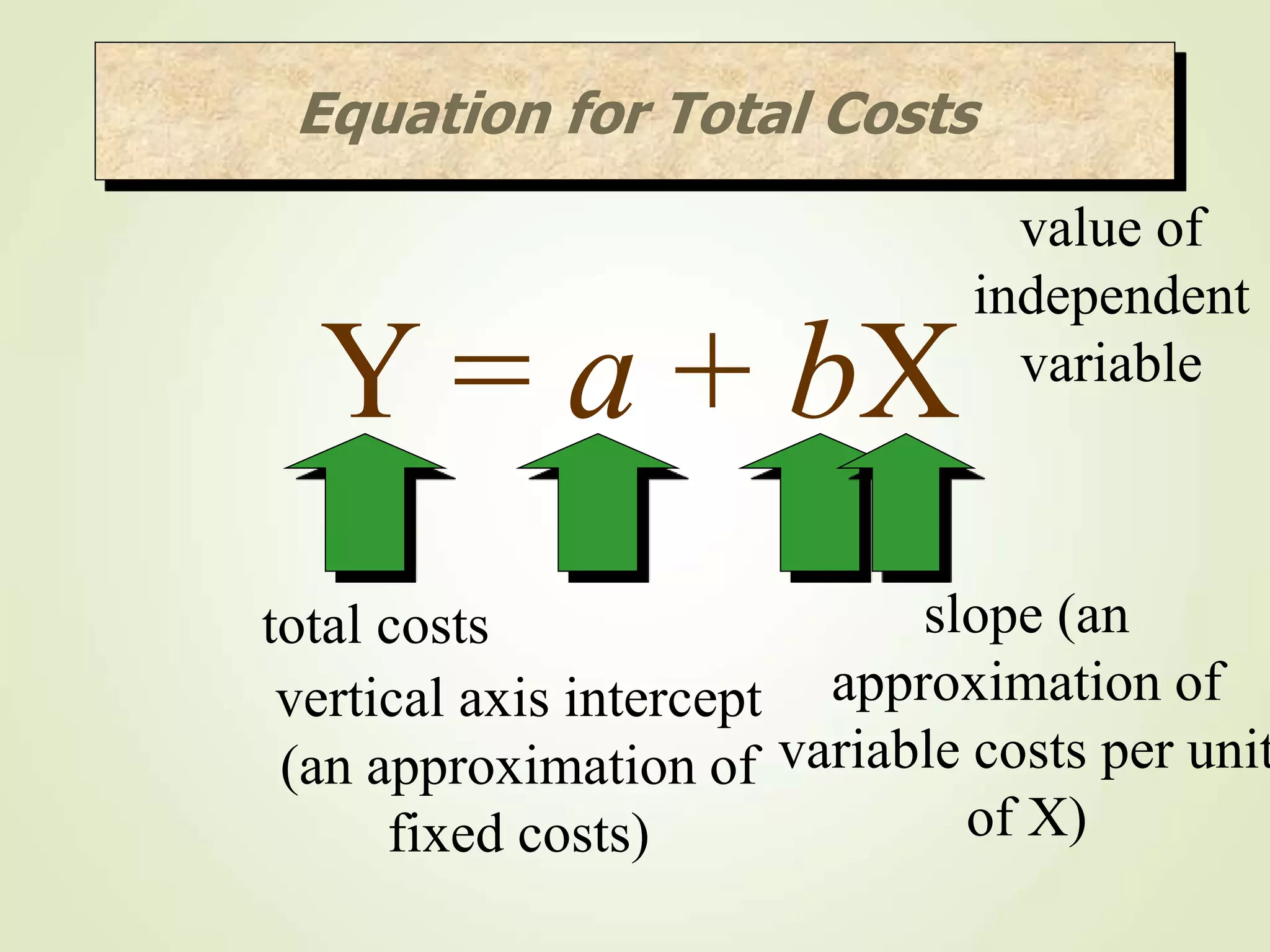
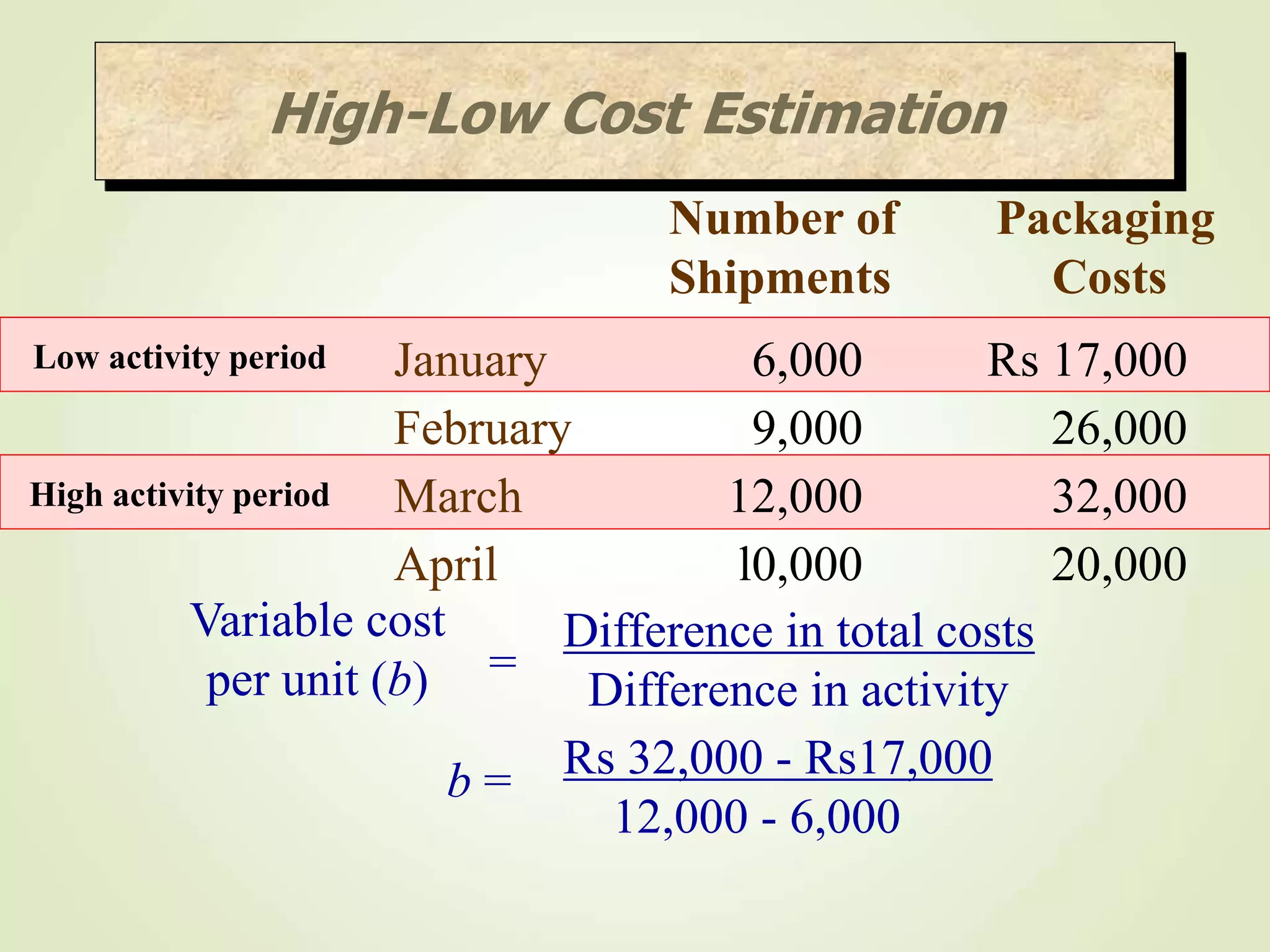
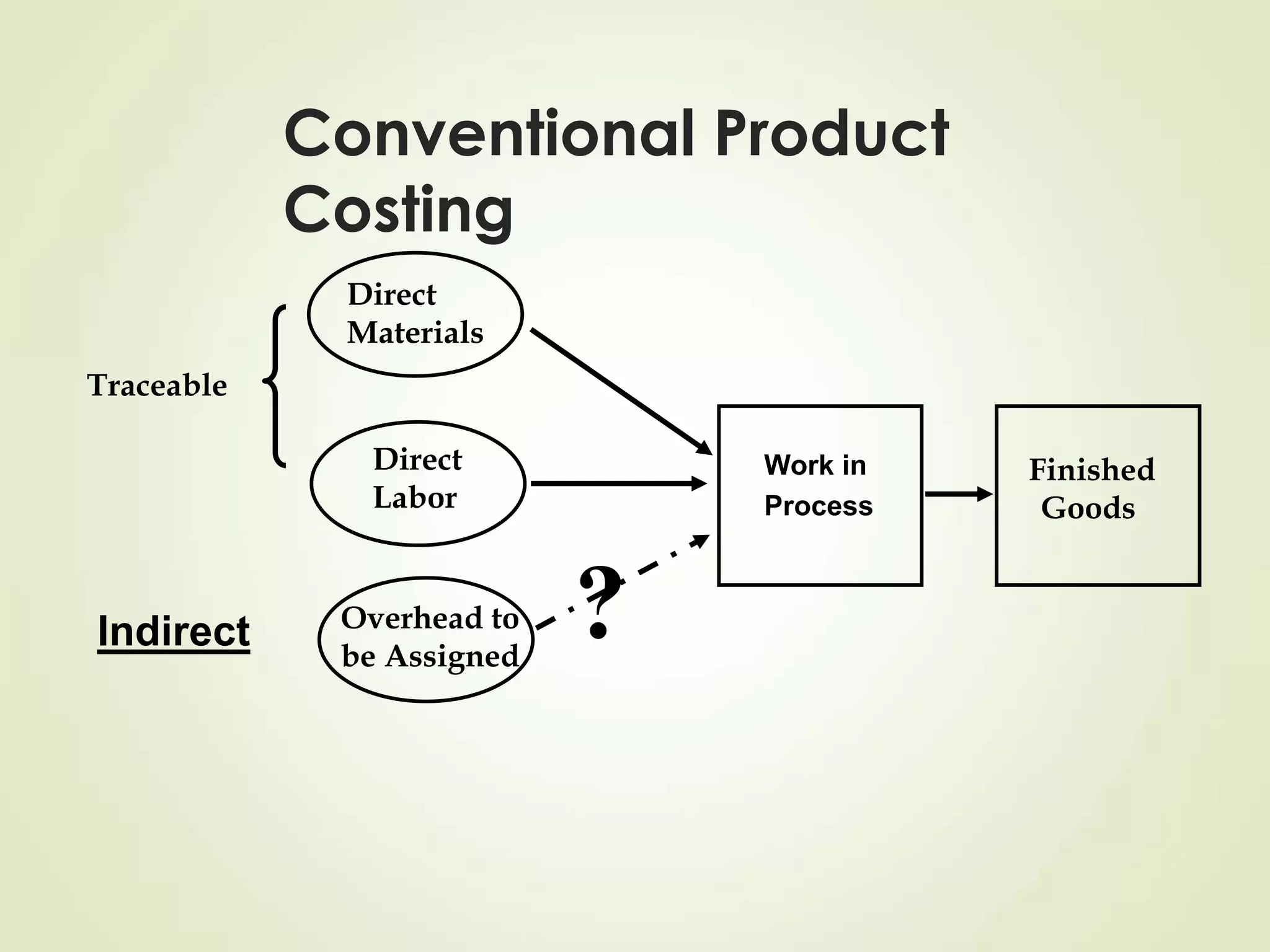
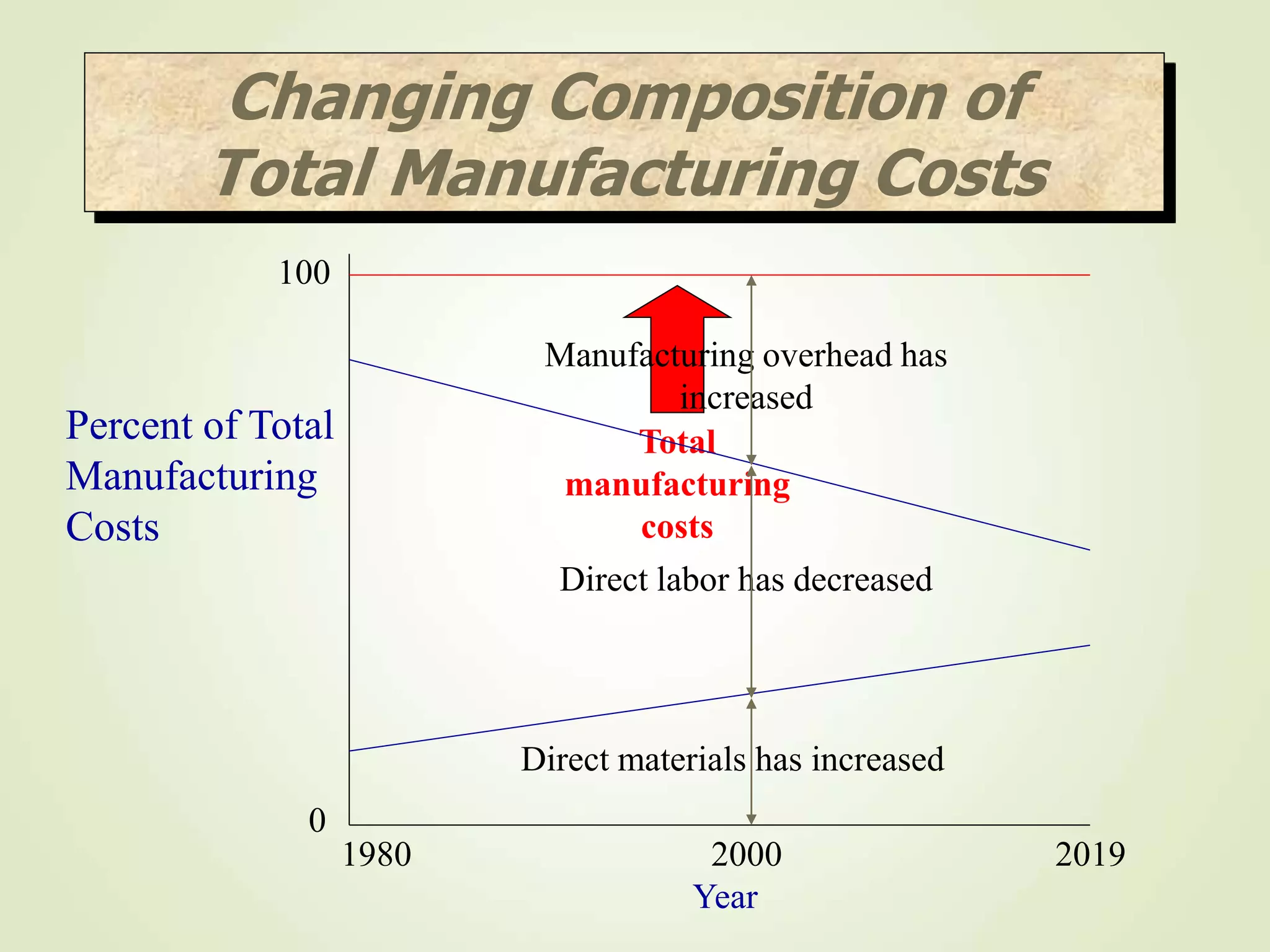
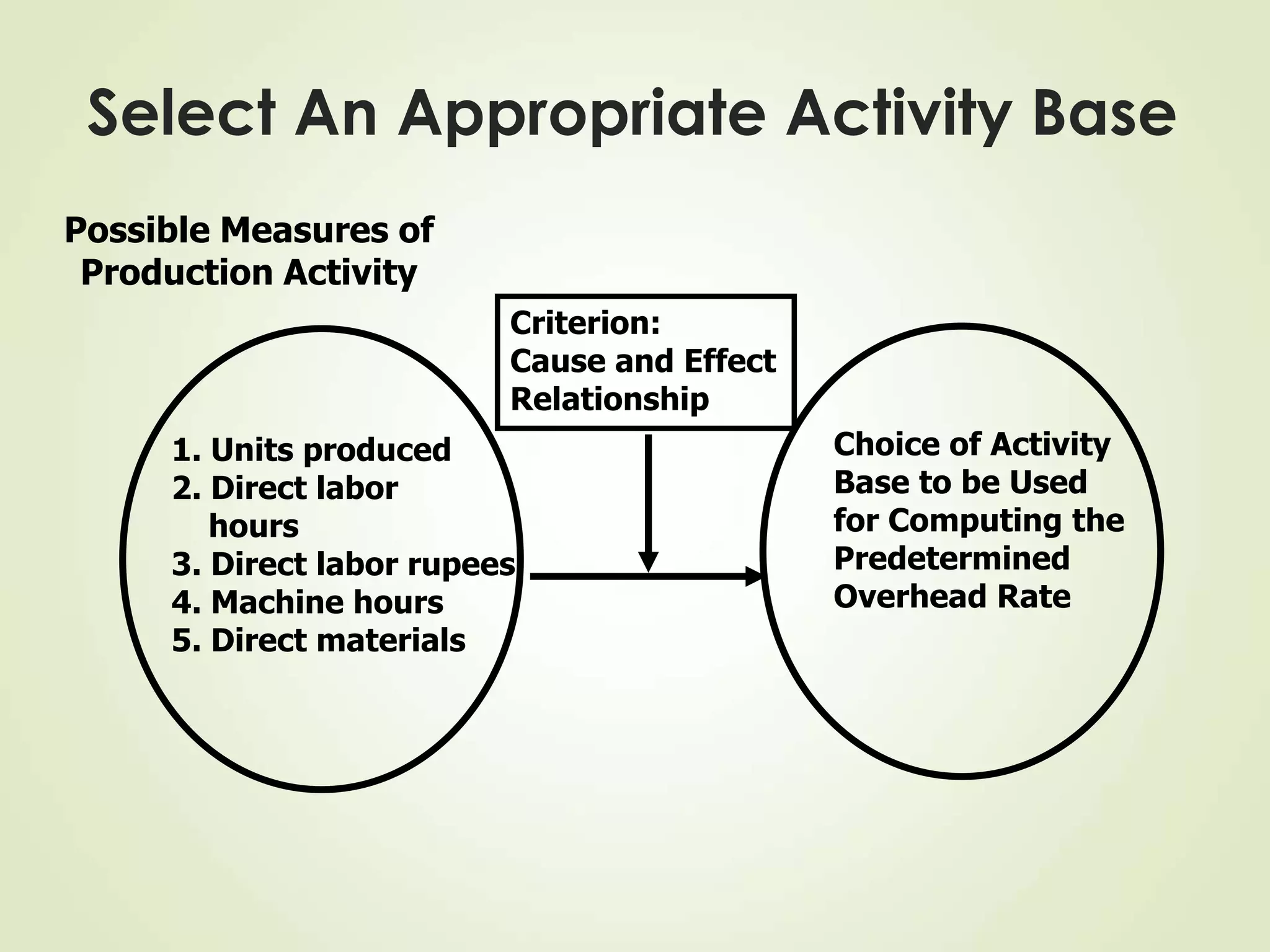
The document discusses various cost terms, concepts, and classifications used in cost accounting. It defines key cost elements like direct and indirect materials, direct and indirect labor, and other direct and indirect expenses. It also explains different cost classifications like fixed vs variable costs, product vs period costs, and classifications used for decision-making, planning, and control. Functional and behavioral cost classifications as well as relevant cost concepts are outlined.