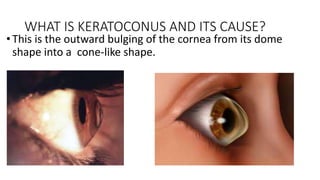
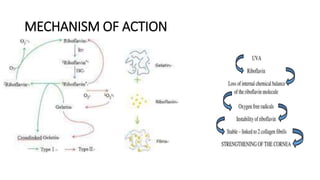
Corneal cross-linking is a treatment for keratoconus that uses riboflavin eye drops and UV light to strengthen the collagen in the cornea. There are two types of cross-linking - epithelium-off which removes the outer corneal layer, and epithelium-on which leaves it intact. Cross-linking adds bonds between collagen fibers to help stabilize the cornea. It is best used early in keratoconus before the cornea becomes severely irregular. Keratoconus causes the cornea to thin and bulge into a cone shape due to weakened collagen from decreased antioxidants. It is diagnosed based on changes in corneal shape and vision problems. Treatment options include glasses, contacts, cross-linking, and