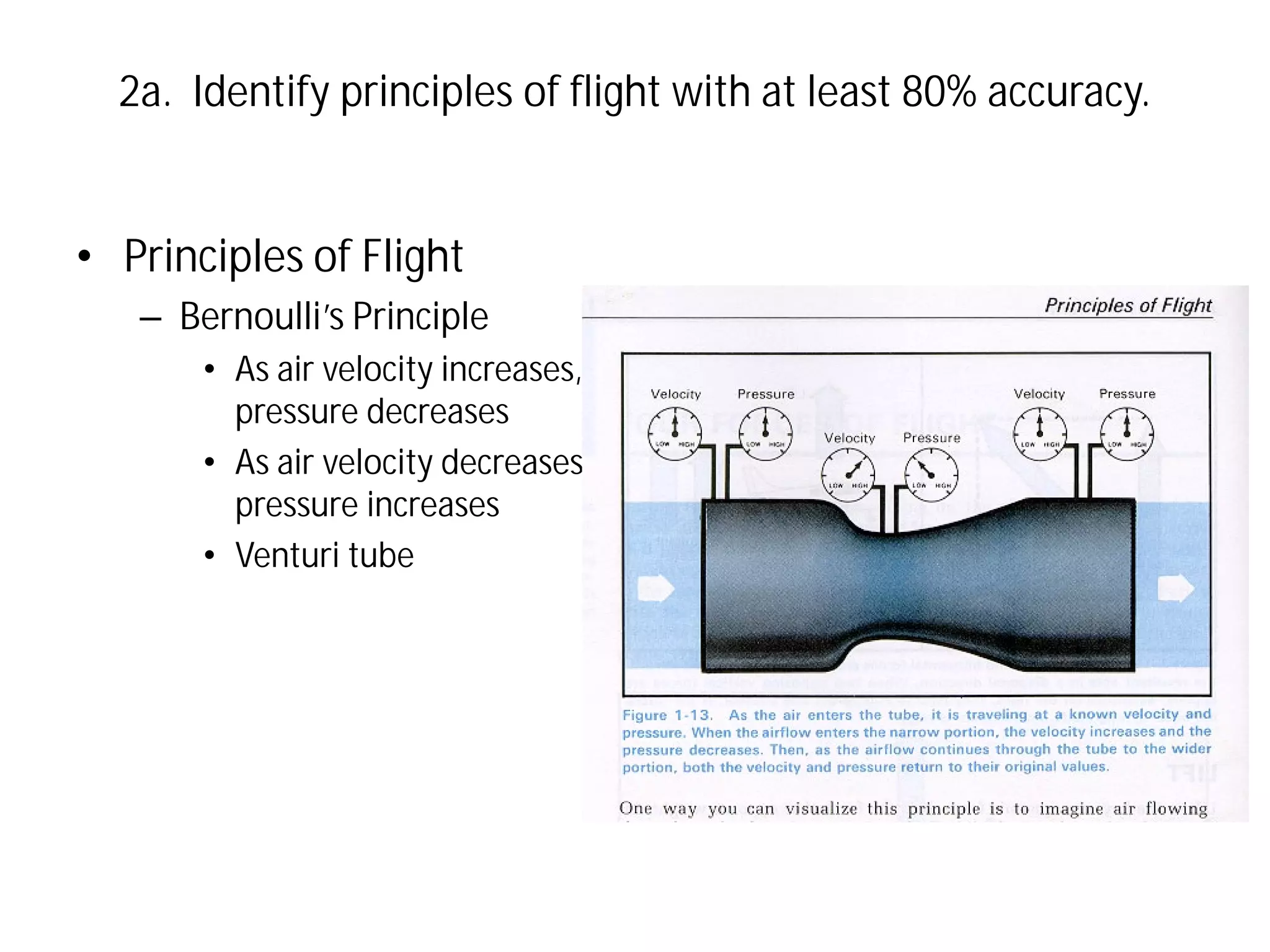
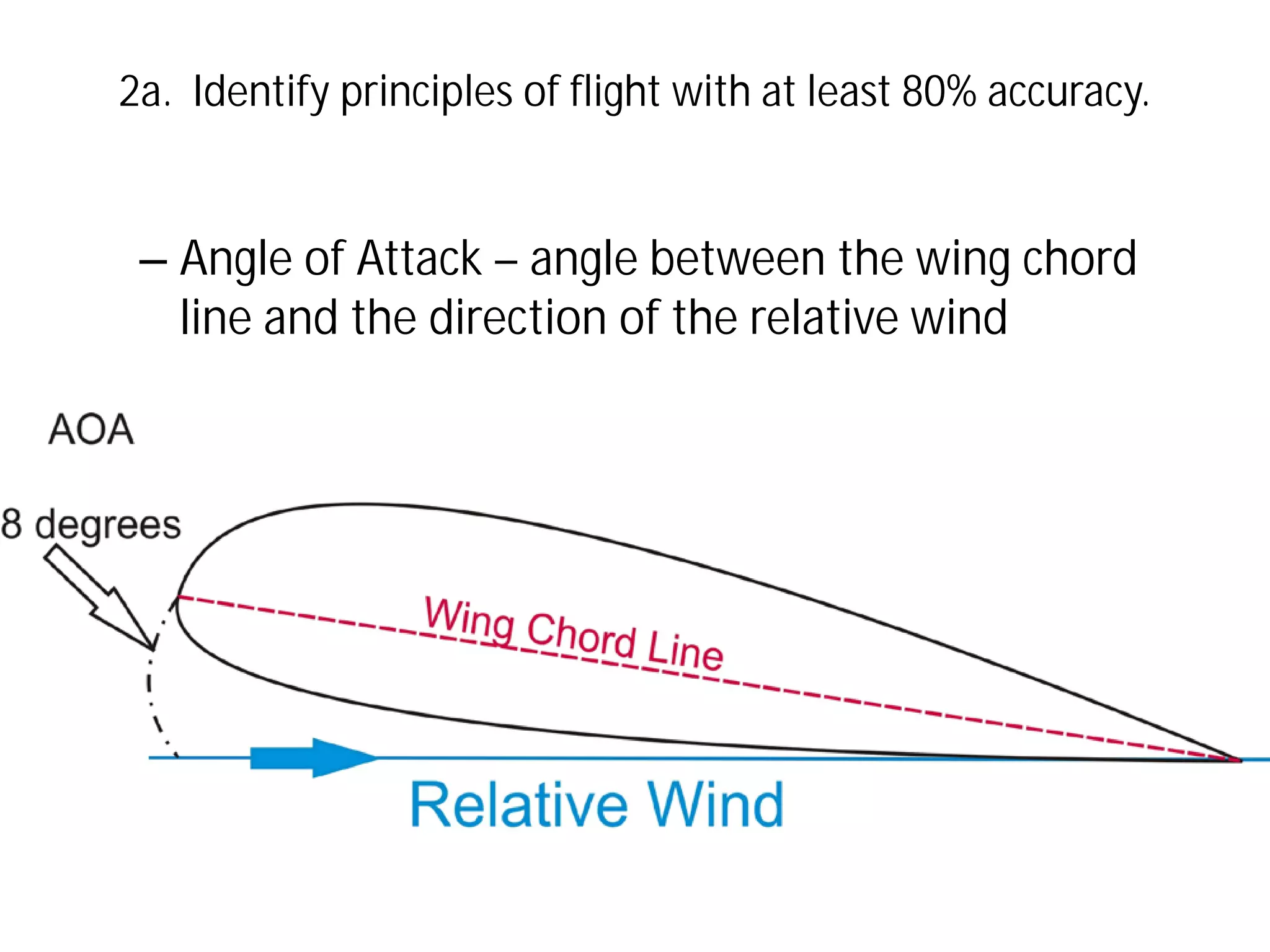
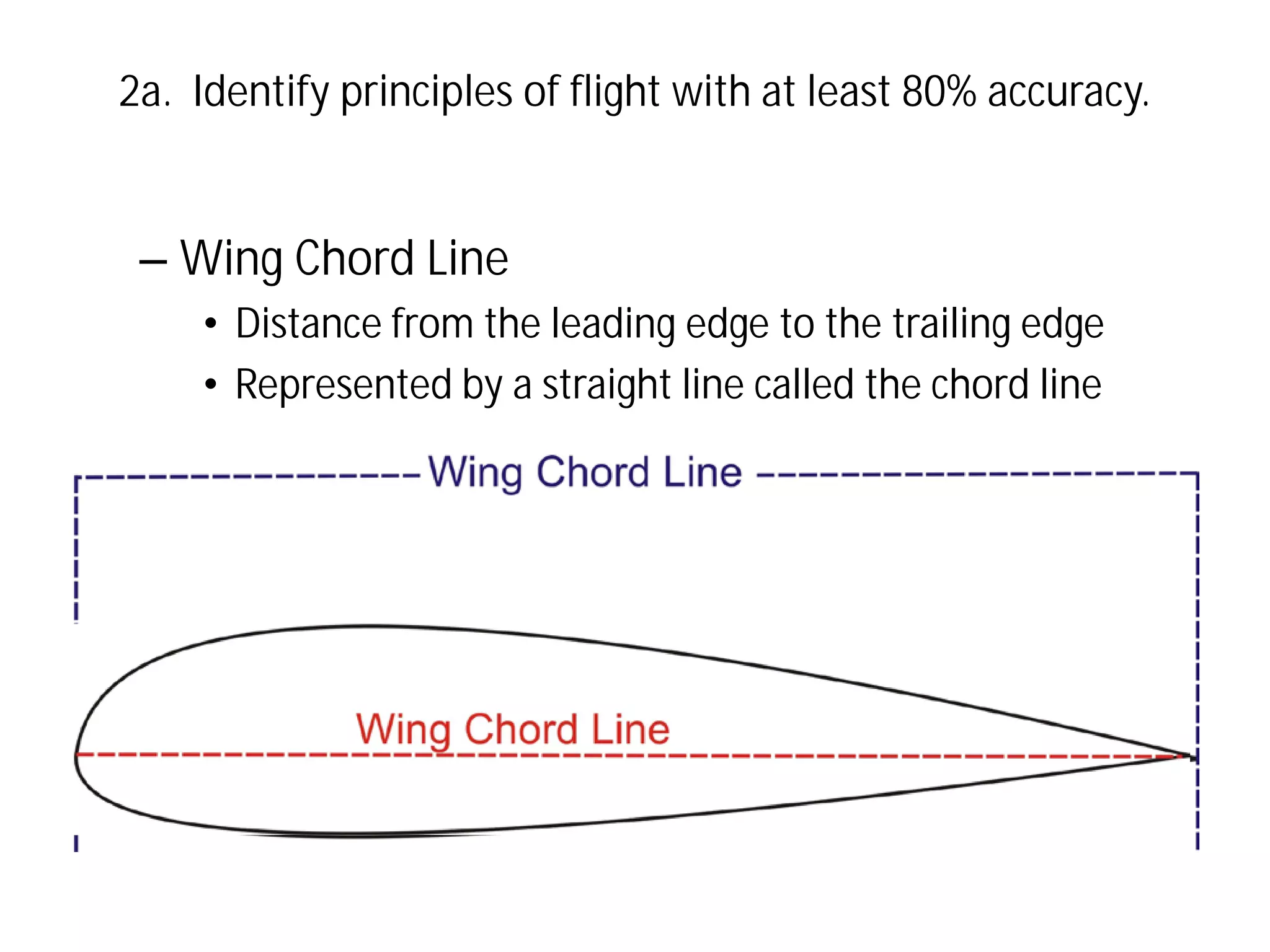
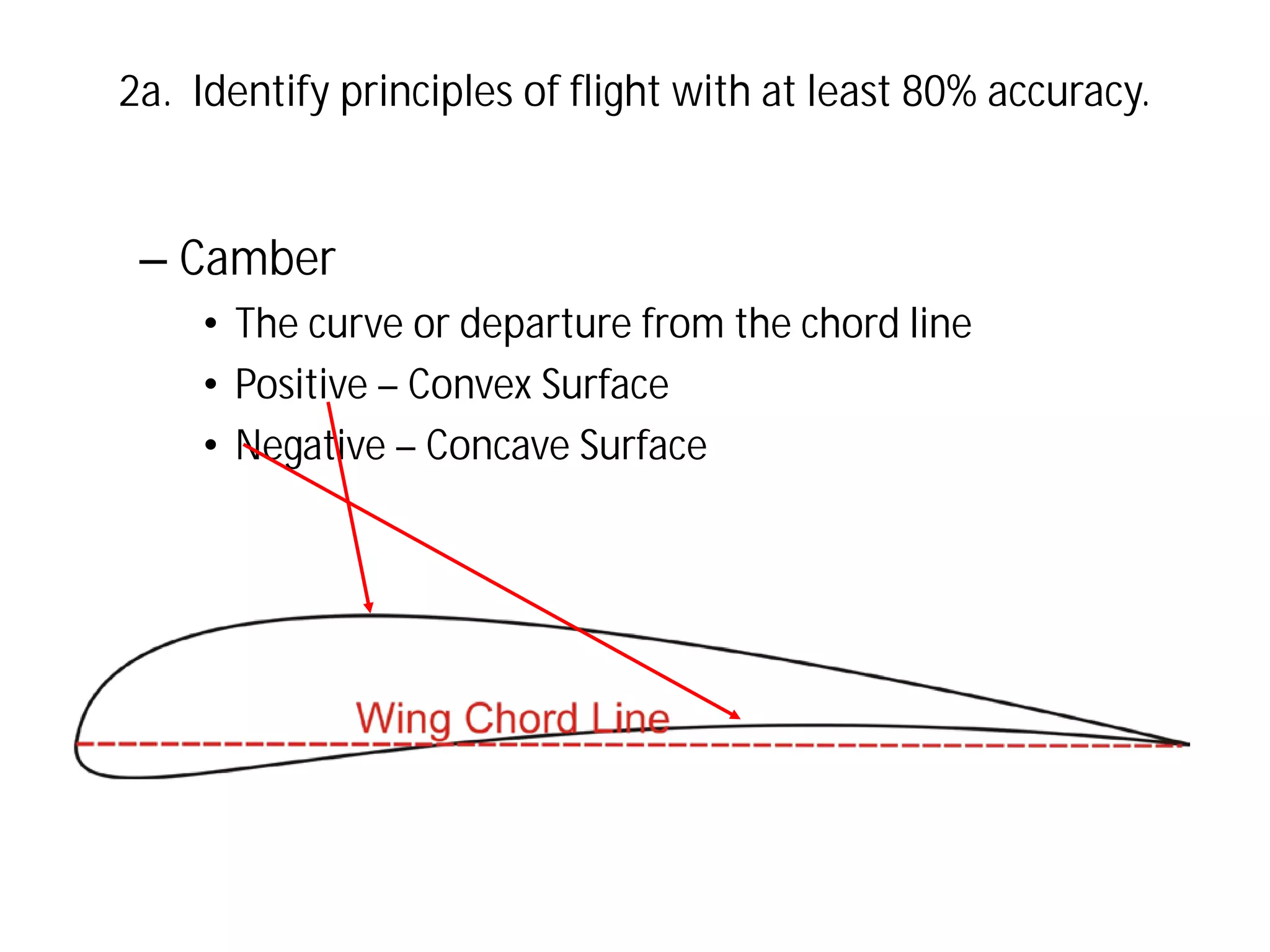
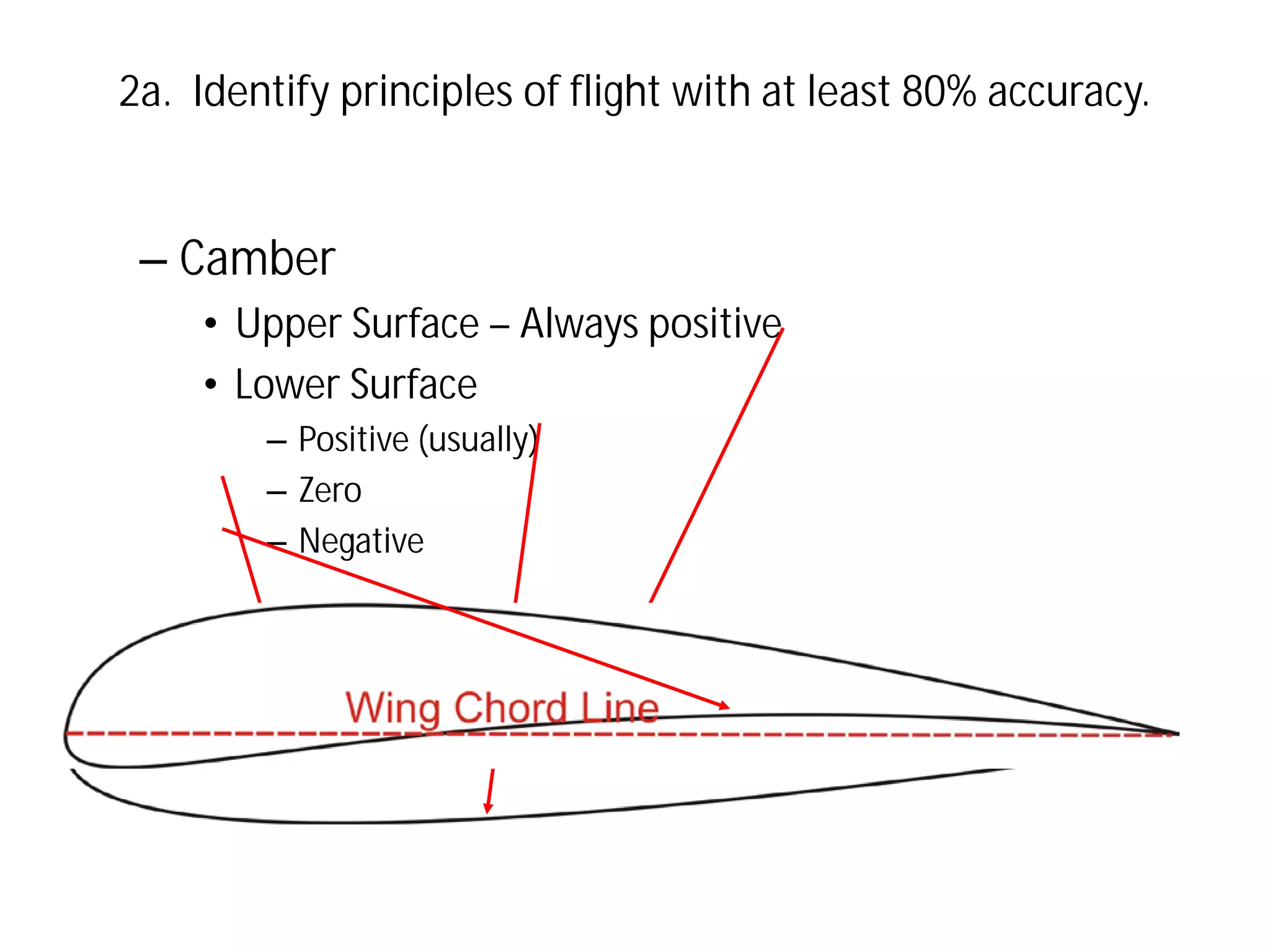
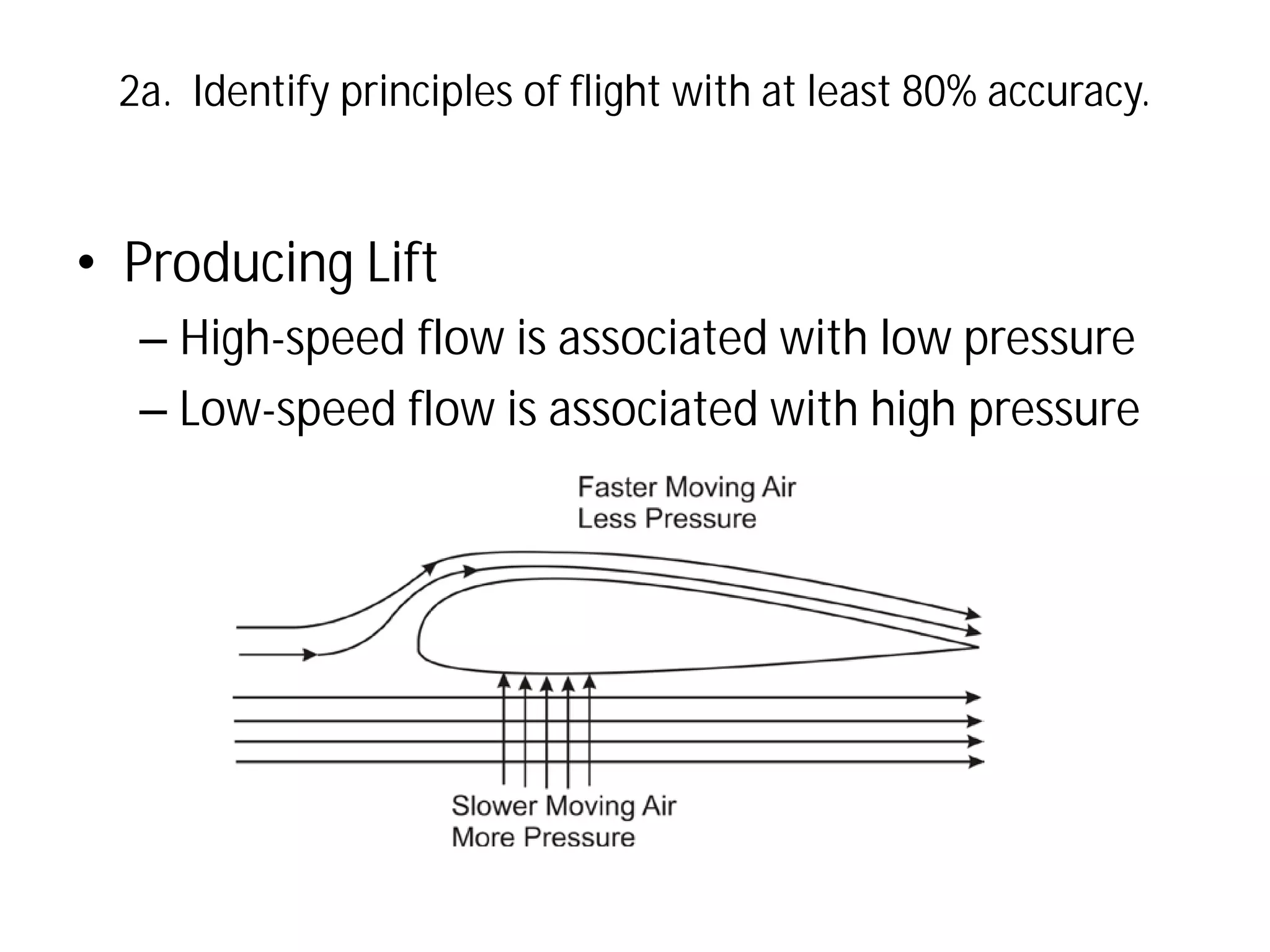
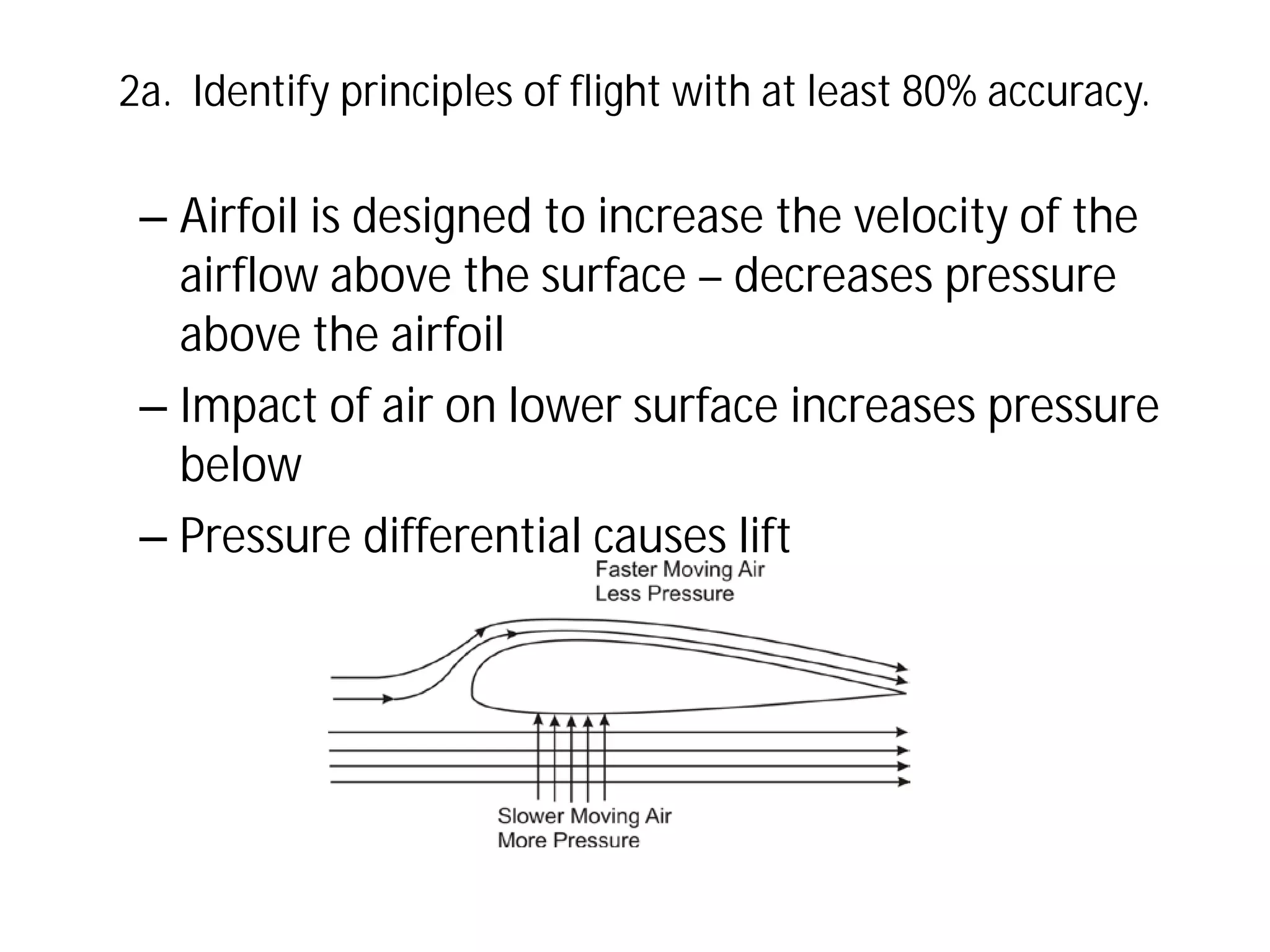
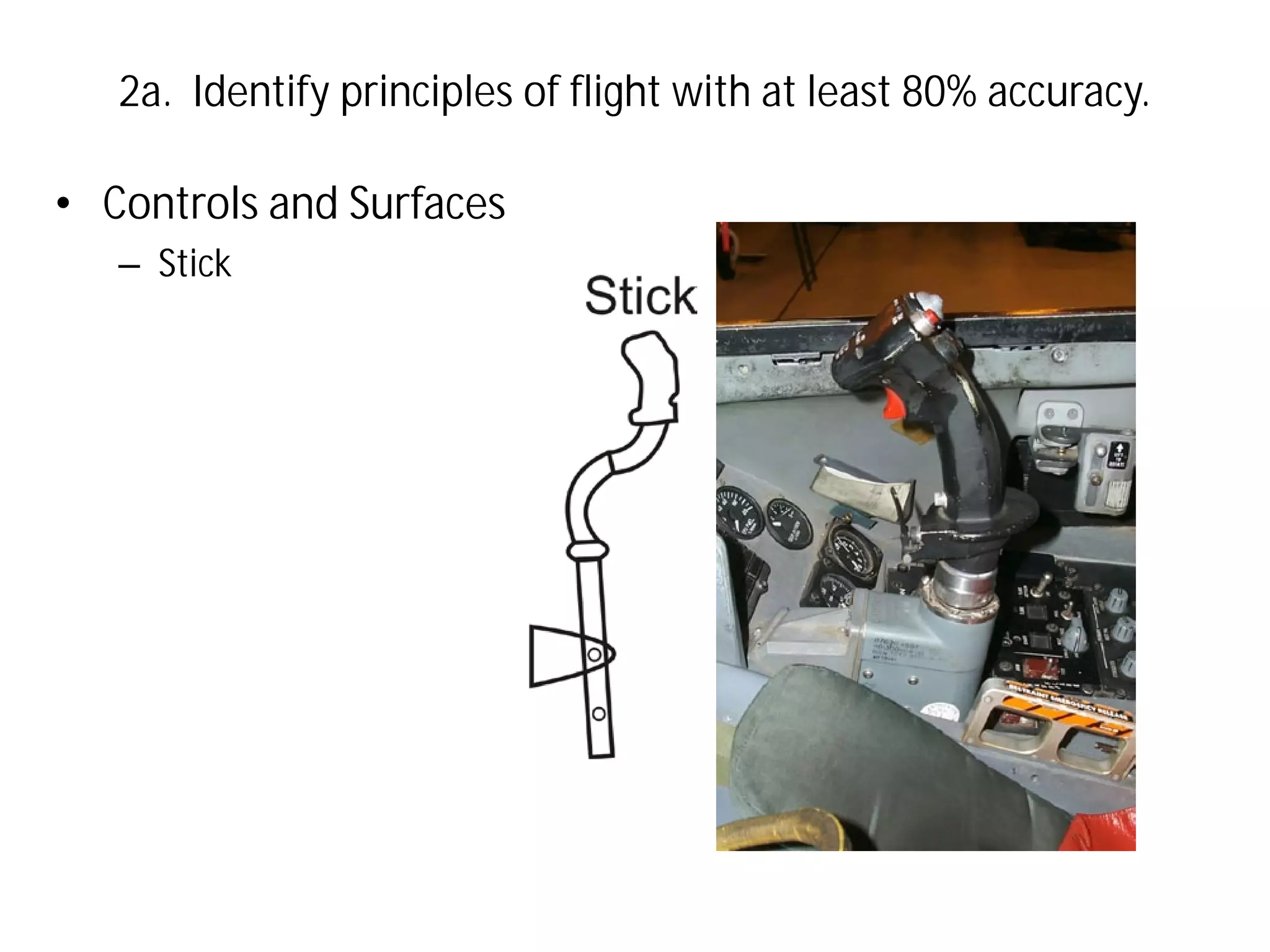
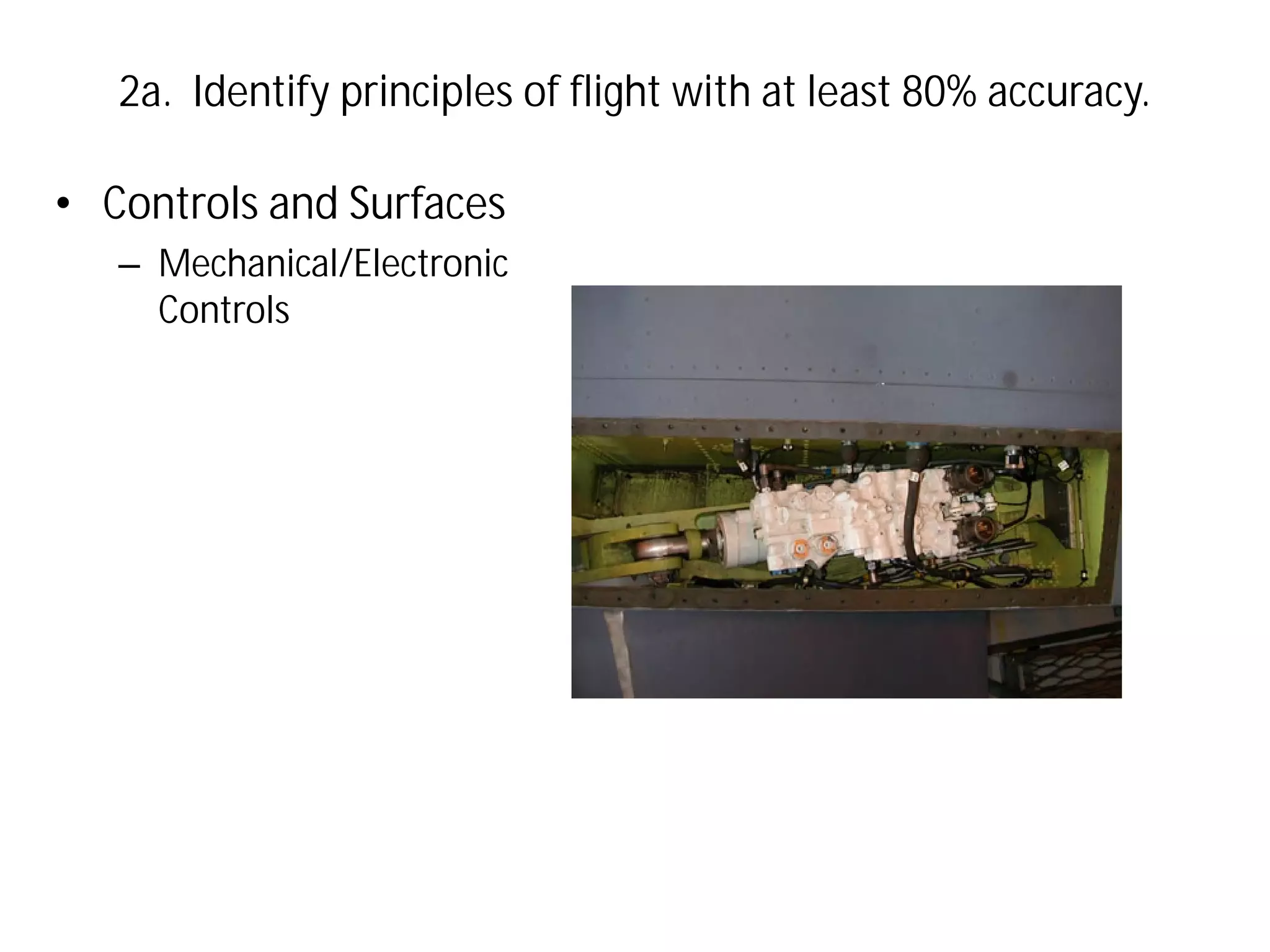
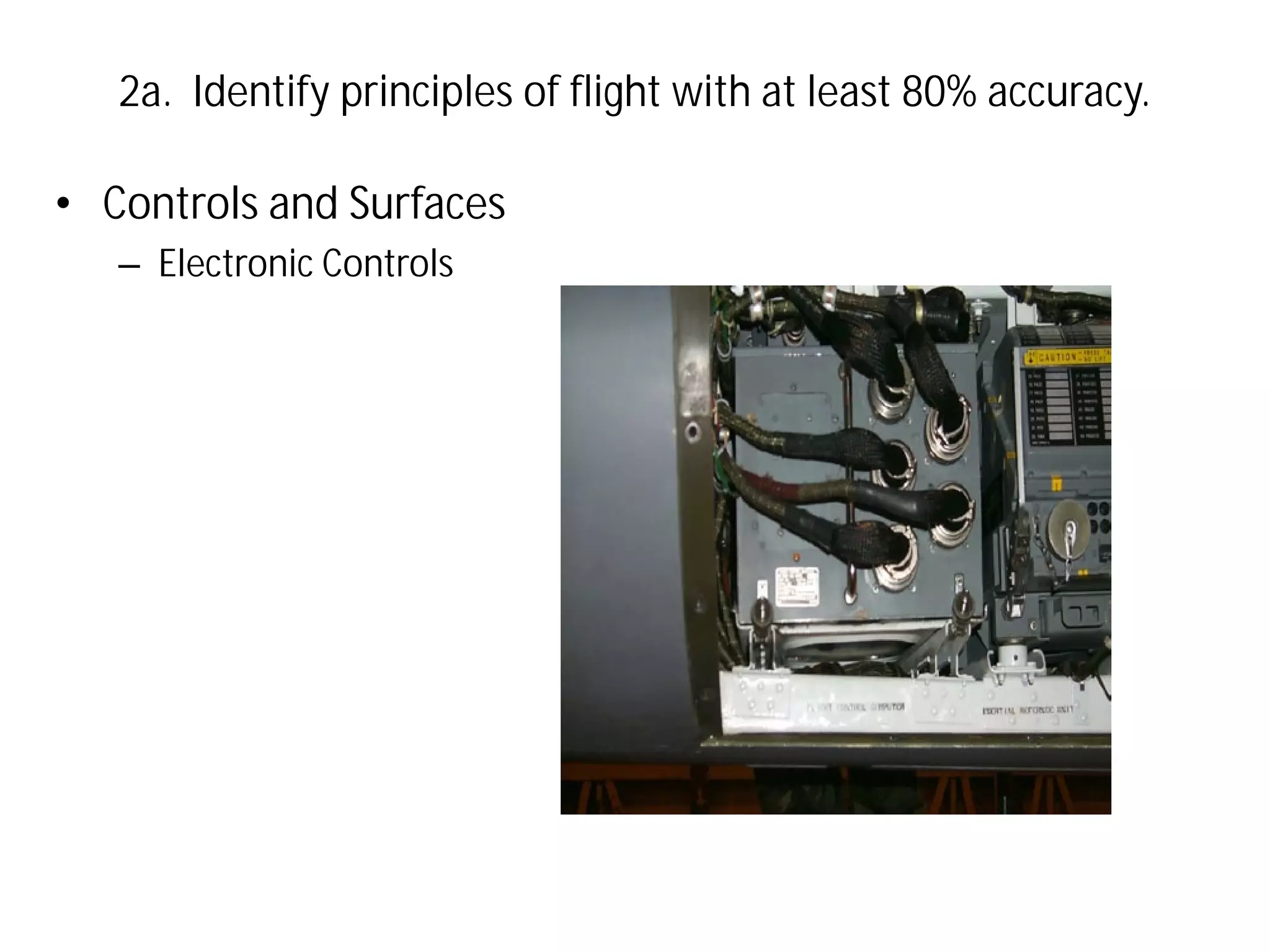
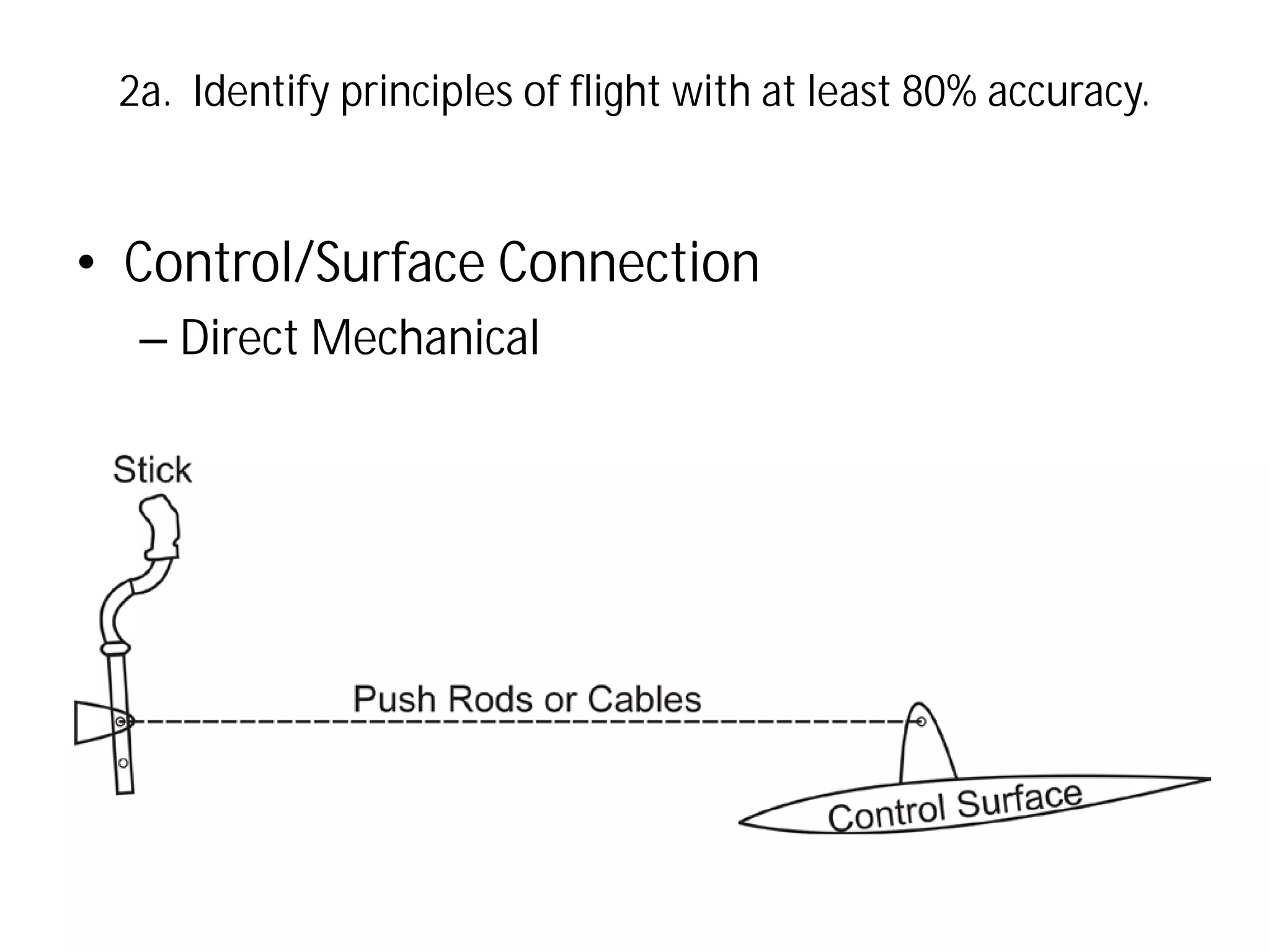
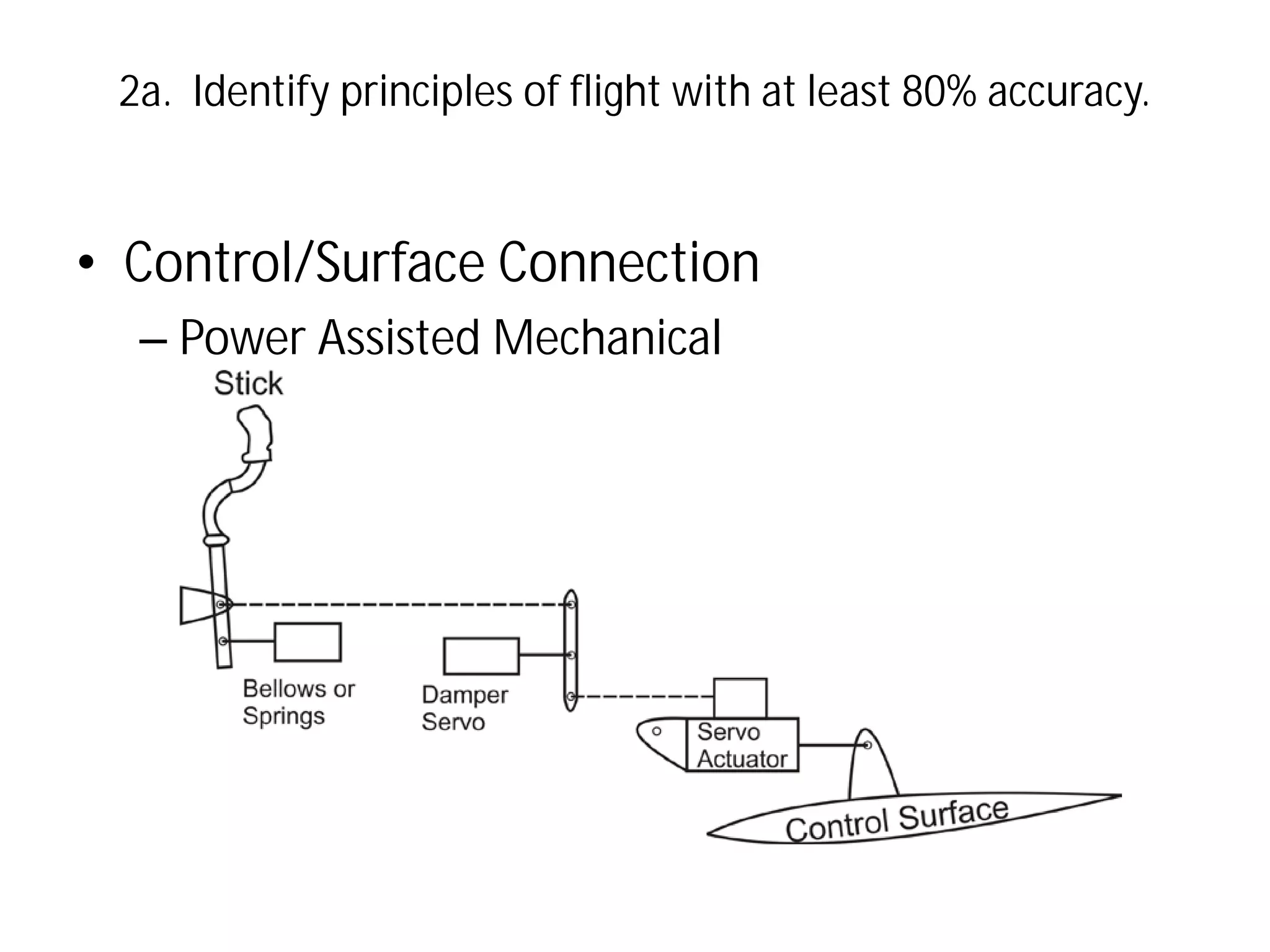
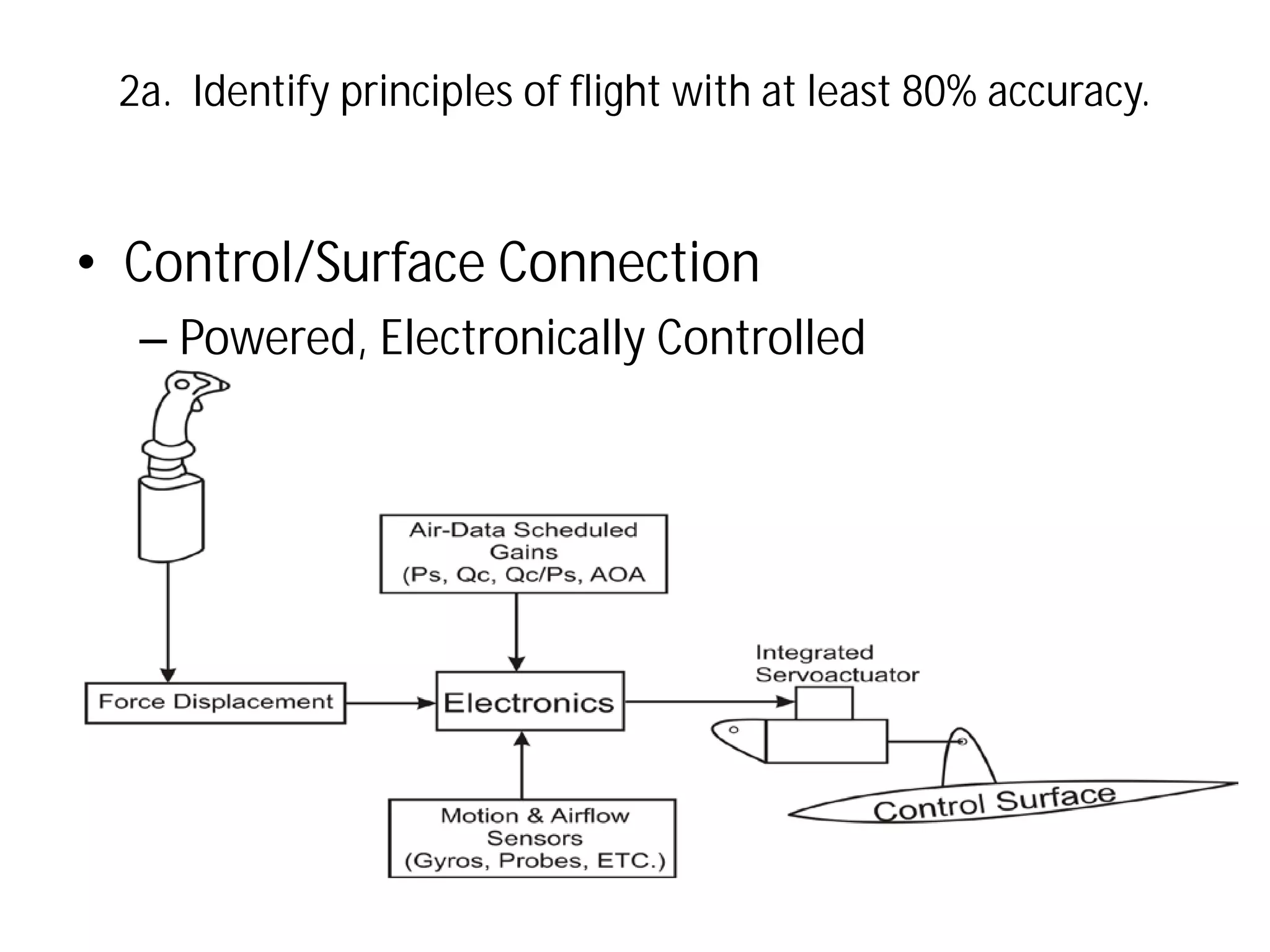
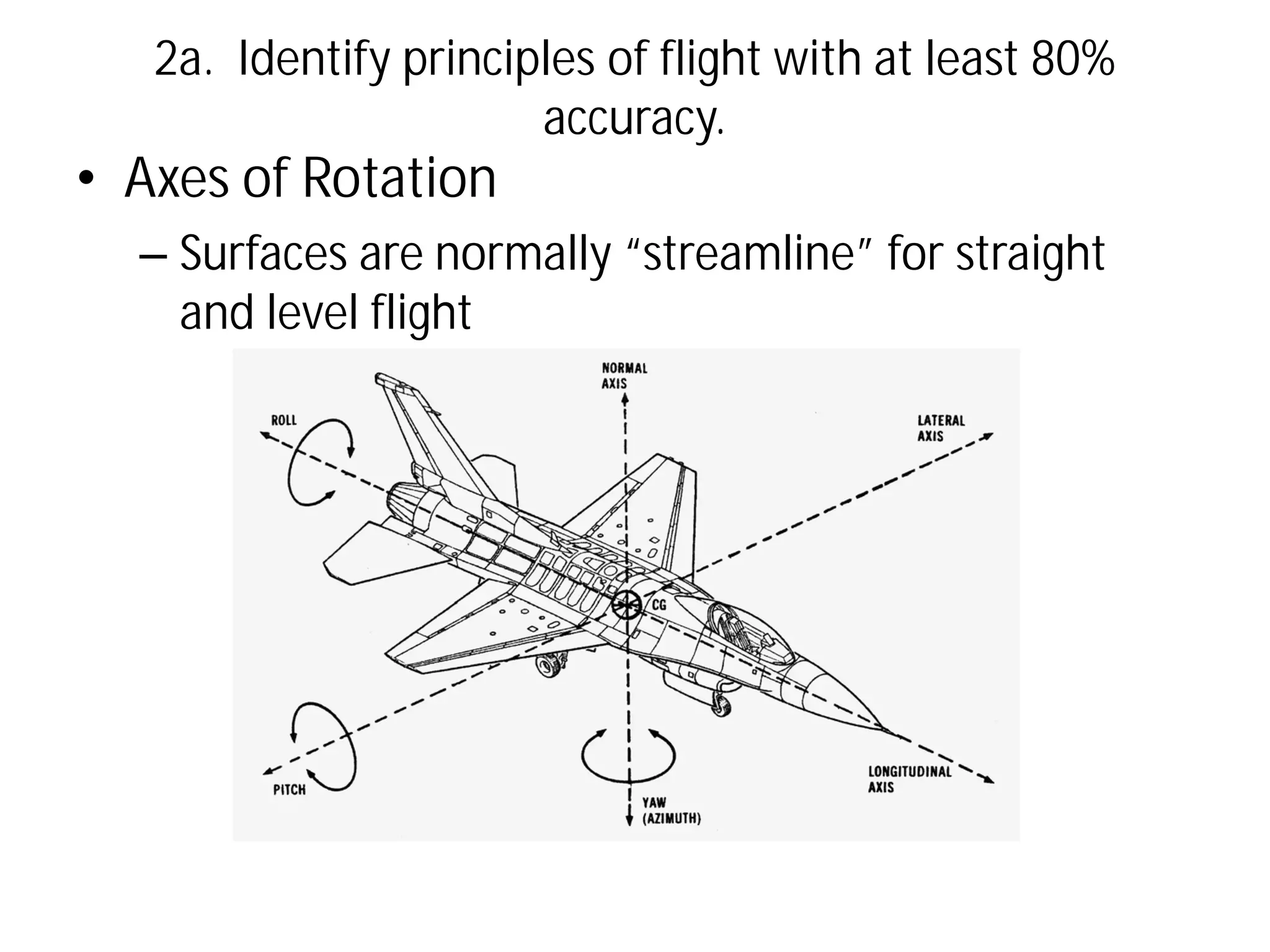
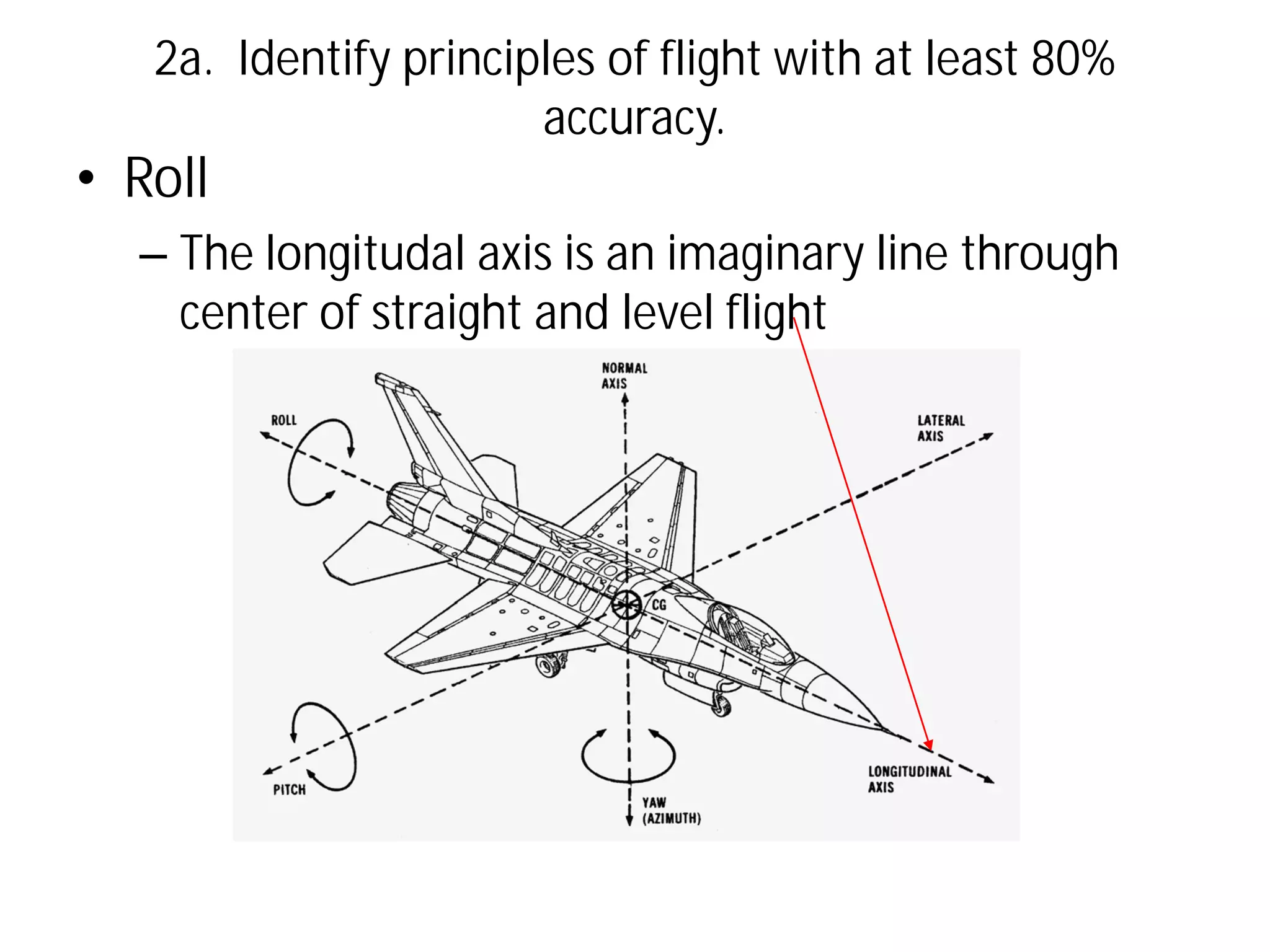
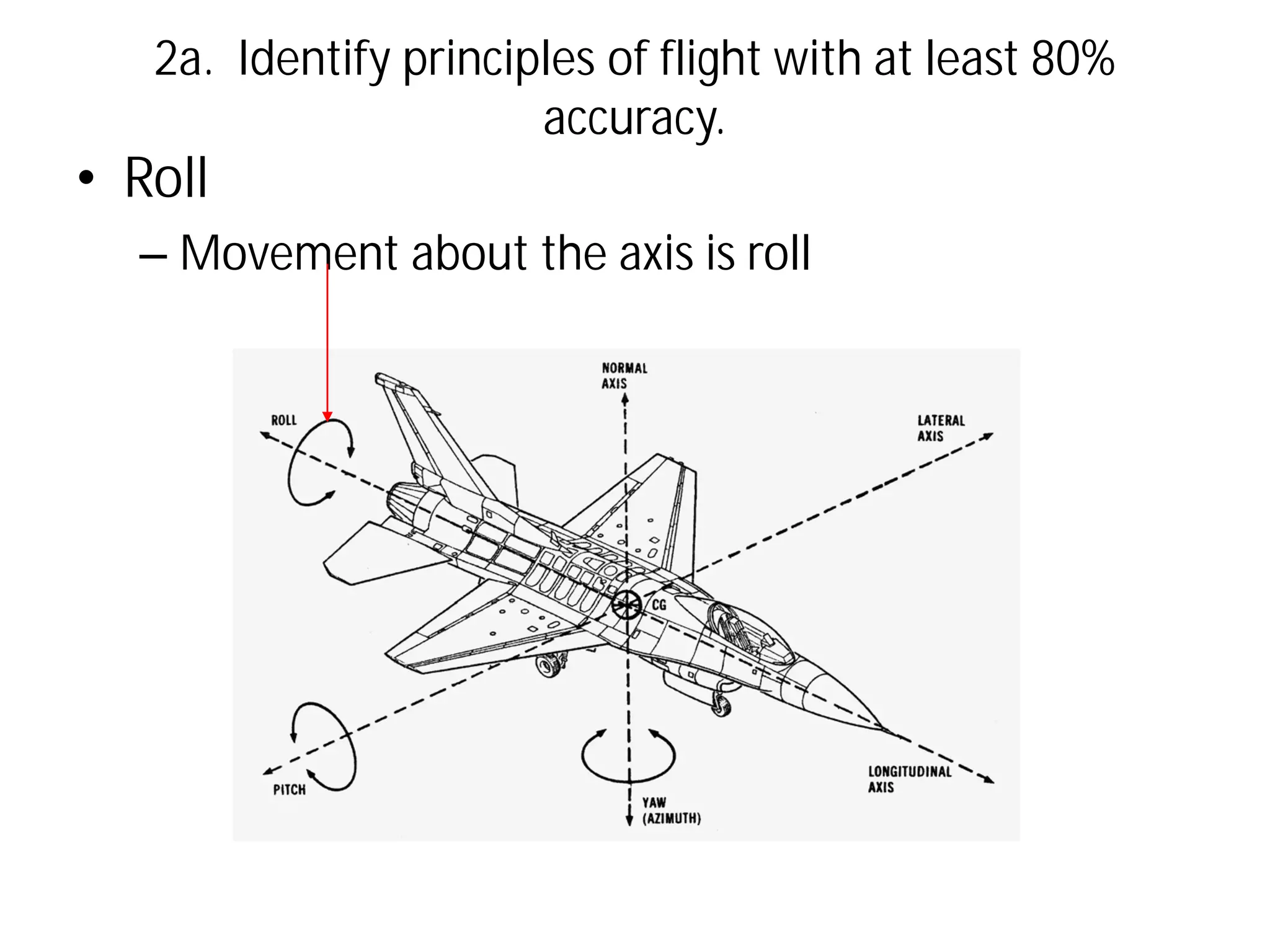
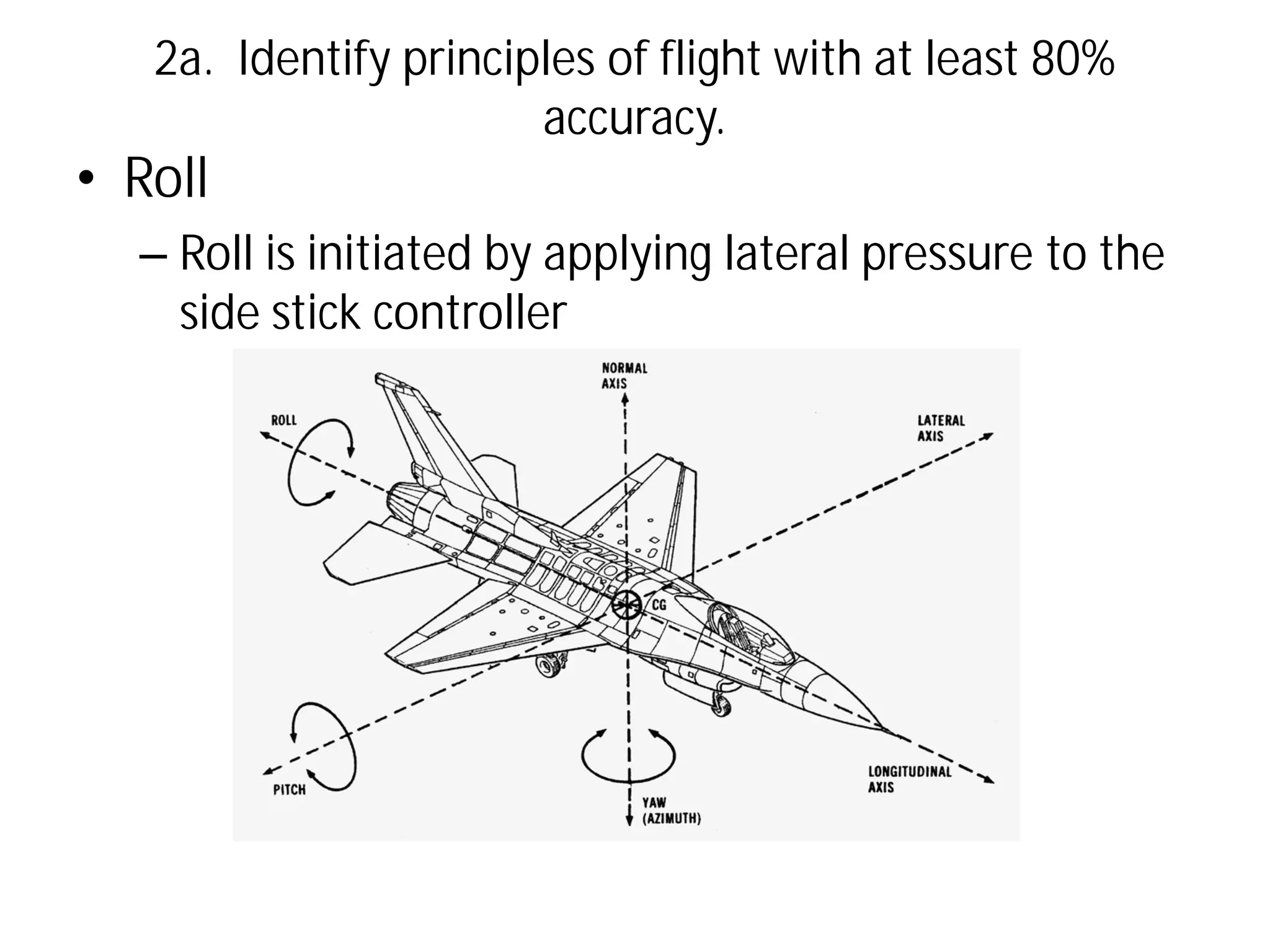
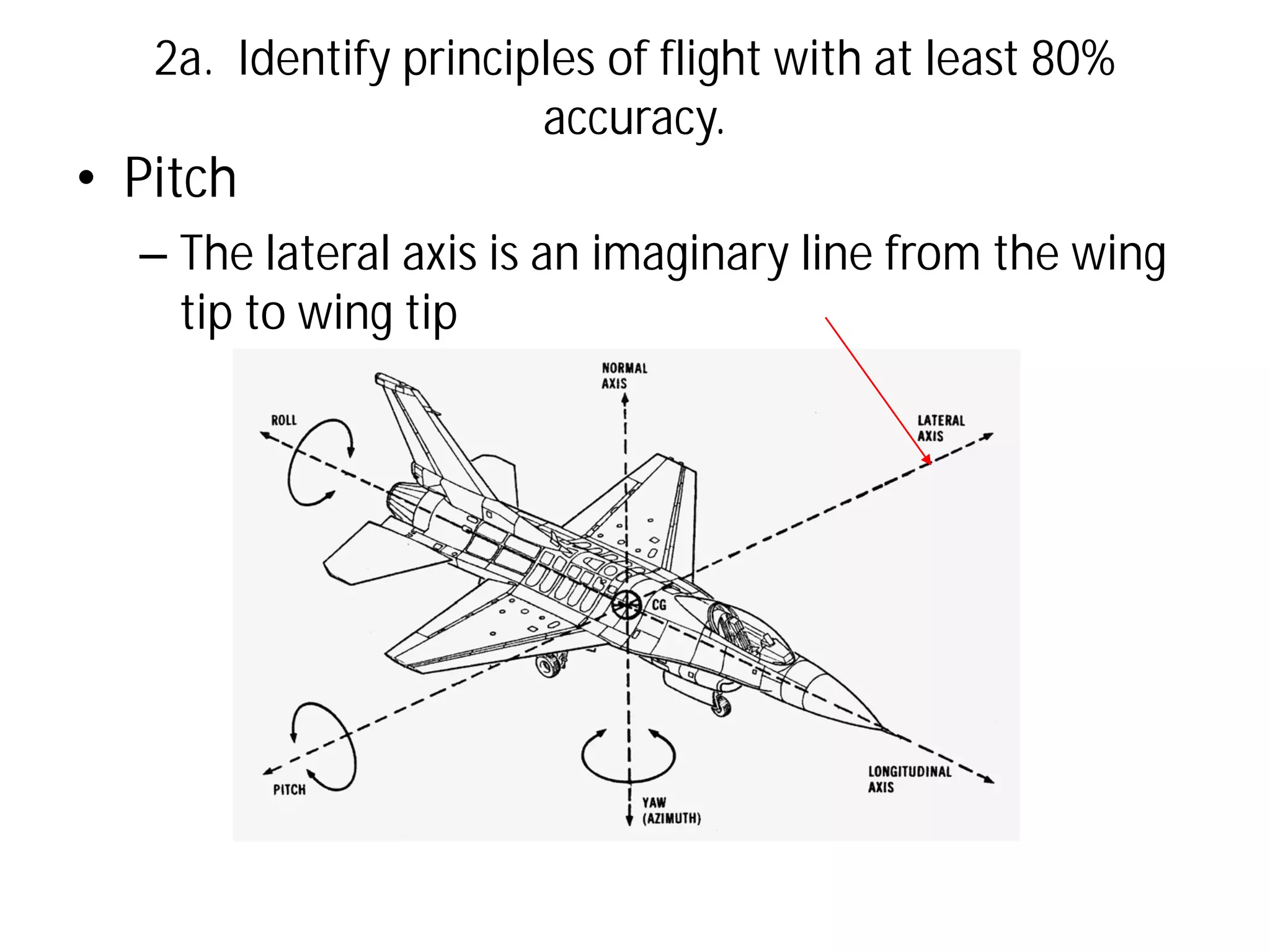
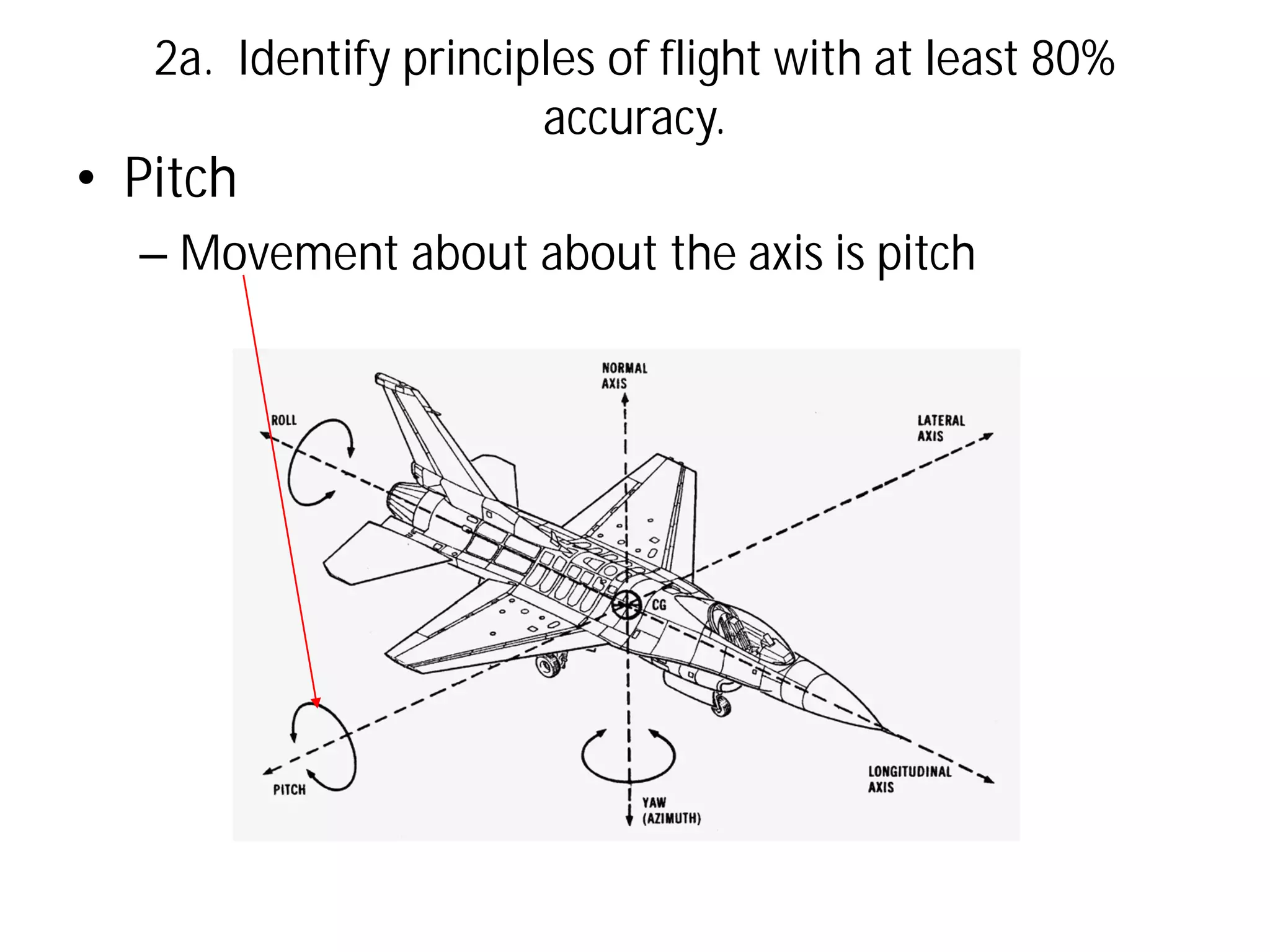
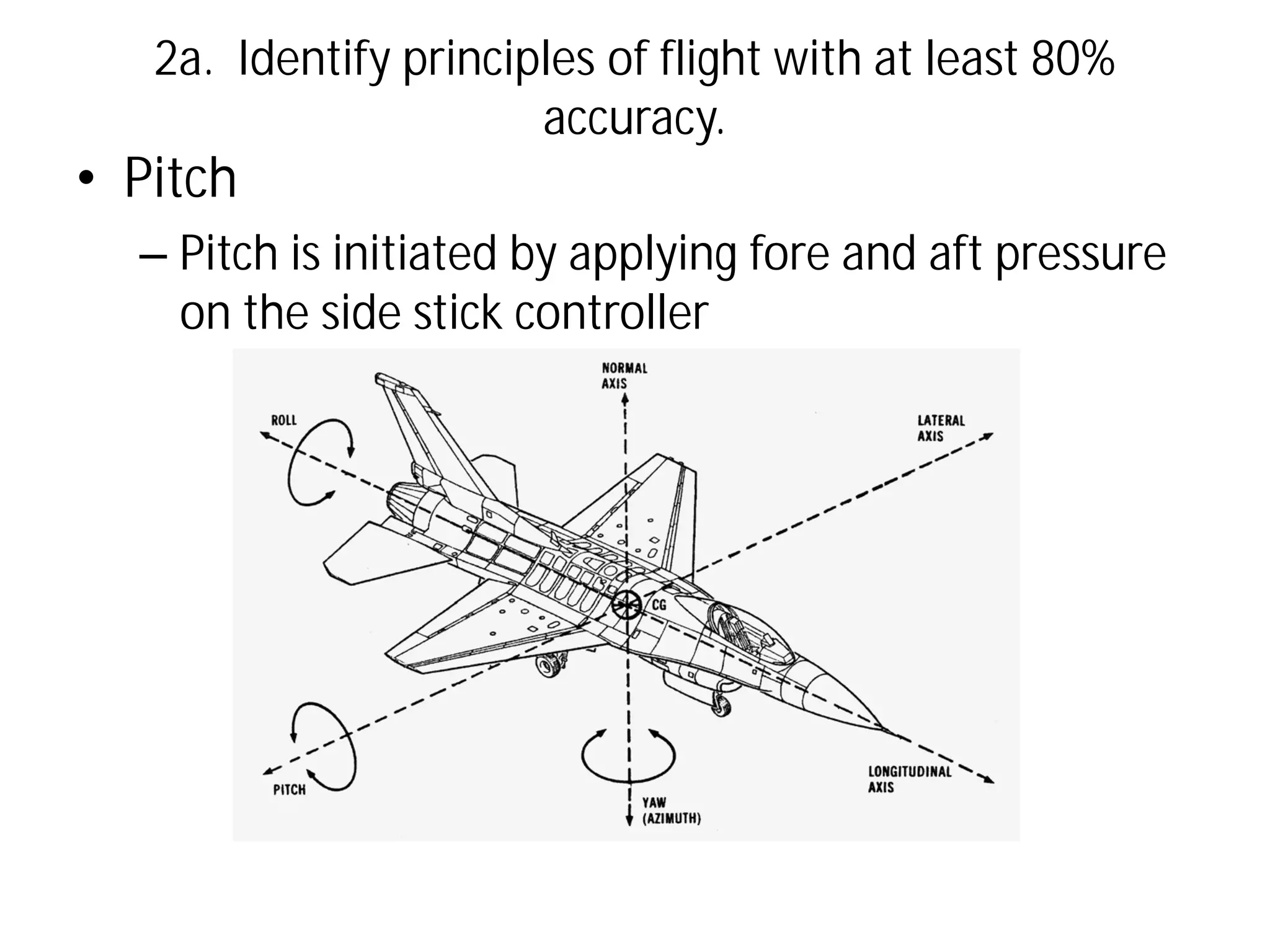
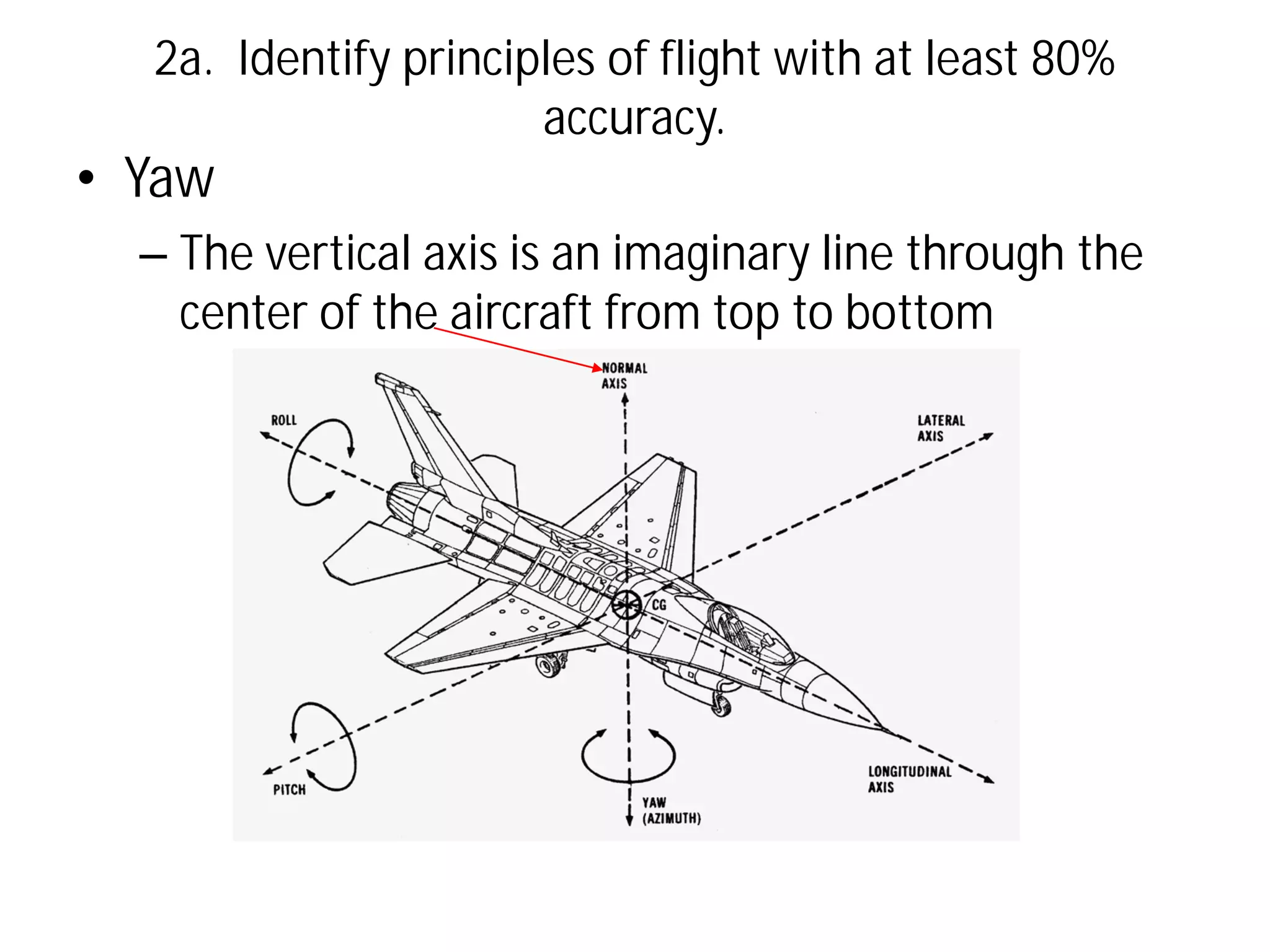
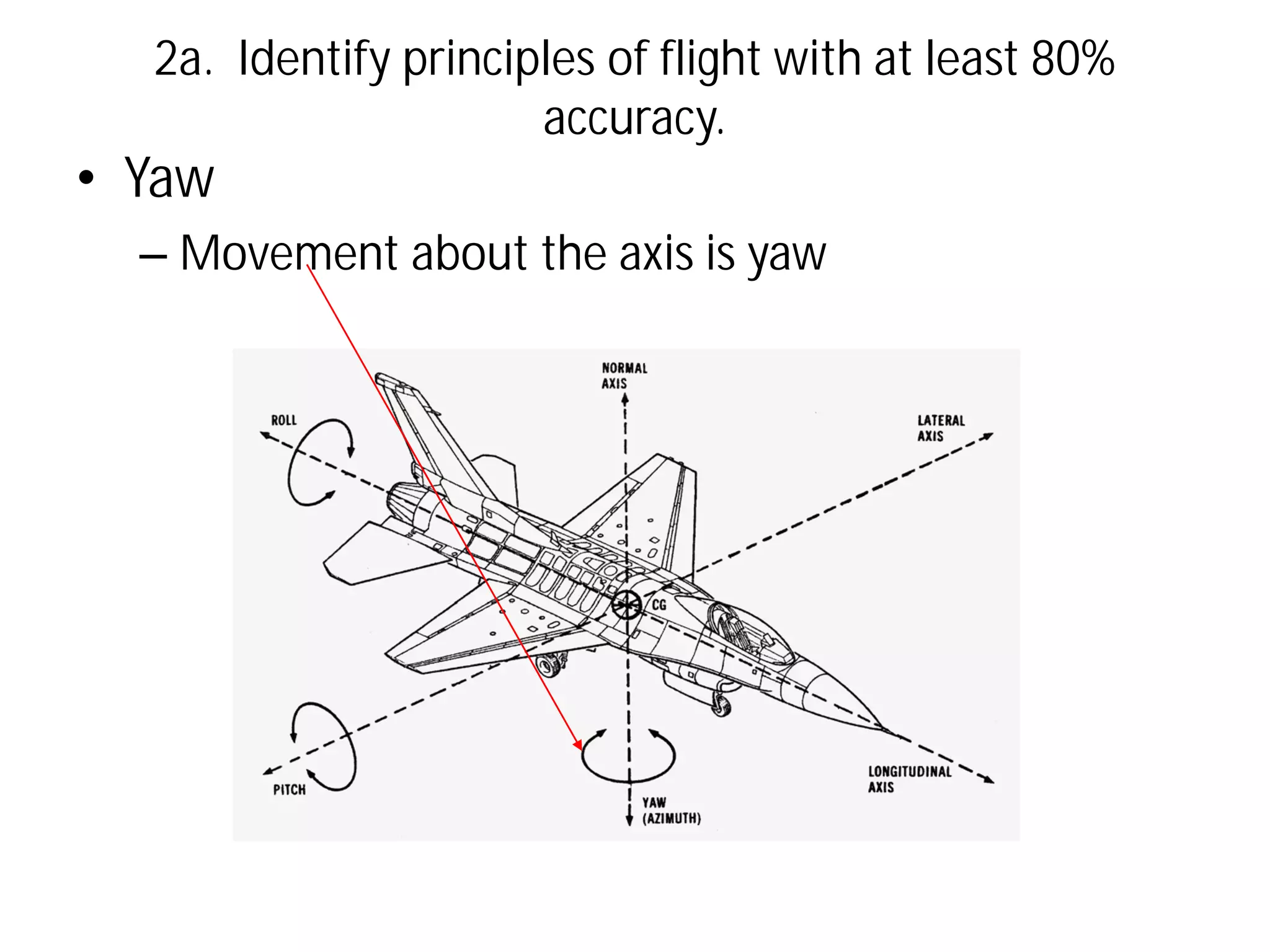
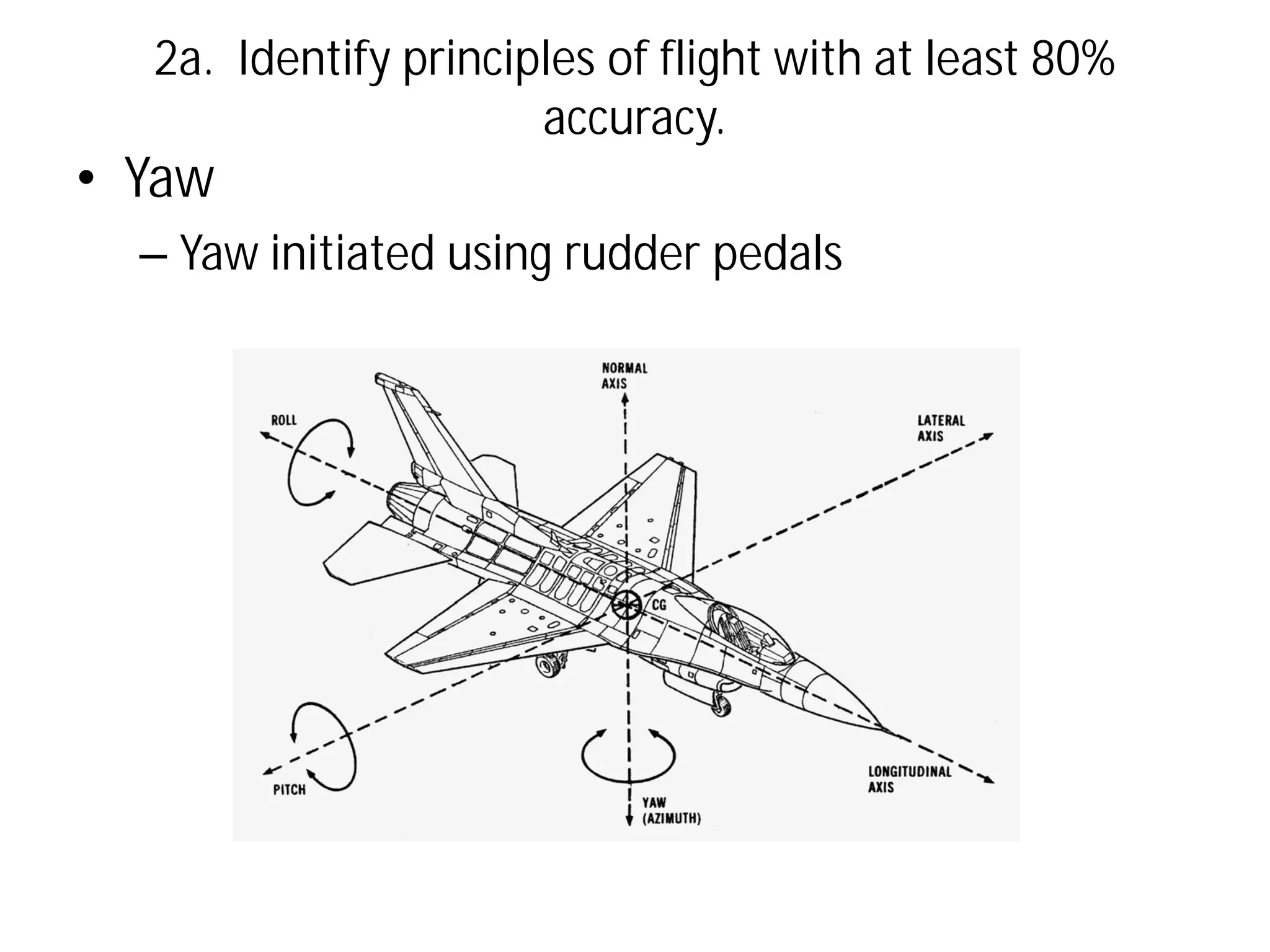
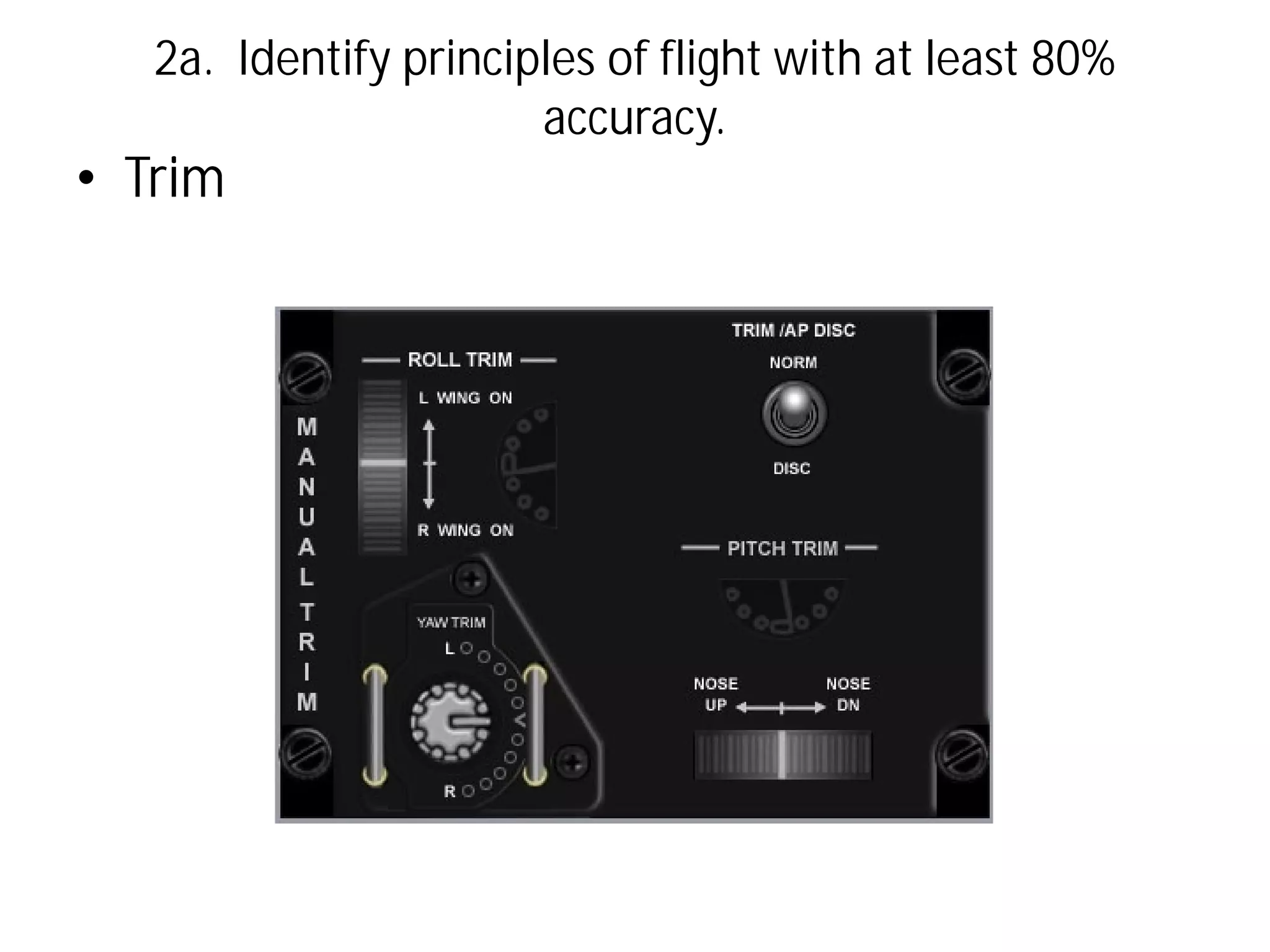
This document discusses the principles of flight, including Bernoulli's principle, air density, humidity, lift, drag, thrust, weight, controls and surfaces like flaps, ailerons, elevators, rudders, and axes of rotation like pitch, roll, and yaw. It provides an overview of these key aerodynamic concepts with the goal of having the reader identify principles of flight with at least 80% accuracy.