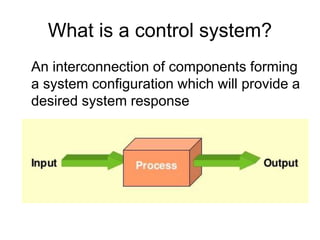
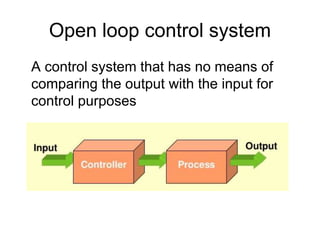
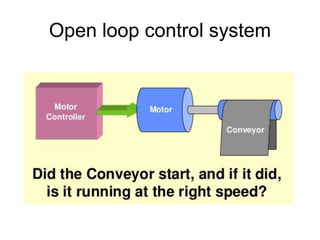
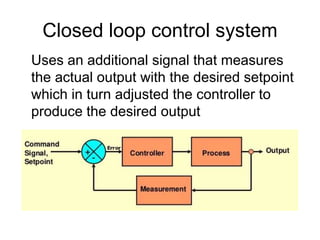
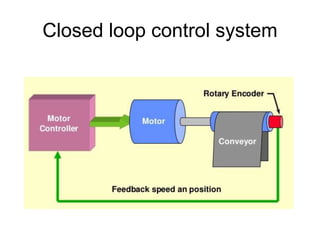
This document provides an overview of control engineering. It defines control as causing a machine or process to function in a predetermined manner. A controller accepts inputs like a command signal and feedback to compare and determine the appropriate output reaction. A control system interconnects components to provide a desired system response. An open loop system has no feedback comparison, while a closed loop system uses feedback to adjust the controller to produce the desired output. The course will cover time and frequency domain analysis, PID controllers, and design methods. Evaluation will consist of a written exam on course knowledge and activities and an oral exam on practical skills and lab activities.