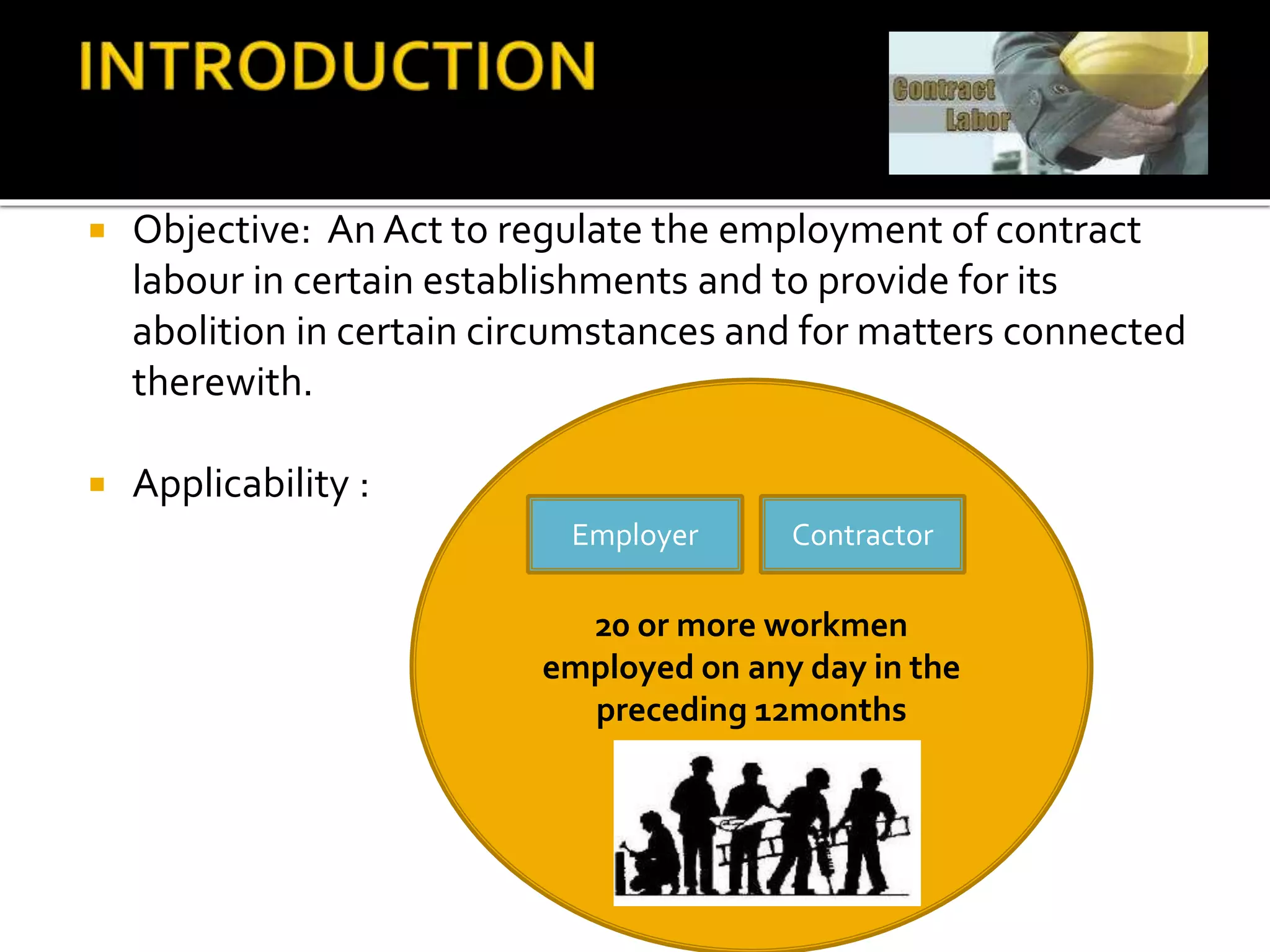
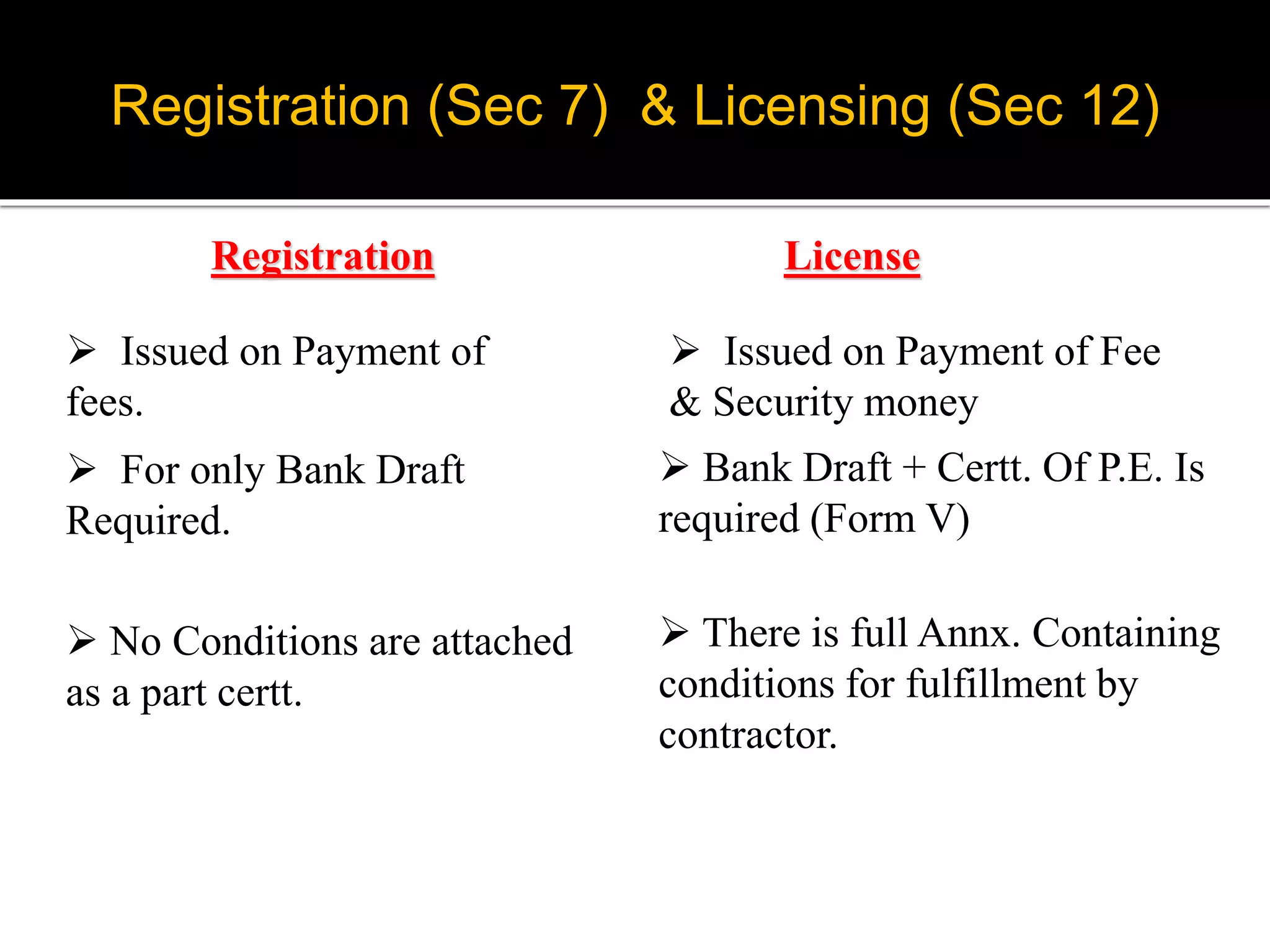
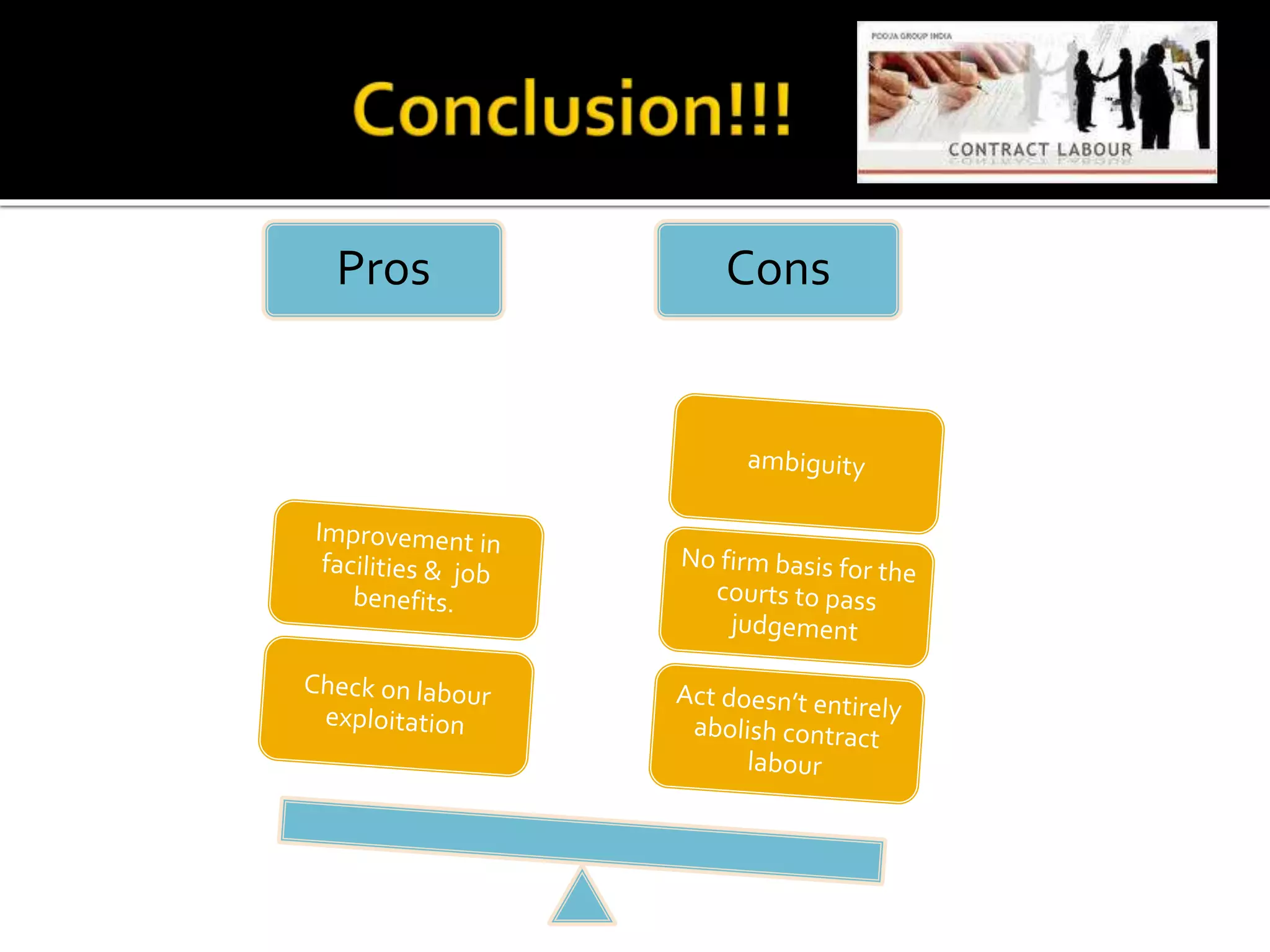
This document provides an overview of the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act of 1970. It discusses the objective to regulate employment of contract labor, applicability to establishments with 20 or more workmen, key terminology, and requirements for contractor registration and licensing. Important sections cover responsibilities of the principal employer for wages, welfare, health facilities and maintaining registers. The document also notes recent amendments, linkages to other labor laws, and case studies related to the act.