Embed presentation
Download to read offline



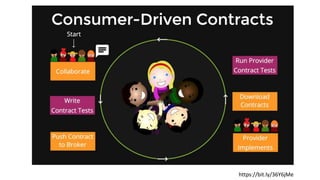


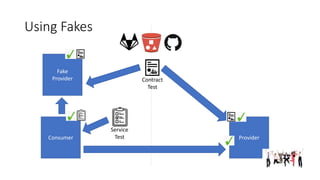


Contract testing involves a suite of tests that validate the API contracts between services, ensuring that both consumer and provider uphold these agreements during development and deployment. The use of contract tests promotes resiliency in production, prevents potential breaks from API changes, and serves as documentation for the API. Fakes are locally developed by consumer teams and allow for testing against a minimal implementation of the production provider, facilitating integration within continuous integration pipelines.







