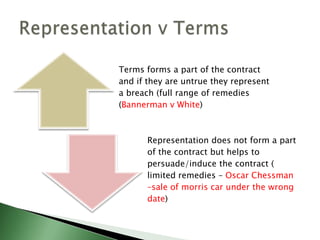
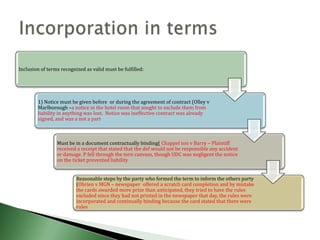
This document discusses key contractual terms, including:
1) Express terms must be incorporated in writing to form part of the contract. Oral statements not formally included do not vary the written terms.
2) Implied terms may be included where the contract is silent on an important matter as determined by law or the parties' conduct.
3) Parol evidence can be used to establish whether the contract is operative or if collateral oral contracts were formed related to but not varying the written terms.