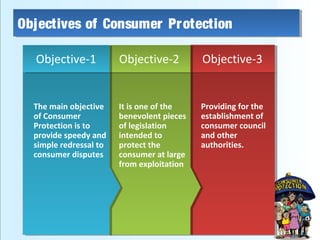
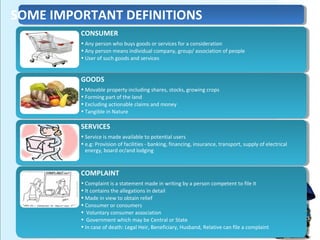
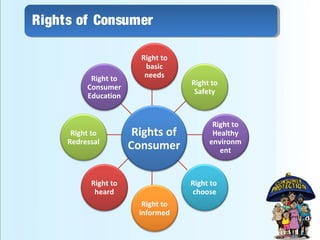
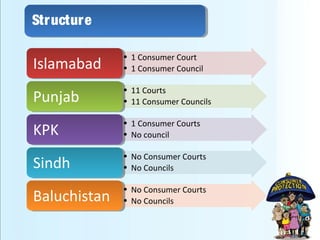
This document provides an overview of consumer protection in Pakistan. It discusses the objectives to protect consumers from exploitation, important definitions, consumer rights, the structure of consumer protection councils and courts, existing laws and acts, common issues, the complaint process, and recommendations to strengthen consumer protections. The key goals are to establish authorities to provide simple and speedy redress for consumer disputes, enact protective legislation at all levels of government, and increase awareness among both consumers and businesses of rights and responsibilities.