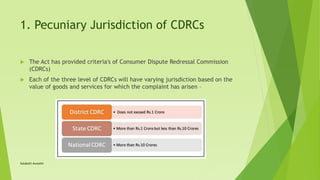
The Consumer Protection Act of 2019 replaces the Consumer Protection Act of 1986, establishing a Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) to enforce consumer rights and impose penalties for violations. The new act introduces six consumer rights, broadens the definition of 'consumer' to include online transactions, and defines 'unfair trade practices' more comprehensively. Additionally, it introduces product liability, heightens the jurisdictional thresholds for consumer disputes, and streamlines the processes for resolving grievances through district, state, and national consumer dispute redressal commissions.






































![II. Case law -
The discovery rule used to decide when the cause of arises in cases of a medical
emergency was first propounded in Ayers v. Morgan [397 Pa.282, 154A.2d 788] by
the US courts and was adopted by the Indian legal jurisprudence In the case
of V.N.Shrikhande vs Anita Sena Fernandes. In the particular case, the
complainant was negligently treated by the doctor resulting in a gauze inside her
stomach creating an infection. The complainant got tested 9 years after the initial
operation in the duration of which she was under constant pain. The respondents
contended that since she did not visit the doctor even once after the operation
and 9 years had passed so the entire complaint was barred by limitation.
So if the damage inflicted by the doctor due to negligence is patent, then the
cause of action arises on the date the act was committed but, on the other hand,
if the act did was latent, then the cause of action arises when the victim realises
the negligence.
The court applying the rule said that the negligence in the case was latent, and
therefore the complaint was within limitation.
Satakshi Awasthi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationconsumer-201109144245/85/Consumer-Protection-Act-2019-40-320.jpg)









