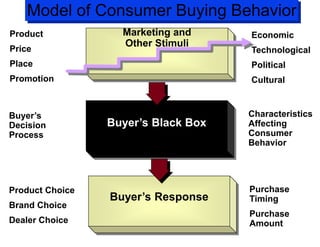
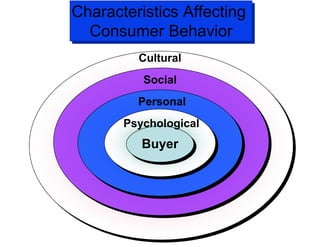
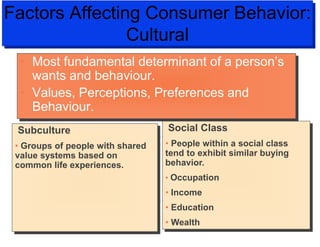
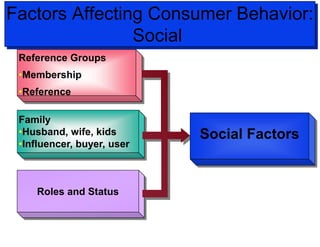
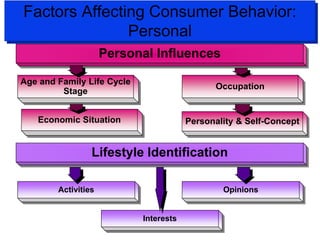
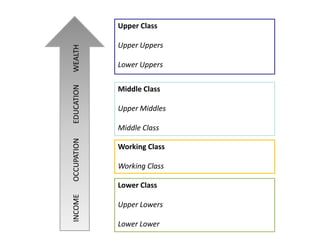
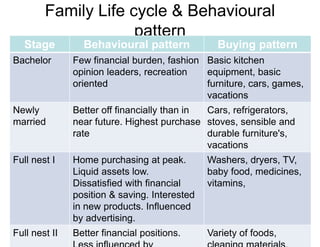
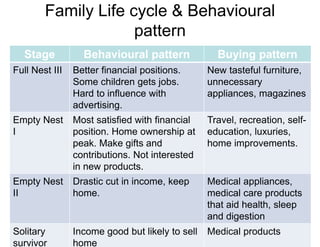
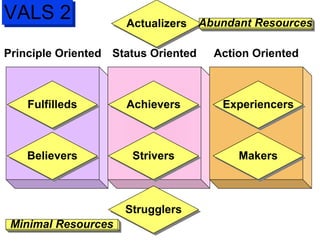
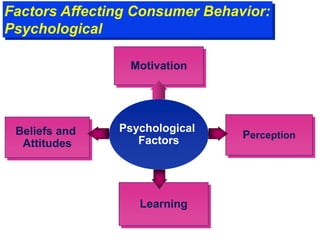
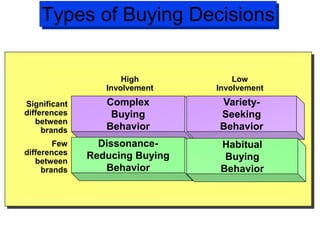
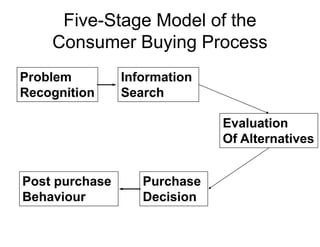
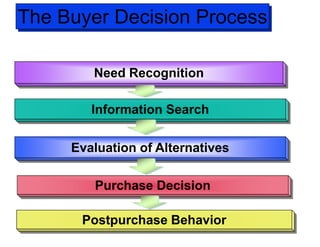
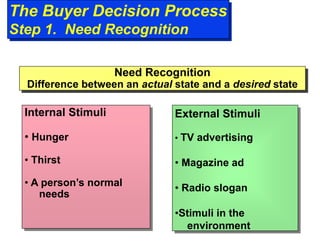
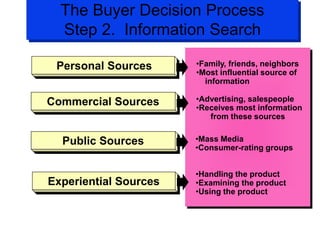
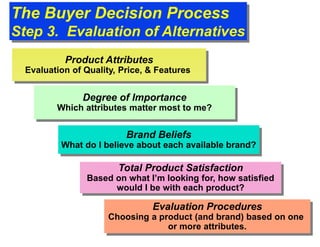
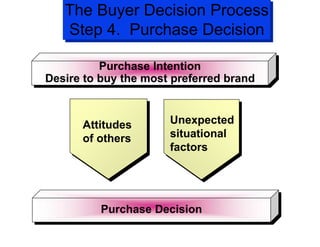
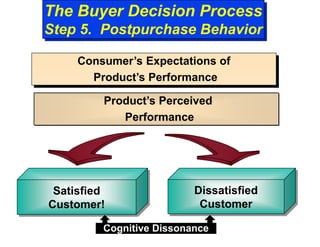
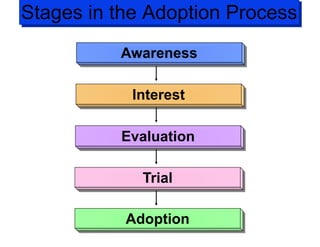
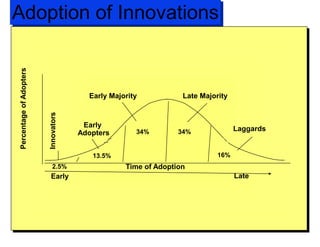
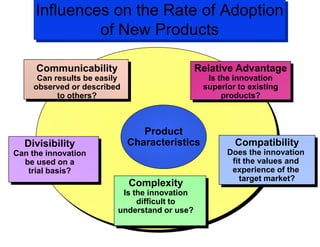
The document discusses factors that influence consumer buyer behavior, including cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. It outlines models of consumer behavior, such as the 7 O's framework that examines occupants, objects, objectives, organizations, operations, occasions, and outlets. It also summarizes the consumer decision process, which involves need recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Key influences on adoption of new products are also outlined.