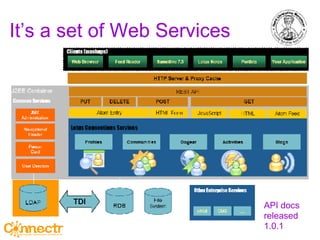
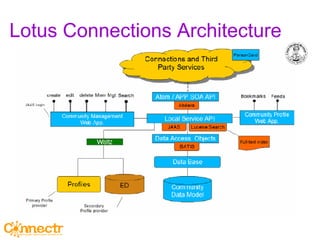
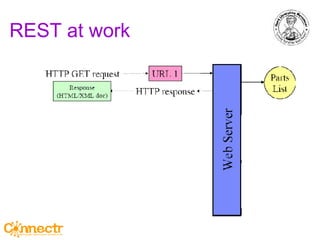
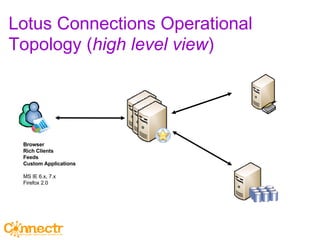
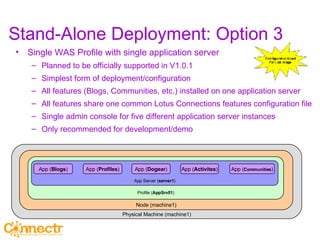
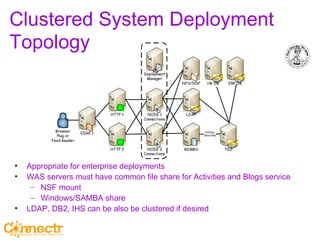
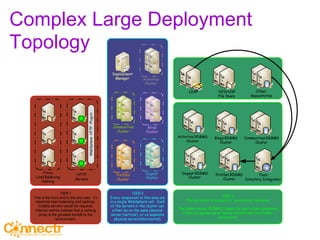
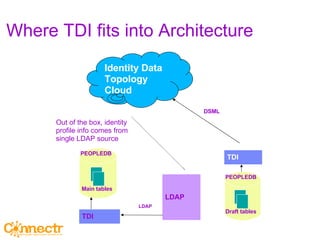
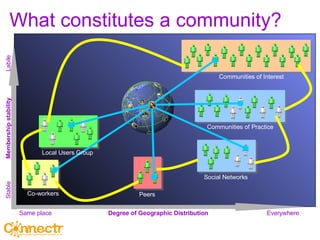
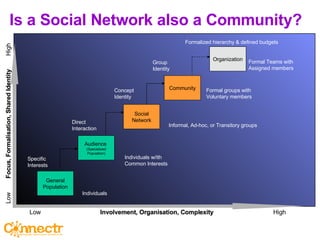
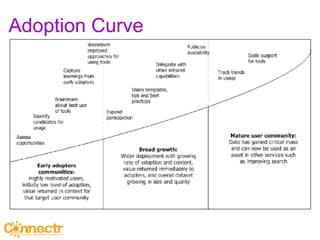
The document discusses social networking using Lotus and WebSphere. It describes IBM Lotus Connections, a set of social software tools for businesses that include profiles, communities, blogs, bookmarks and activities. It also discusses how Lotus Connections uses open standards and REST APIs to make it extensible. Finally, it talks about best practices for adoption, including running pilots, defining adoption plans and identifying evangelists to encourage use of social networking within an organization.