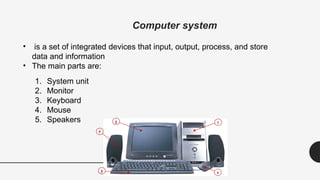
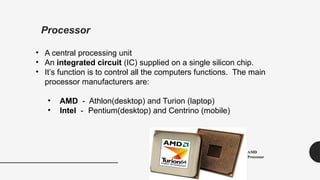
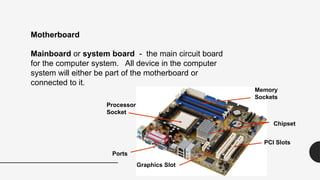
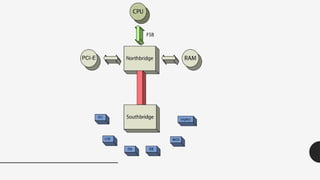
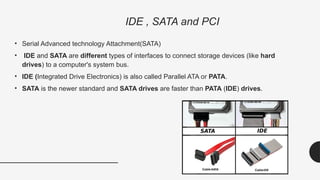
The document provides an introduction to computer hardware as part of an ICT lab course, detailing the components and functions of a computer system. It explains the roles of essential hardware such as the system unit, processor, memory types (RAM and ROM), motherboard, and various peripherals. Additionally, it outlines the purpose and operation of computer power supplies and connections like SATA and PCI.