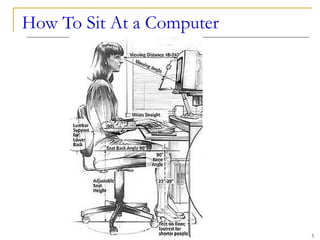
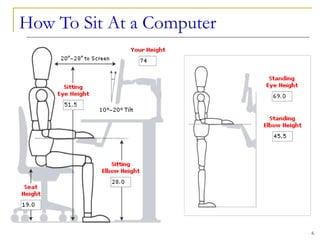
The document discusses ergonomics in computing, emphasizing the importance of ergonomically designed tools to prevent repetitive strain injuries (RSI) caused by improper body positioning and misuse of devices. It examines various input devices, including keyboards, mice, touch screens, and game controllers, and explains techniques to reduce the risk of injury while using these tools. Additionally, it covers optical input devices such as scanners and microphones, highlighting their roles in converting physical input into digital formats.