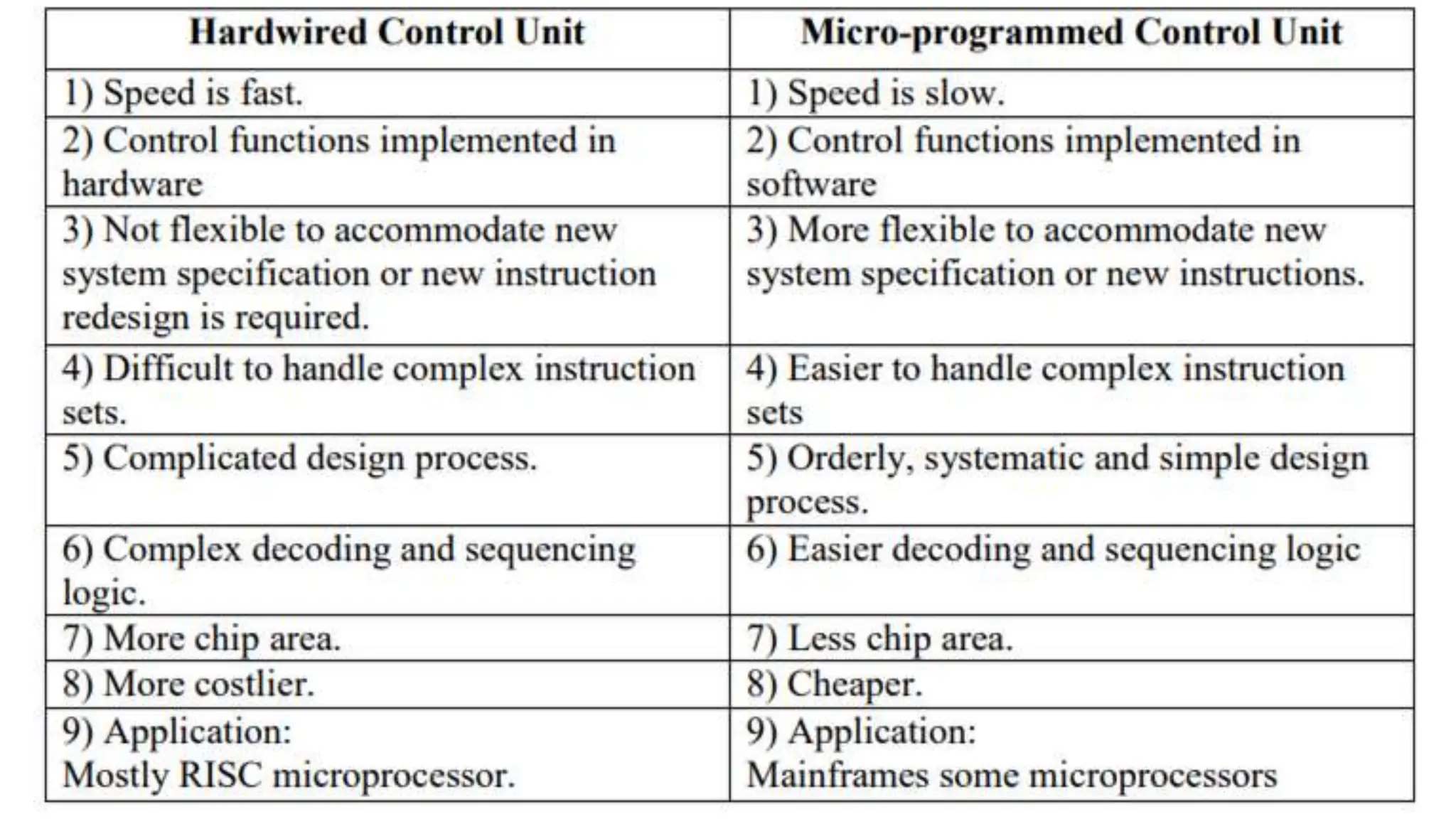
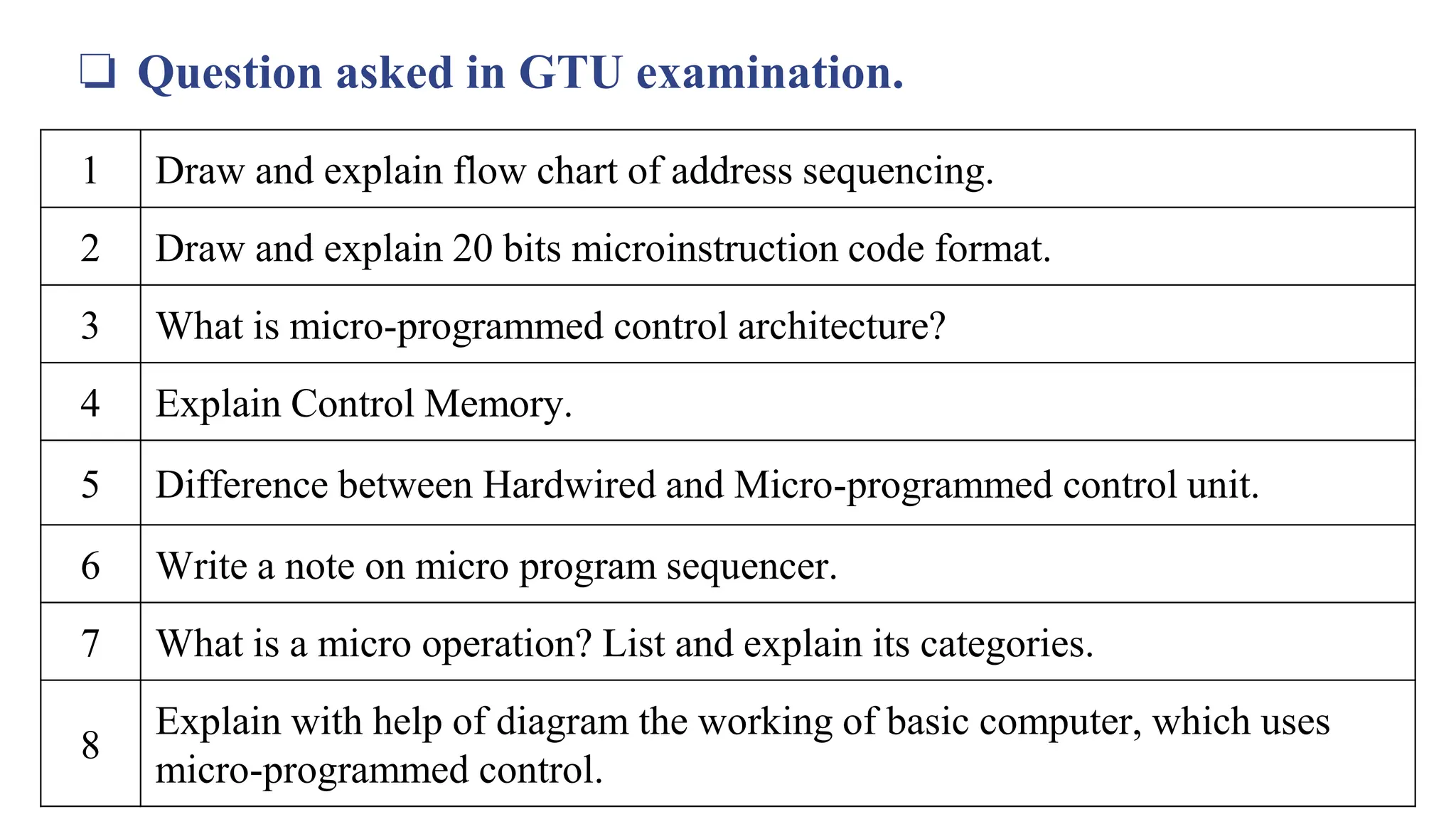
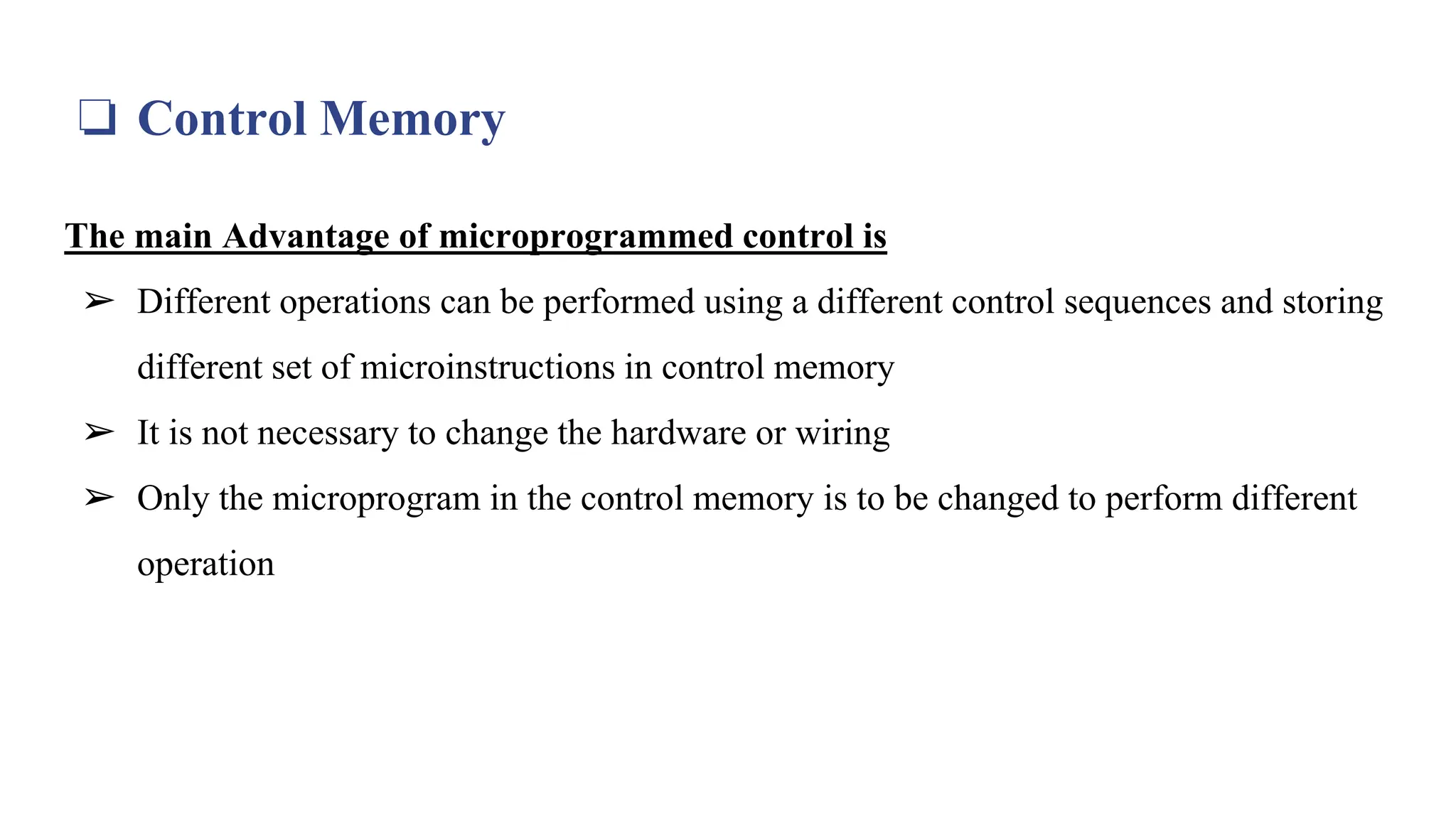
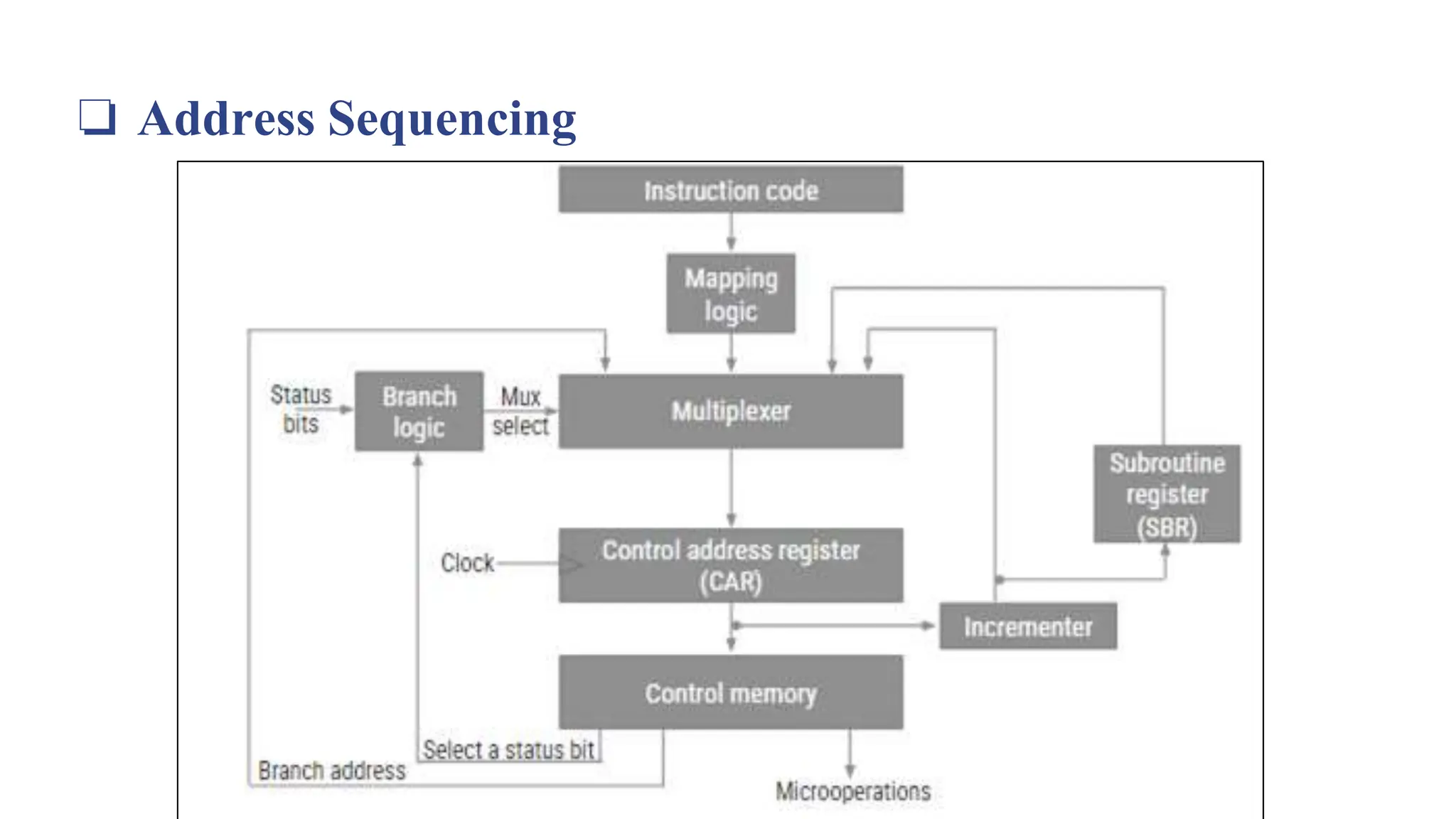
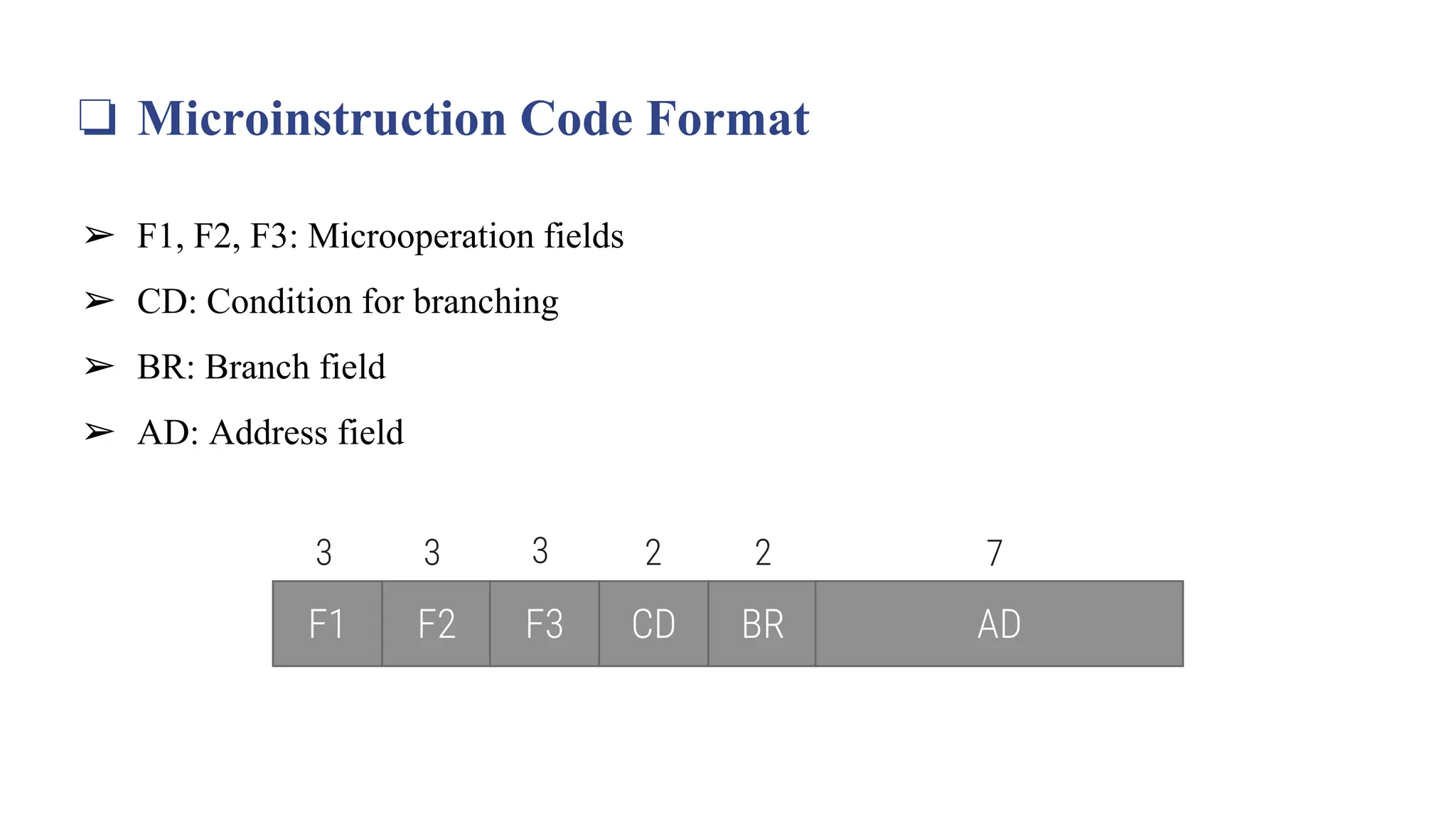
This document provides information about the Computer Organization and Architecture course for the 4th semester of the B.E. program at Laxmi Institute of Technology, Sarigam. It includes details about the course content which covers topics such as computer data representation, assembly language programming, CPU, and memory organization. The document then focuses on the topics of control memory, address sequencing, and microprogram examples. It provides explanations of control memory, the advantages of microprogrammed control, and the addressing capabilities required for control memory. Finally, it includes the format and coding for microinstructions along with examples.





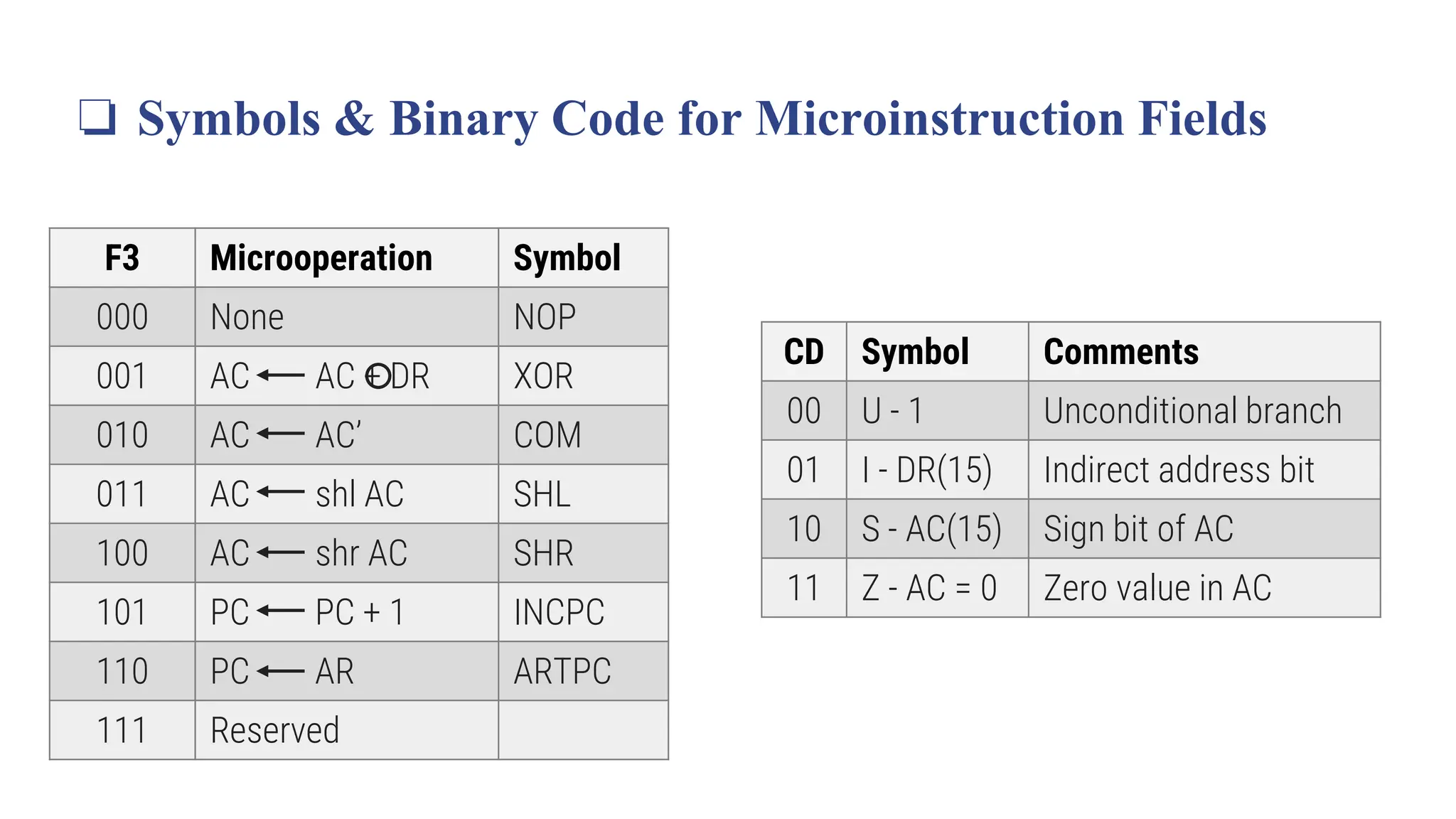
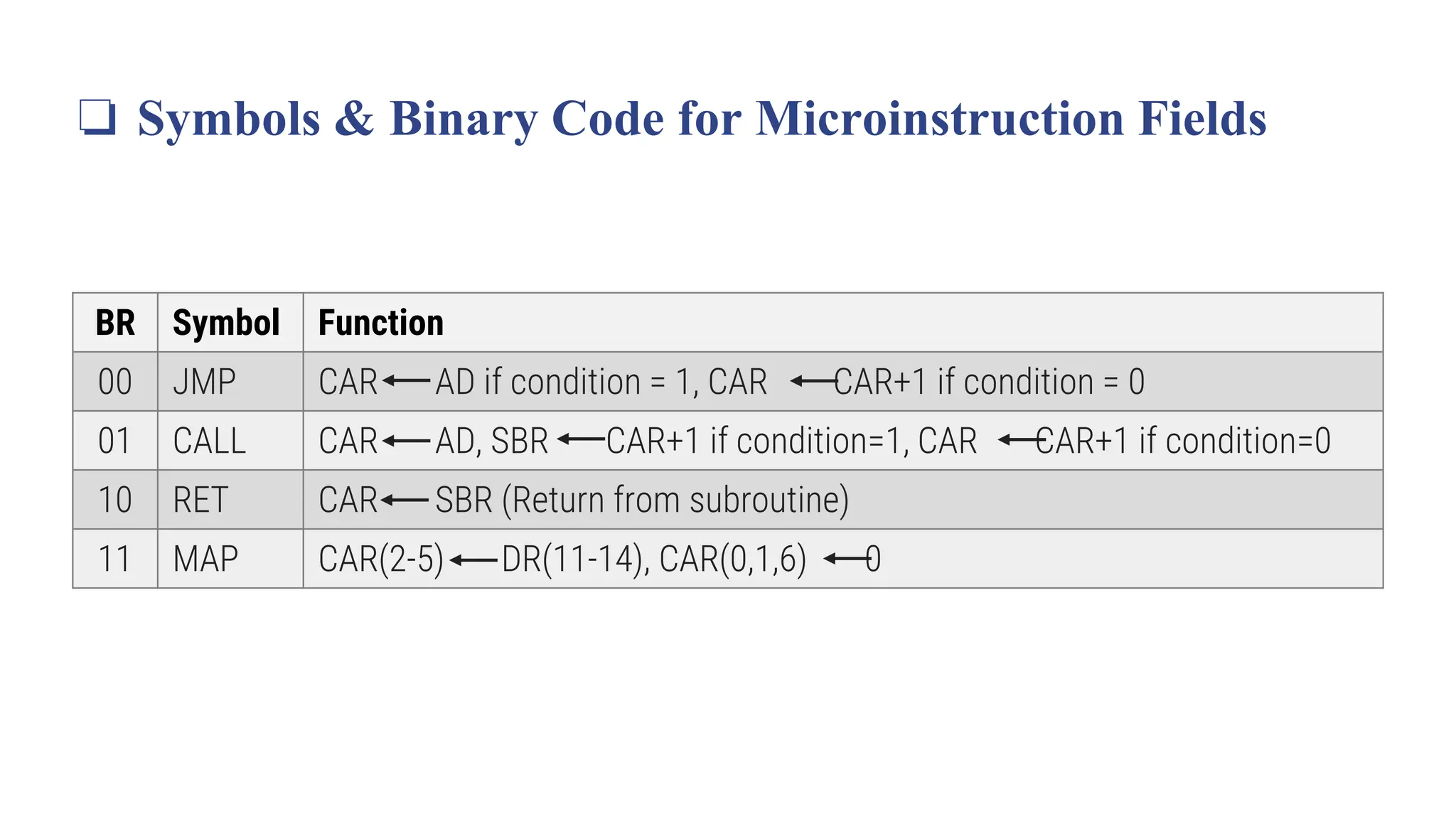
![❏ Symbols & Binary Code for Microinstruction Fields
F1 Microoperation Symbol
000 None NOP
001 AC AC + DR ADD
010 AC 0 CLRAC
011 AC AC + 1 INCAC
100 AC DR DRTAC
101 AR DR(0-10) DRTAR
110 AR PC PCTAR
111 M[AR] DR WRITE
F2 Microoperation Symbol
000 None NOP
001 AC AC - DR SUB
010 AC AC DR OR
011 AC AC DR AND
100 DR M[AR] READ
101 DR AC ACTDR
110 DR DR + 1 INCDR
111 DR(0-10) PC PCTDR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coaunit4-240410132739-072026e0/75/Computer-Organization-Architecture-COA-Unit-4-11-2048.jpg)