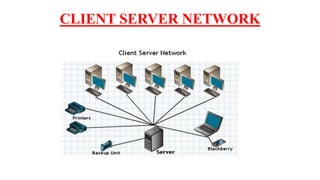
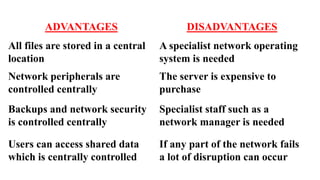
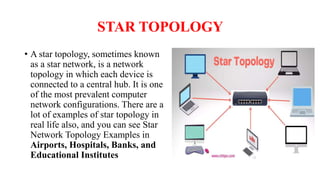
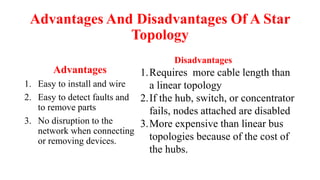
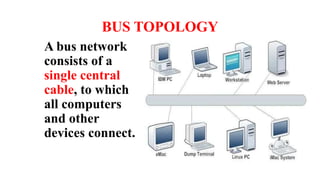
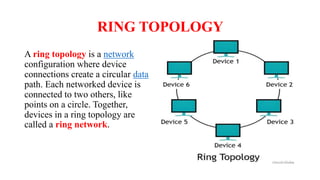
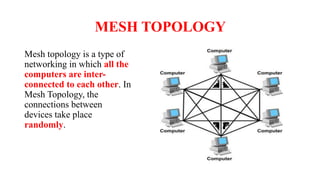
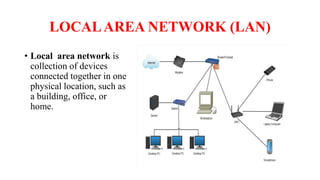
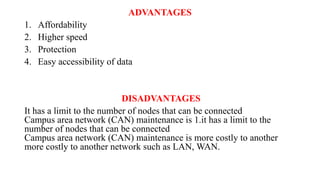
A client-server network connects client computers to a central server computer. The server provides services like file storage and sharing to the clients. Key advantages include centralized backups, security and data access, though the server is an expensive single point of failure. Common network topologies include star, bus, ring and mesh configurations that connect devices in different patterns and have tradeoffs in cable needs, expansion and fault tolerance. Factors like computer types, distances, speeds and growth influence topology selection.