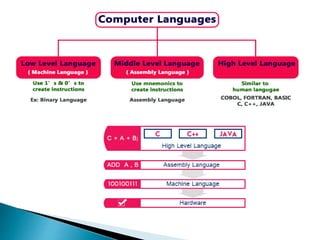
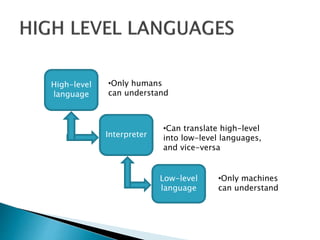
The document discusses the evolution of computer languages from low-level to high-level and classifies languages. Low-level machine languages contain binary instructions that computers understand directly. Middle-level assembly languages use mnemonics translated to machine code by assemblers. High-level languages are easiest for humans to read and write but require compilers or interpreters to convert them to low-level code for computer execution. Examples of high-level languages given are C, C++, Java, and HTML.