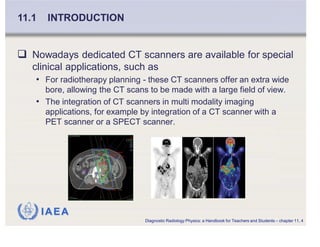
This document is a 190 slide summary of Chapter 11 from the IAEA publication "Diagnostic Radiology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students". The chapter discusses Computed Tomography (CT) scanning principles, including how CT was initially used for brain imaging in 1971 and has since become a versatile 3D whole body imaging technique used in various medical applications such as oncology, cardiology, and interventional radiology. It also describes how CT is used for diagnosis, treatment planning, and screening and mentions specialized CT applications for radiotherapy planning and multi-modality imaging with PET/CT or SPECT/CT systems.