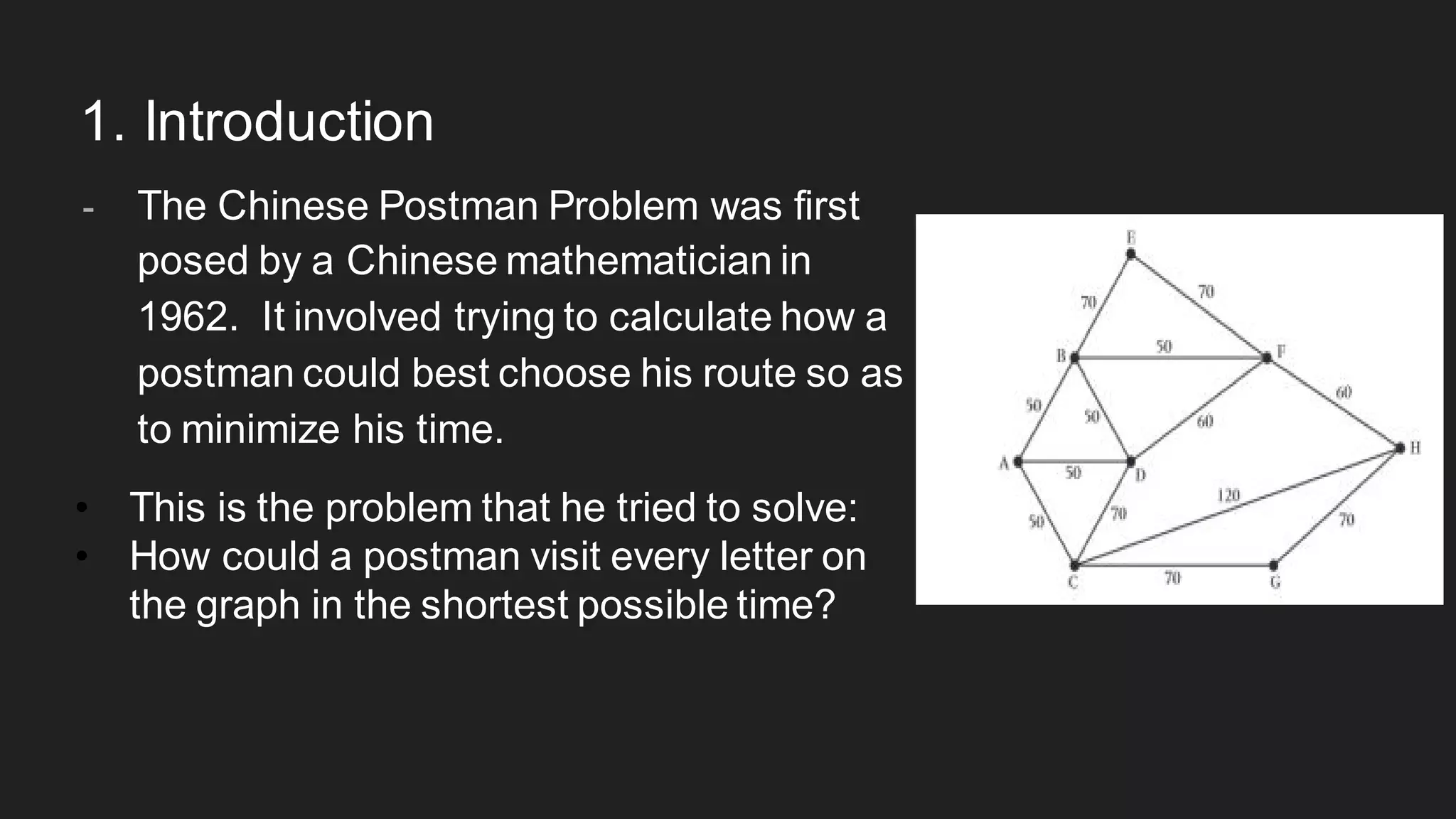
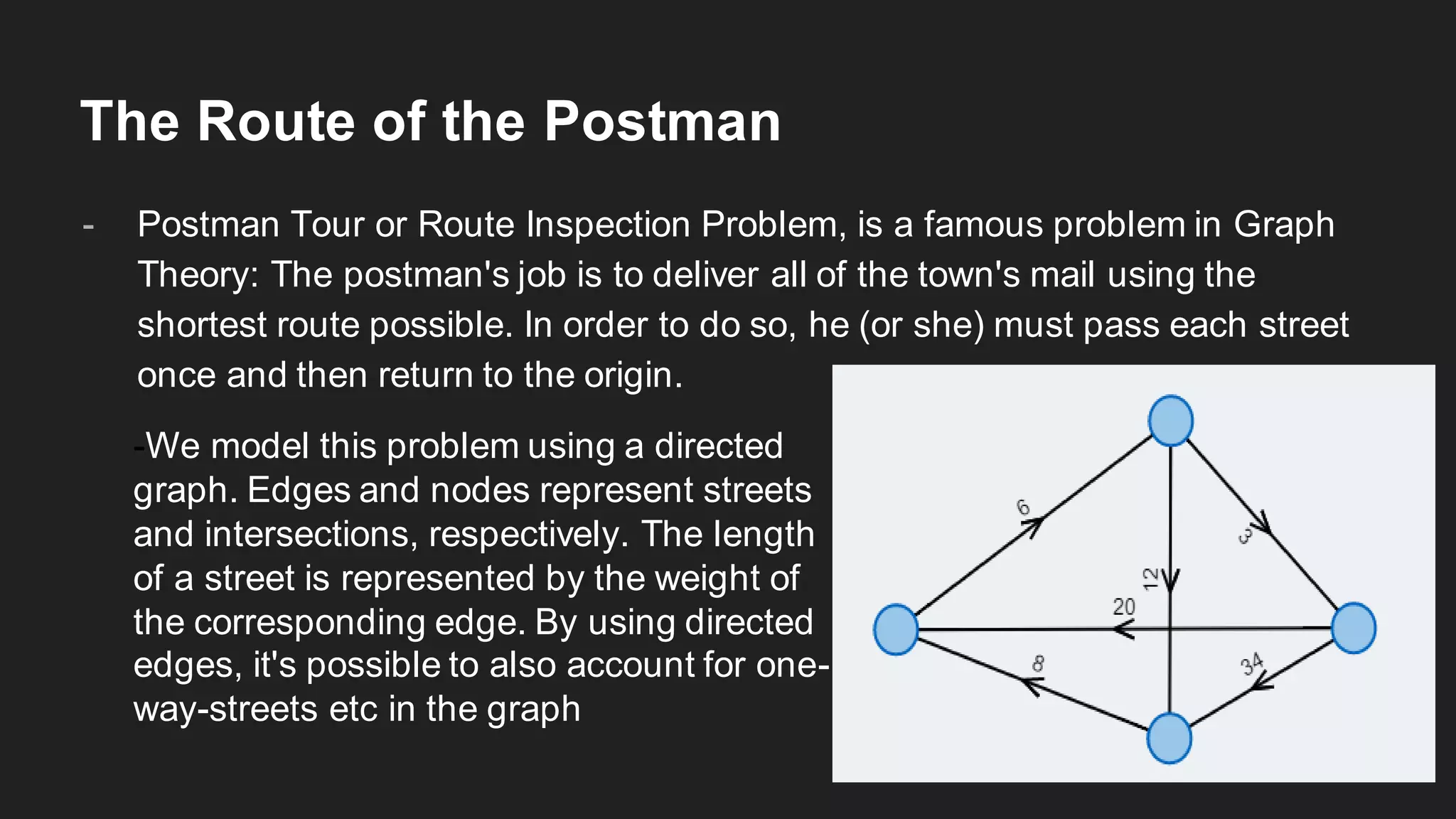
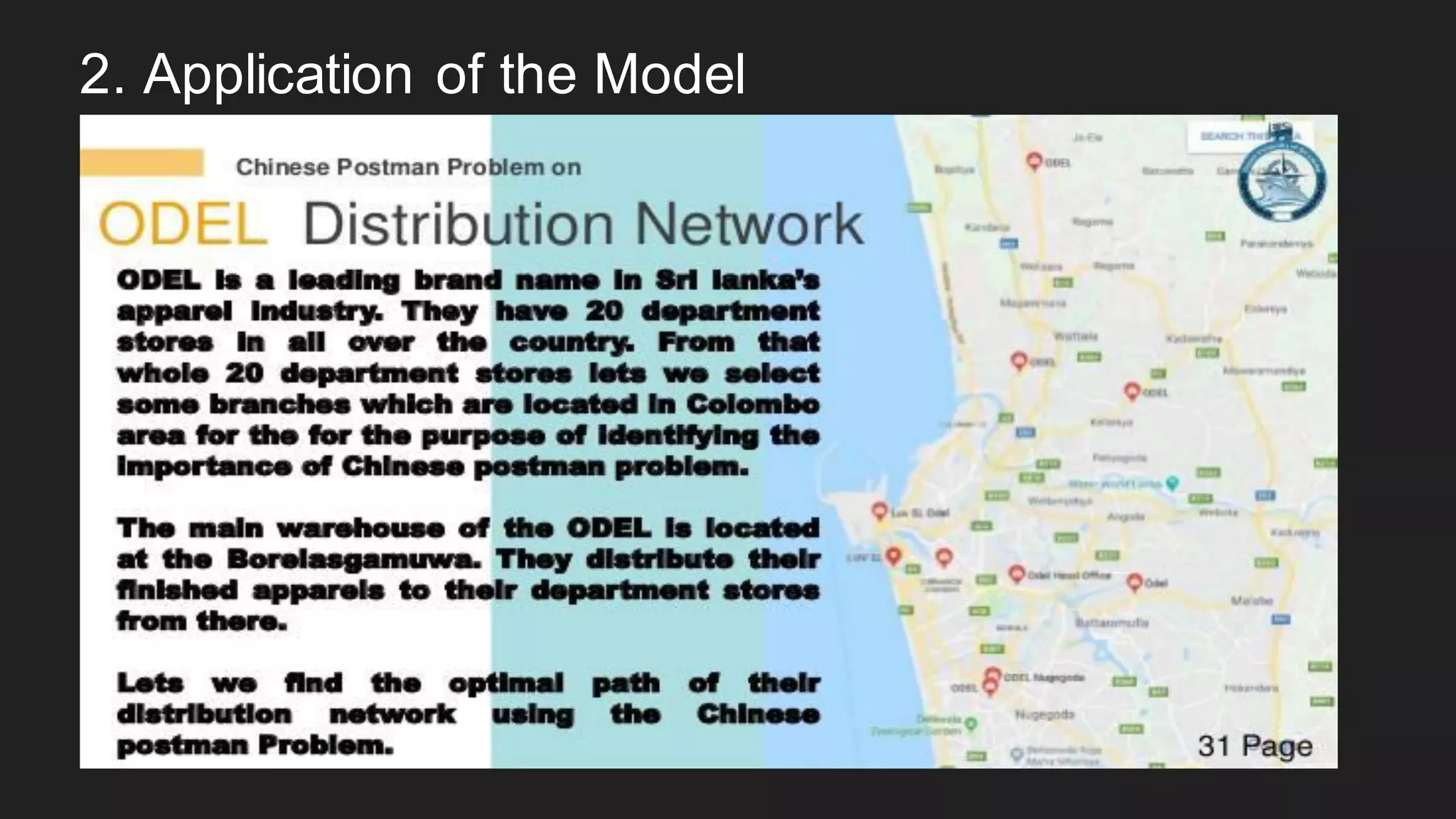
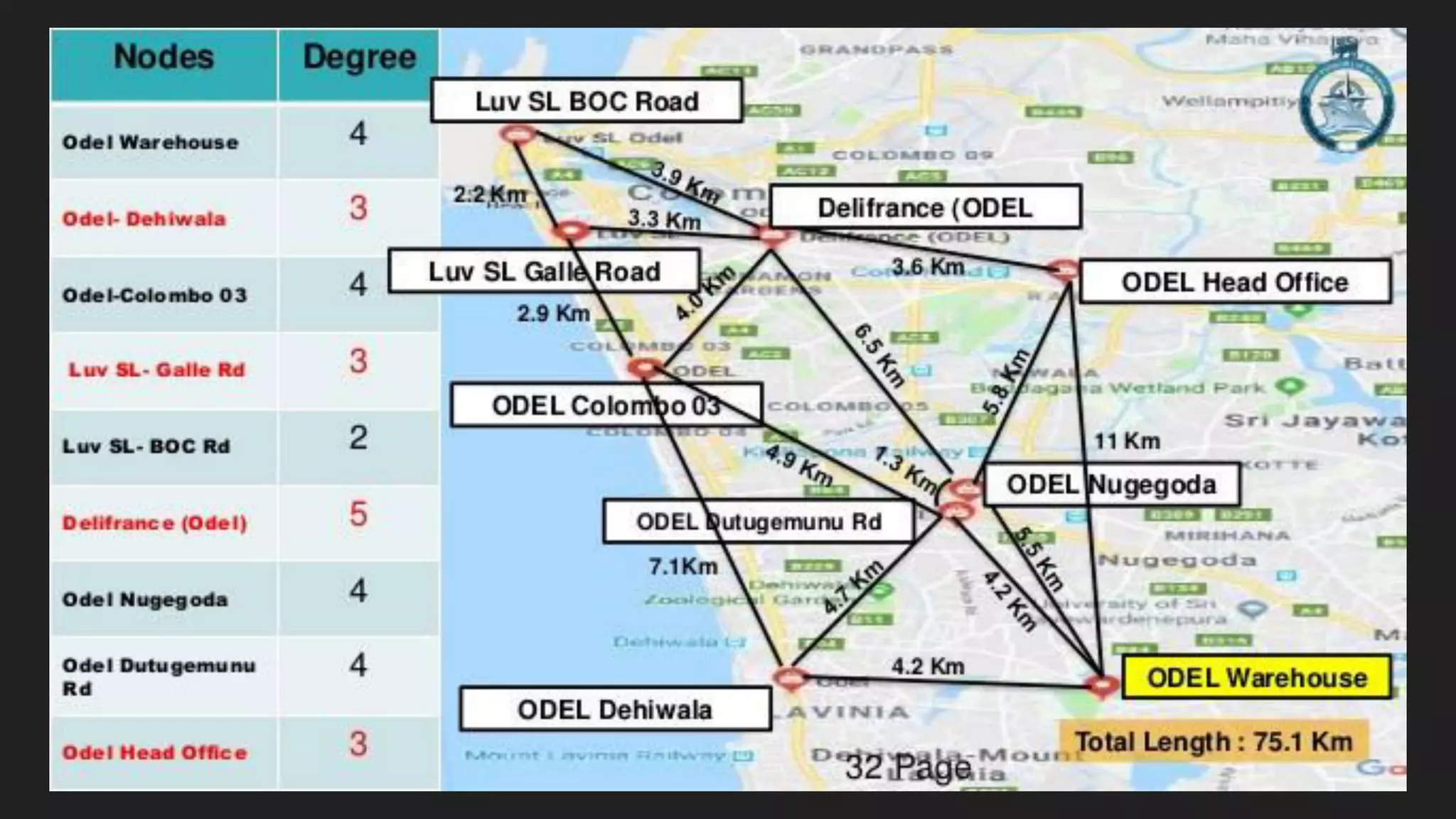
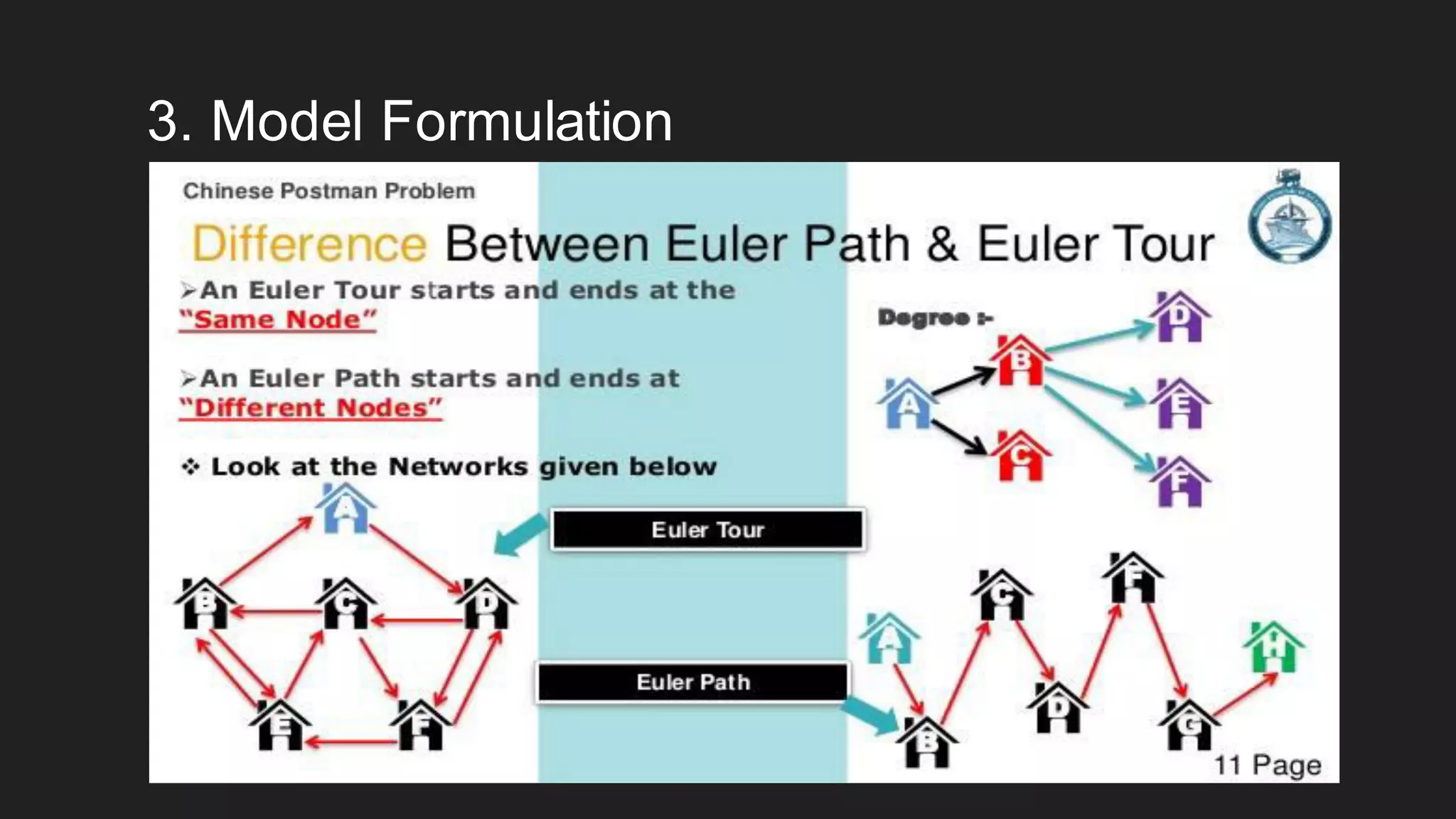
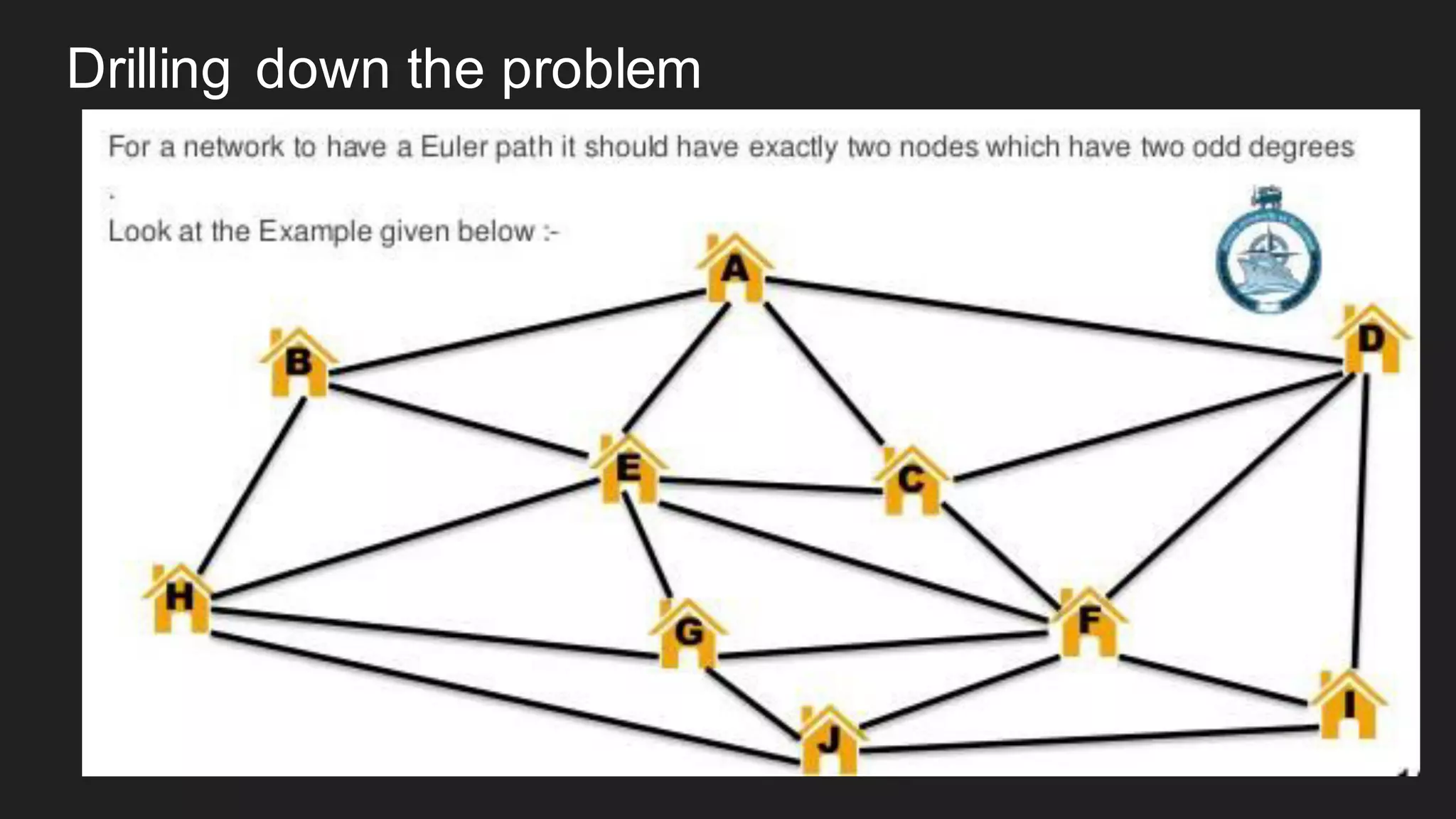
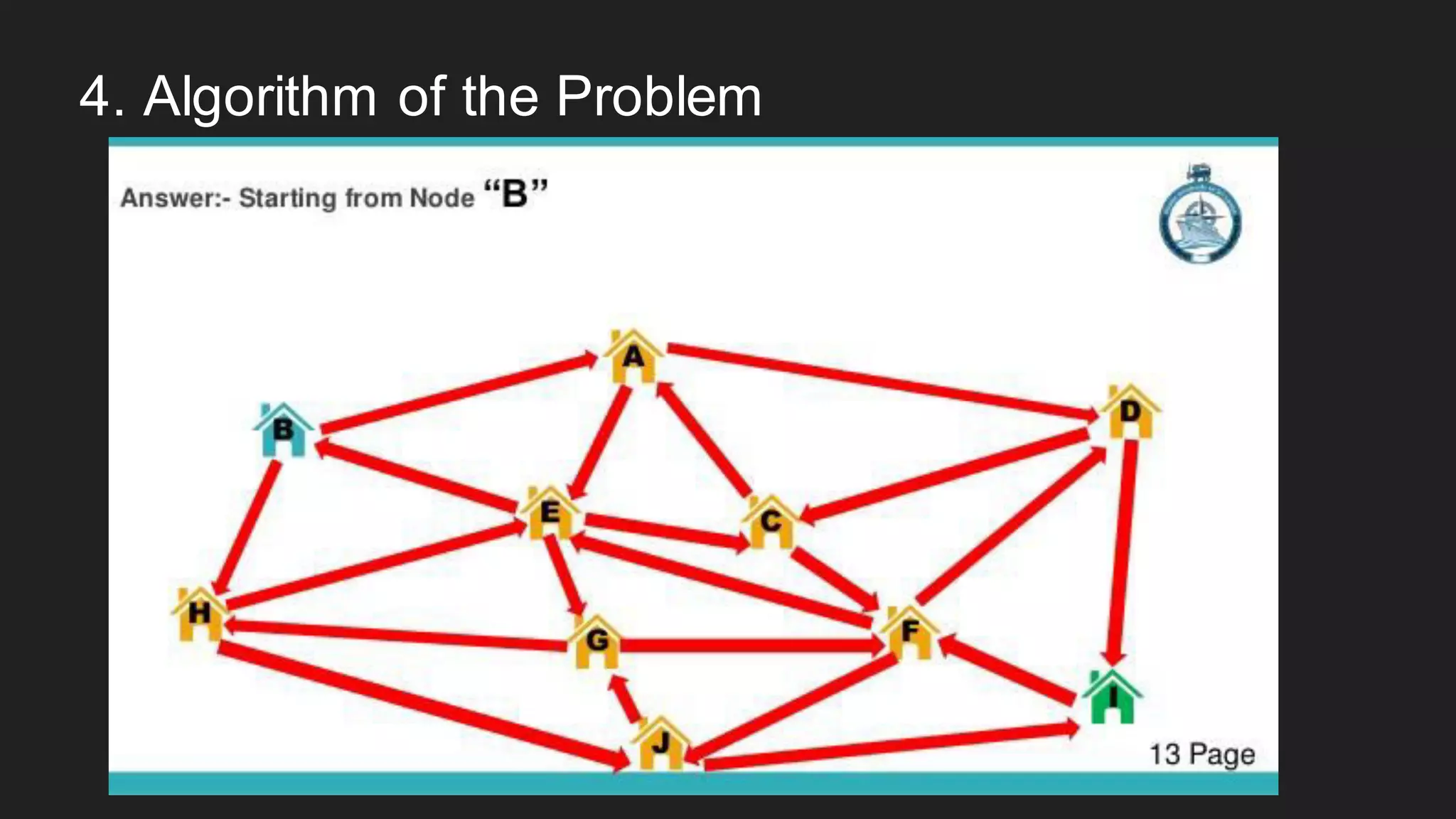
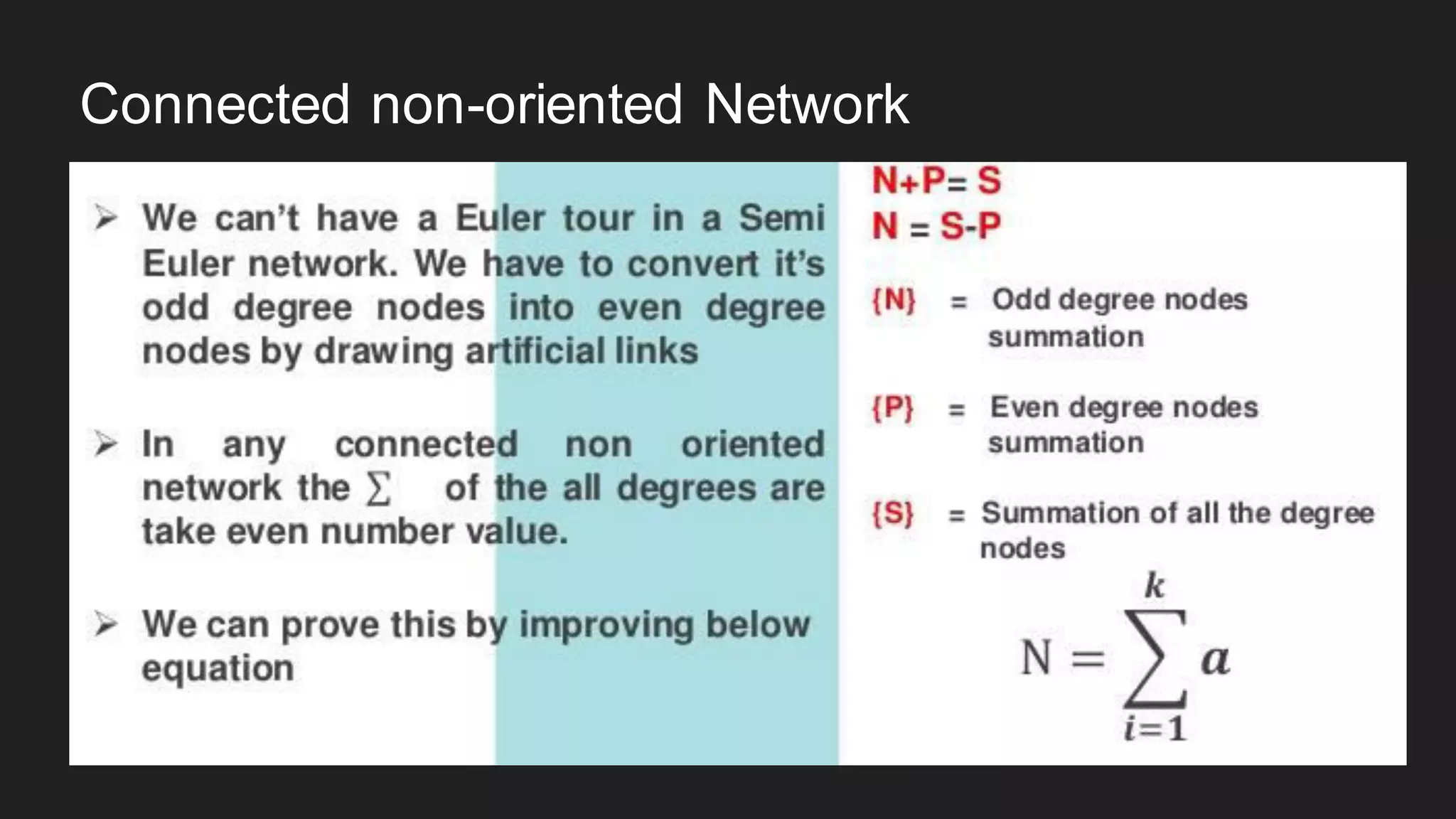
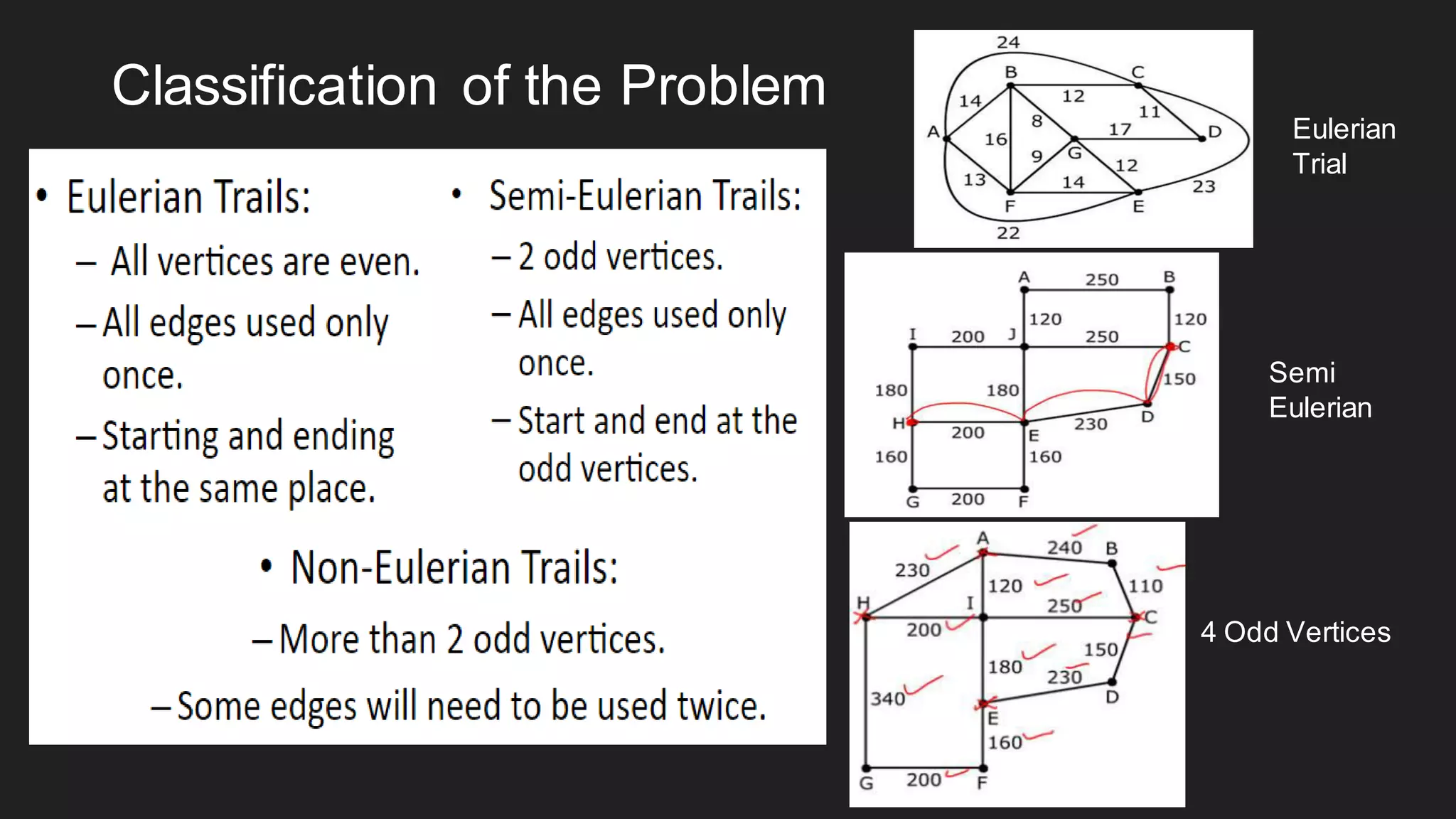
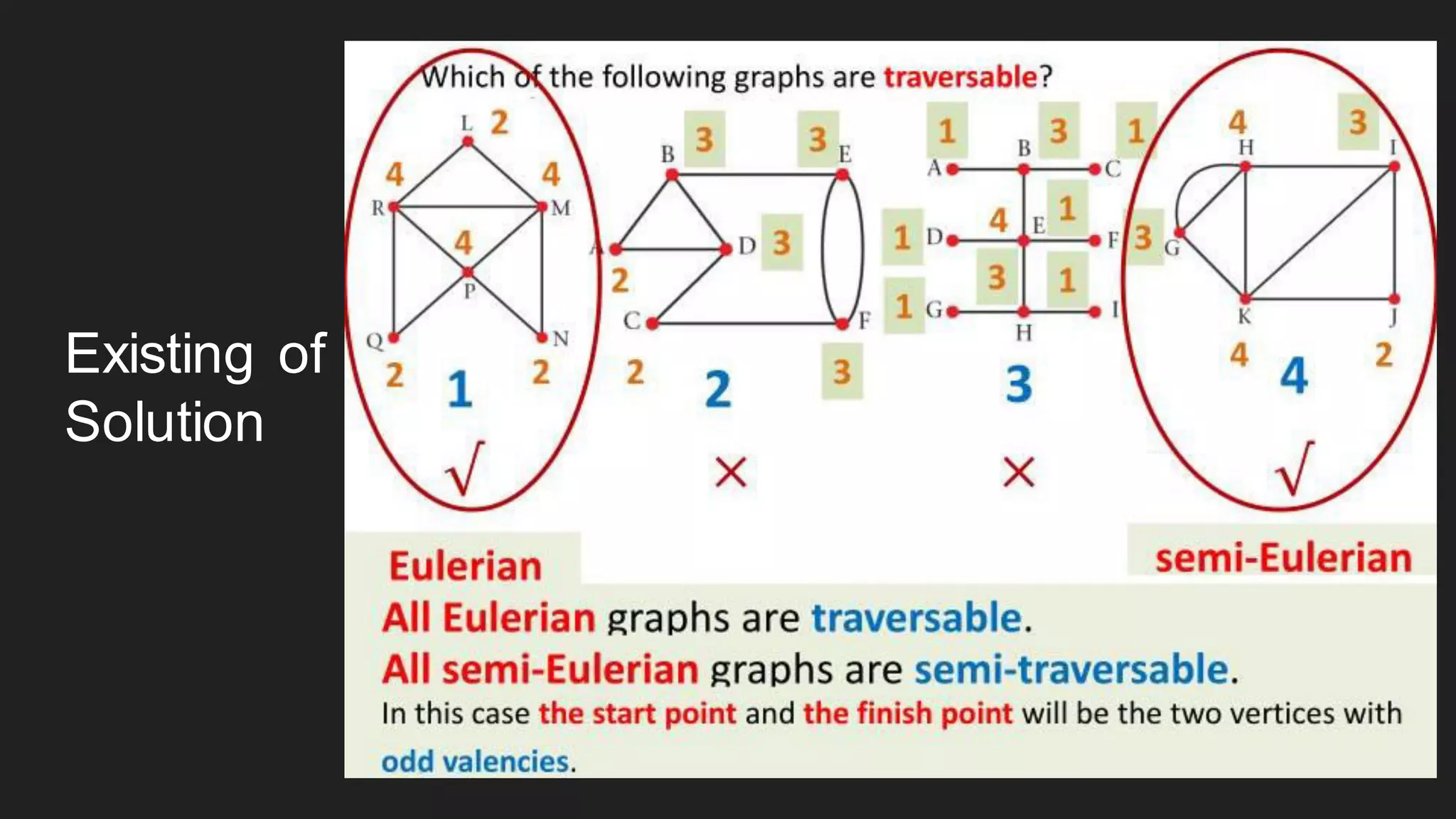
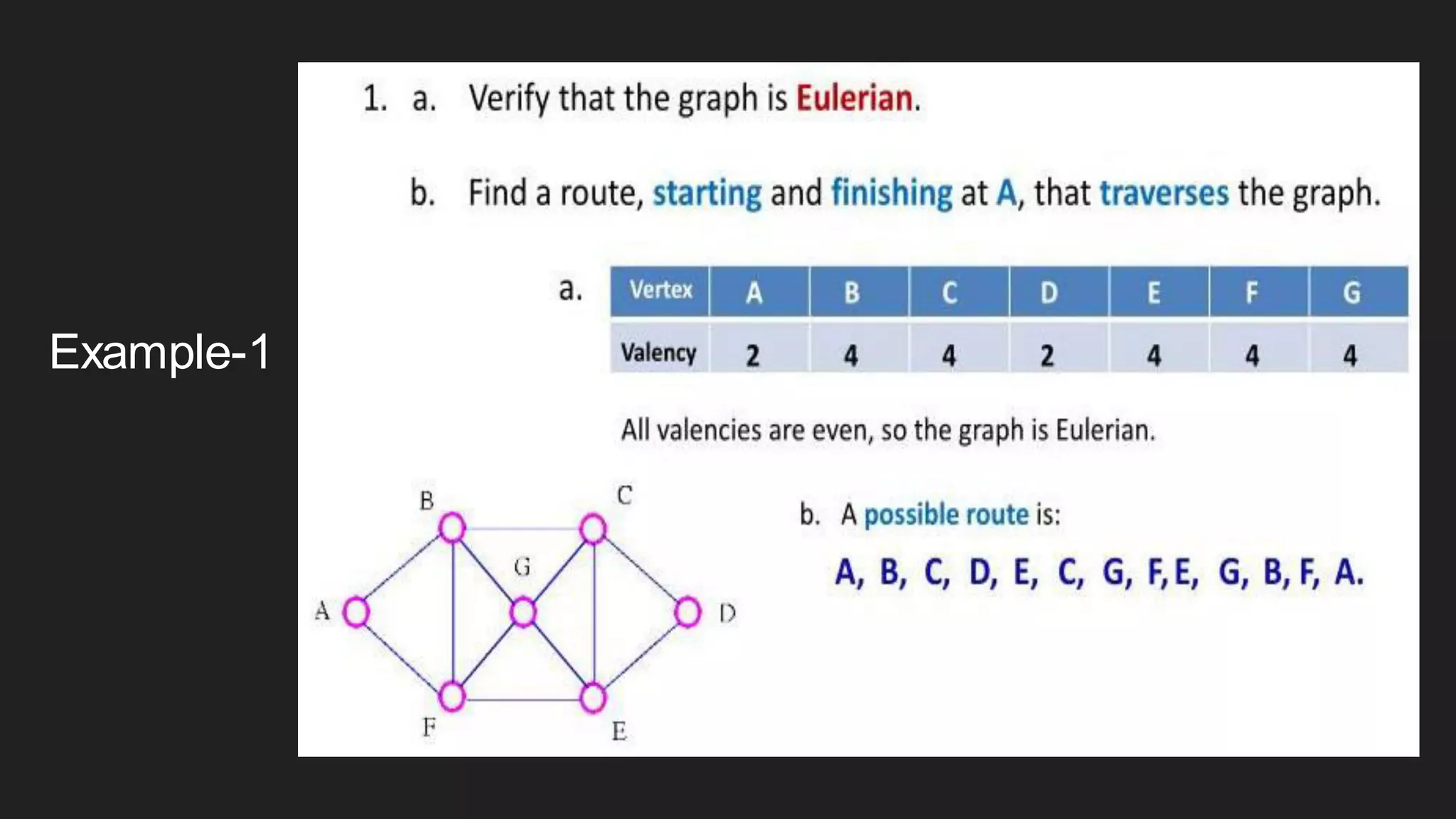
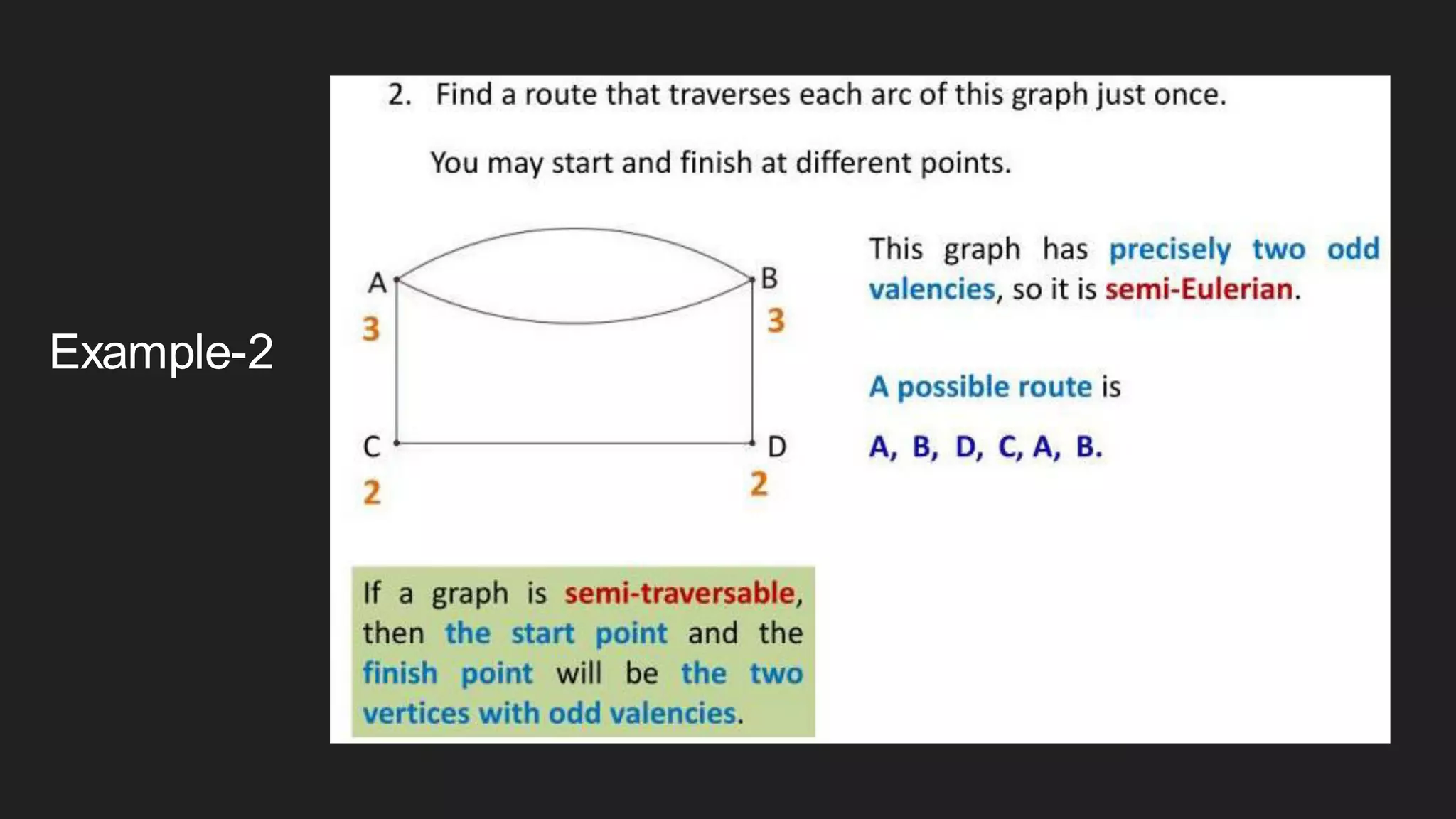
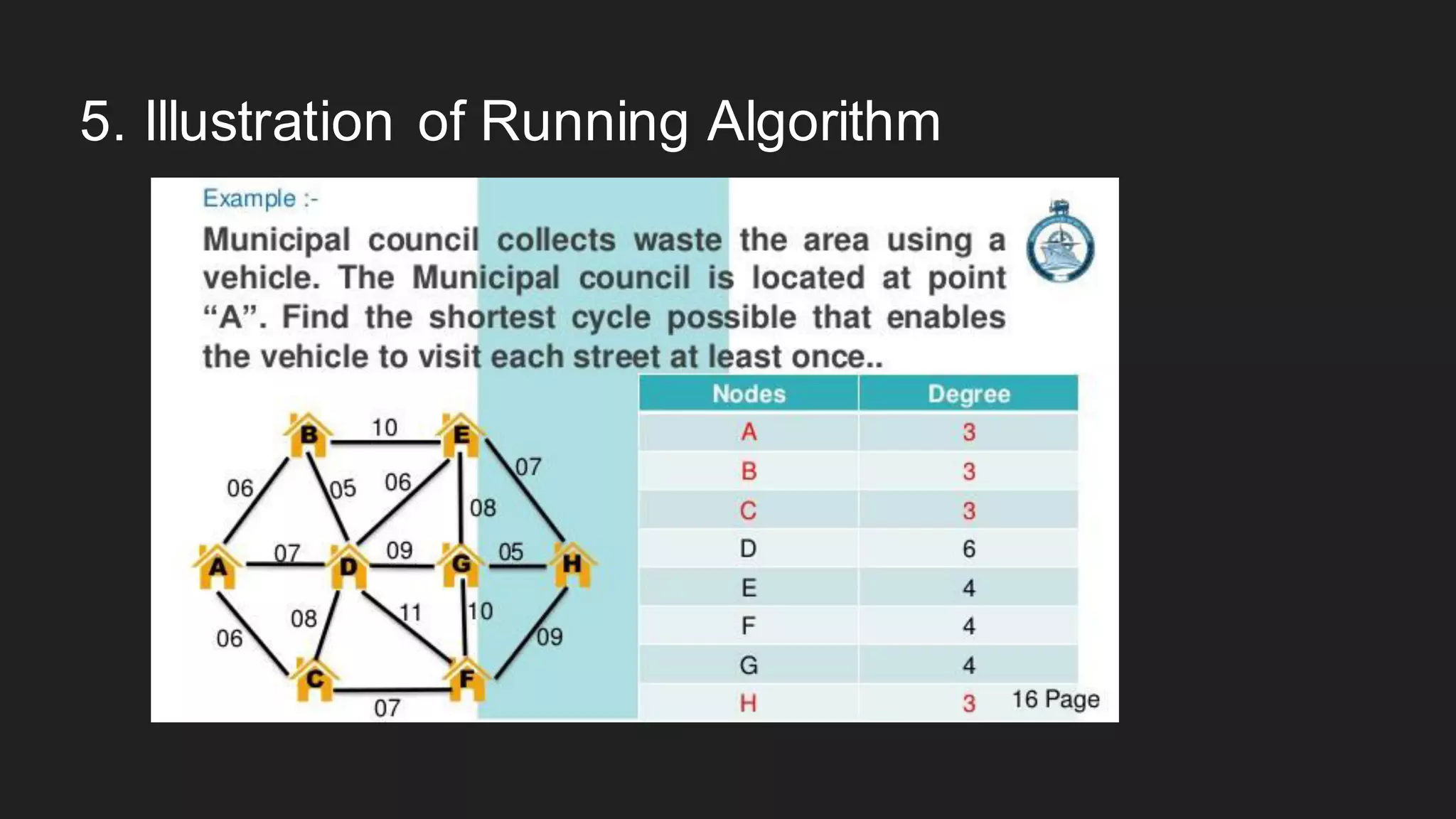
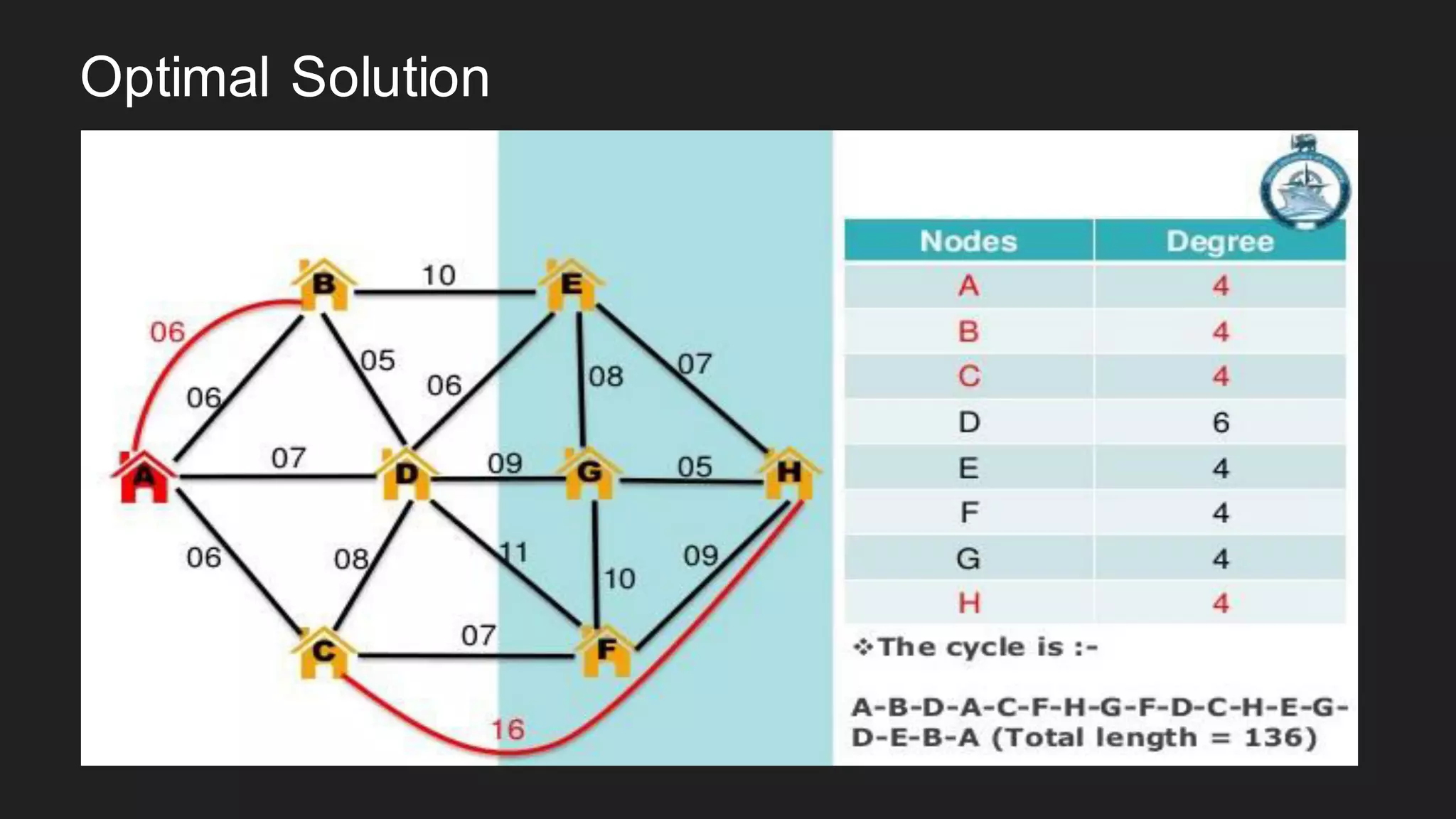
The document discusses the Chinese Postman Problem, which involves finding the shortest route for a postman to deliver mail to every address on a graph. It introduces the problem, models it using a directed graph with edges representing streets and nodes representing intersections, and outlines the algorithm for solving it. The algorithm involves classifying the graph as Eulerian, trial, or semi-Eulerian and using different approaches depending on the classification to find an optimal solution.