It covers,
Introduction and basics of Components of an intelligent system
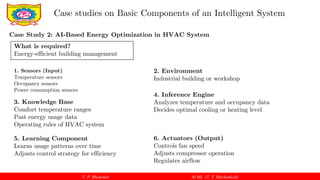
1. Sensors (Input unit),
2. Environment,
3. Knowledge Base,
4. Inference or Decision-Making Engine,
5. Learning Component,
6. Actuators (Output unit),
7. two case studies – Quality inspection and HVAC system

![V. P. Bhaurkar AI ML (T. Y. Mechanical)
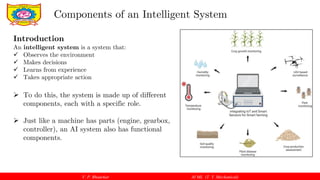
Basic Components of an Intelligent System
A] Sensors (Input Component)
Meaning:
Sensors are used to collect information from the environment.
They act as the eyes and ears of the intelligent system.
Examples:
Images from cameras
Temperature, pressure, vibration data
Sound and signals
Mechanical Engineering Examples:
Vibration sensor on a motor
Camera for surface inspection
Temperature sensor in heat treatment
Without sensors, the system cannot sense anything.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-ml-unit1-part3-260116061242-28e615b9/85/Components-of-an-artificial-intelligent-system-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![V. P. Bhaurkar AI ML (T. Y. Mechanical)
Basic Components of an Intelligent System
B] Environment
Meaning:
The environment is the surrounding system
where the AI operates.
Examples:
Manufacturing shop floor
Robotic work cell
Power plant
Vehicle system
The environment provides continuous data to the
system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-ml-unit1-part3-260116061242-28e615b9/85/Components-of-an-artificial-intelligent-system-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![V. P. Bhaurkar AI ML (T. Y. Mechanical)
Basic Components of an Intelligent System
C] Knowledge Base
Meaning:
The knowledge base stores information
required for decision making.
It contains:
1. Facts
2. Rules
3. Past experiences
4. Data patterns
Example:
Normal and abnormal vibration levels
Rules like:
IF temperature is high → reduce load
It is the memory of the intelligent system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-ml-unit1-part3-260116061242-28e615b9/85/Components-of-an-artificial-intelligent-system-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![V. P. Bhaurkar AI ML (T. Y. Mechanical)
Basic Components of an Intelligent System
D] Inference Engine (Decision-Making Unit)
Meaning:
The inference engine analyzes the data and draws
conclusions.
It applies:
Rules
Logic
Stored knowledge
Mechanical Engineering Example:
1. Identifying fault type based on sensor data
2. Deciding whether a machine should continue
running
This component is the brain of the system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-ml-unit1-part3-260116061242-28e615b9/85/Components-of-an-artificial-intelligent-system-pdf-7-320.jpg)
![V. P. Bhaurkar AI ML (T. Y. Mechanical)
Basic Components of an Intelligent System
E] Learning Component
Meaning:
The learning component helps the system to
improve its performance over time.
What it does:
1. Updates the knowledge base
2. Learns from new data
3. Improves accuracy
Mechanical Engineering Example:
Improving fault prediction accuracy
Learning new defect patterns in products
This makes the system adaptive, not fixed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-ml-unit1-part3-260116061242-28e615b9/85/Components-of-an-artificial-intelligent-system-pdf-8-320.jpg)
![V. P. Bhaurkar AI ML (T. Y. Mechanical)
Basic Components of an Intelligent System
F] Actuators (Output Component)
Meaning:
Actuators convert decisions into physical or control
actions.
Examples:
Motors
Valves
Robotic arms
Control signals
Mechanical Engineering Example:
Stopping a machine
Rejecting a defective part
Adjusting speed or feed rate
This is where the system acts on its decision.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-ml-unit1-part3-260116061242-28e615b9/85/Components-of-an-artificial-intelligent-system-pdf-9-320.jpg)