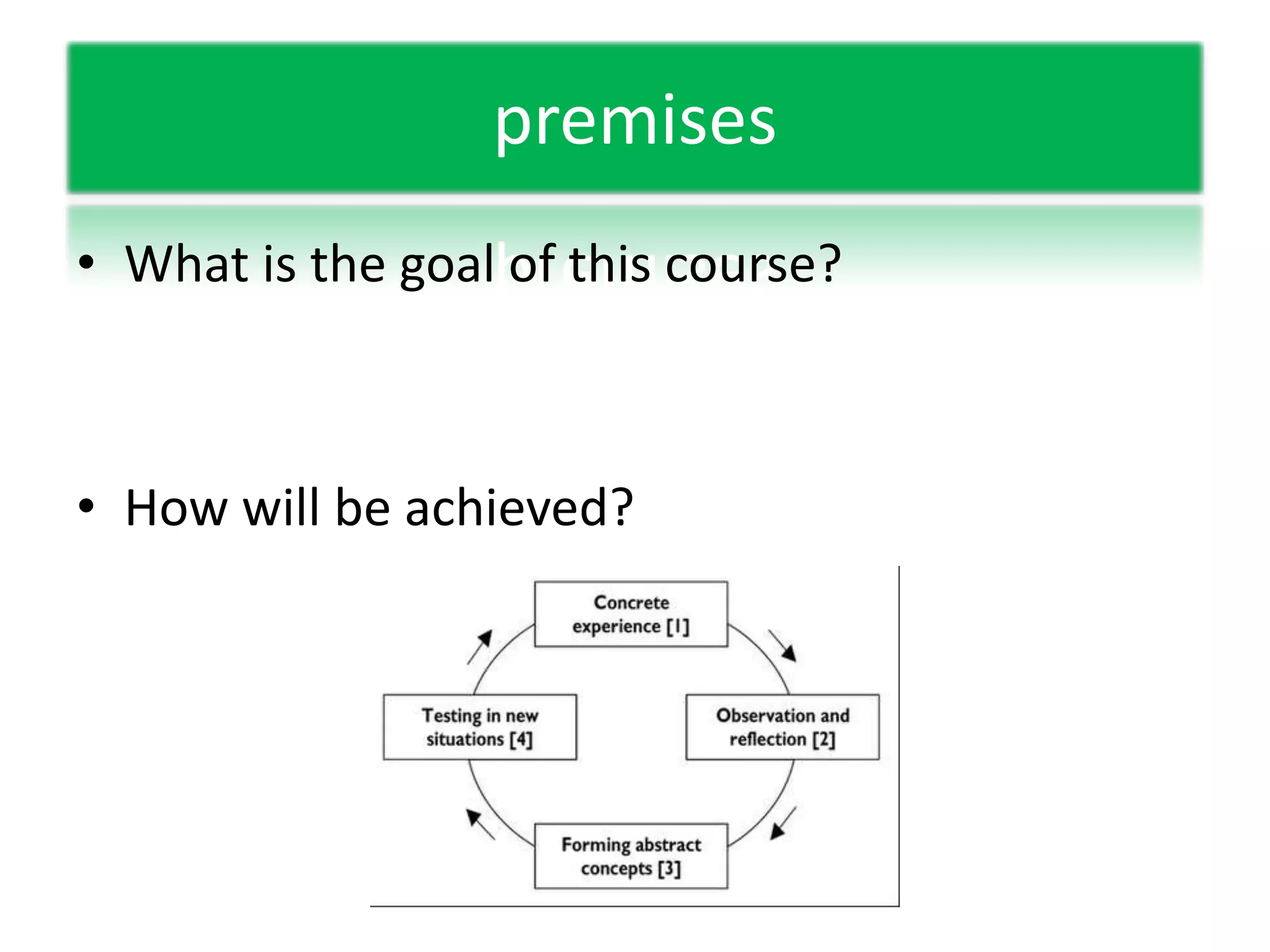
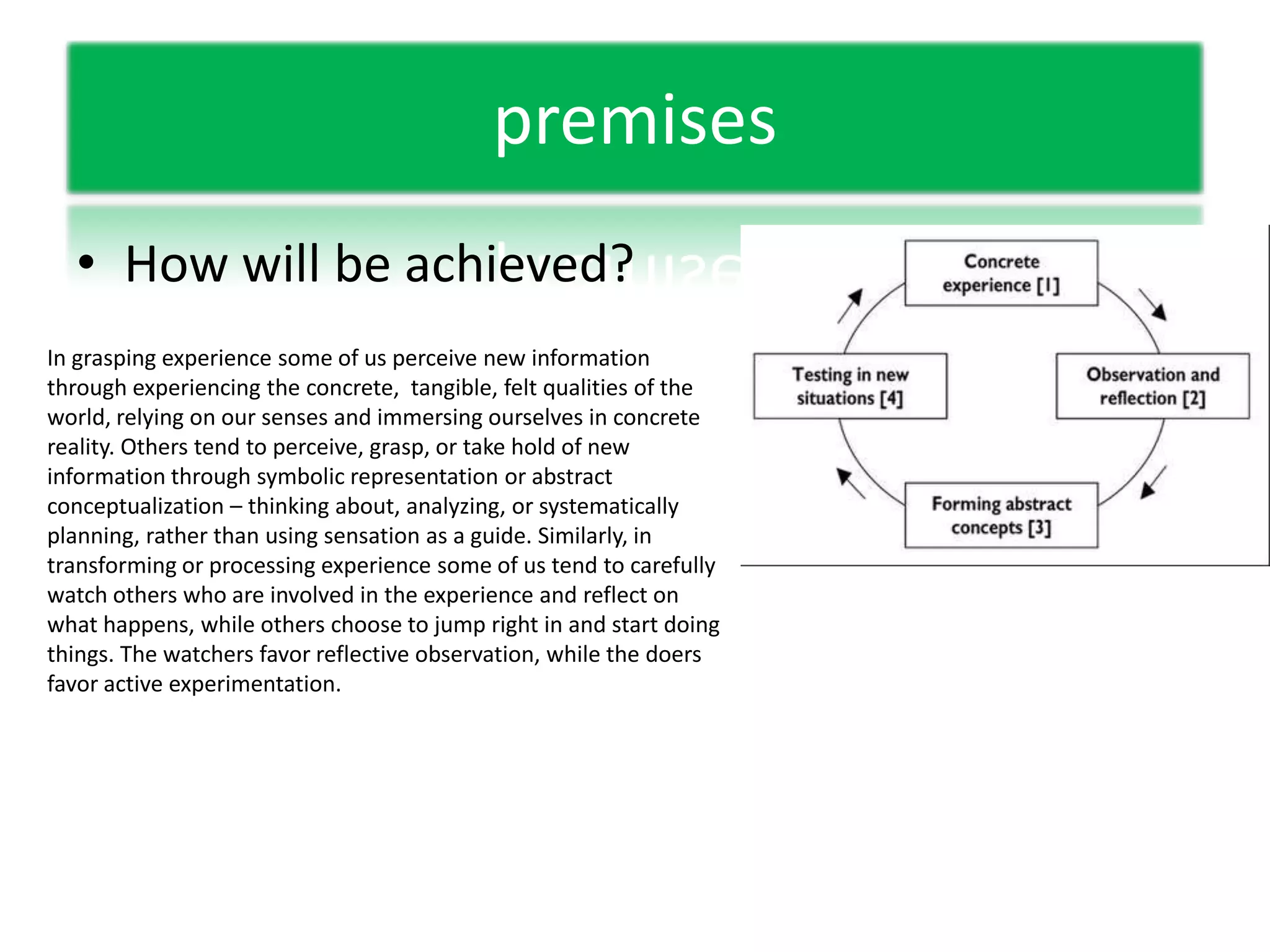
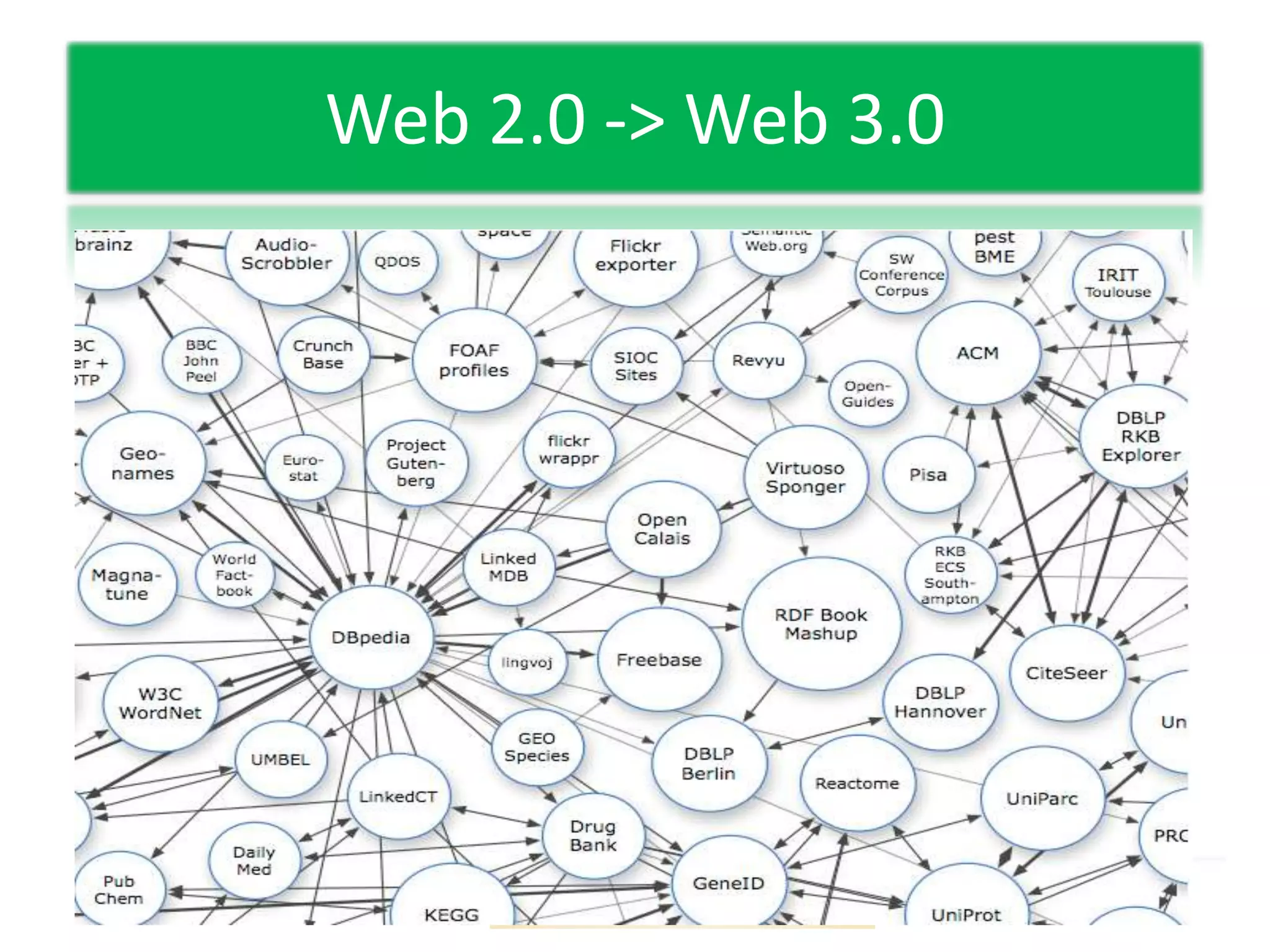
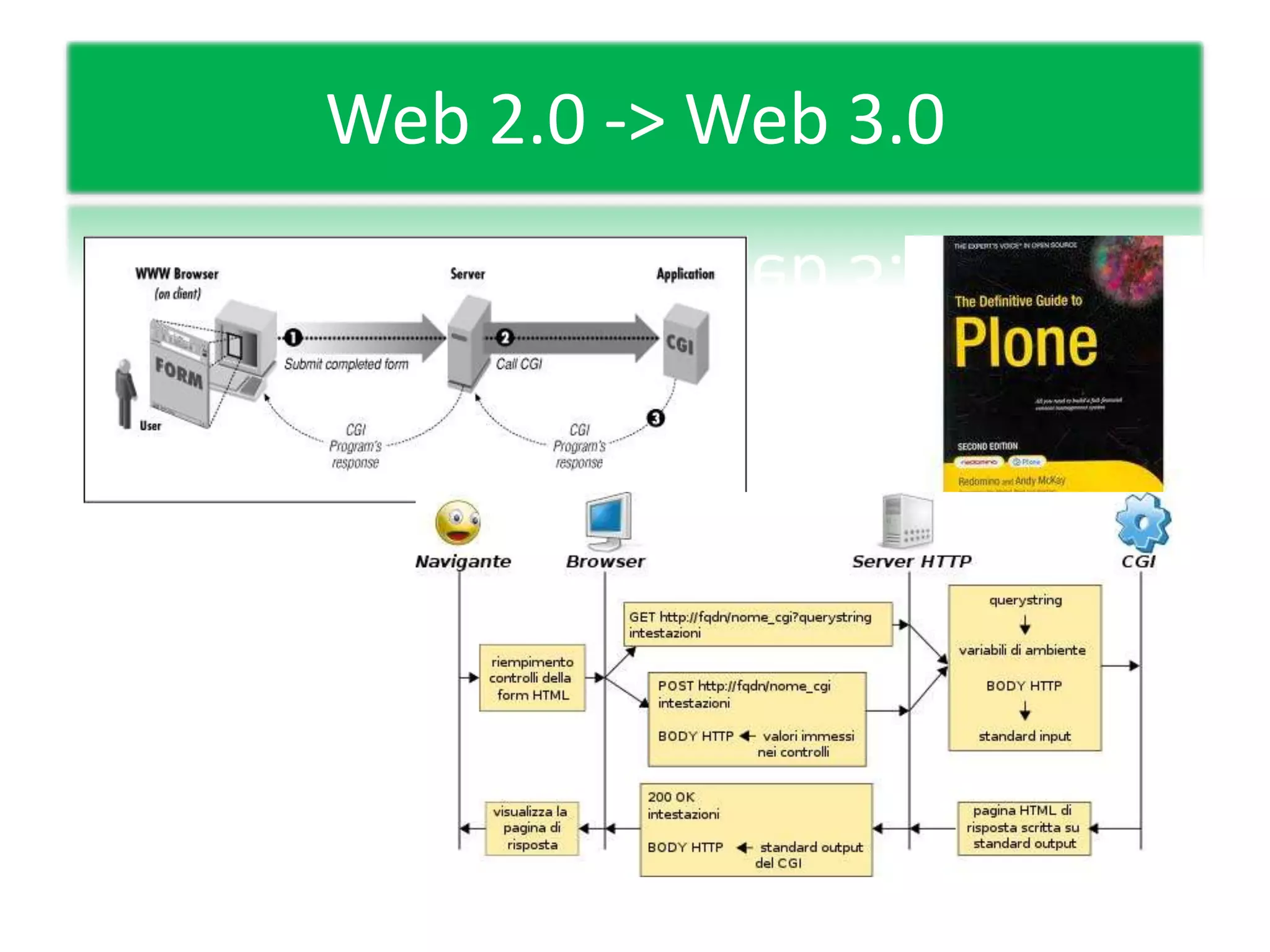
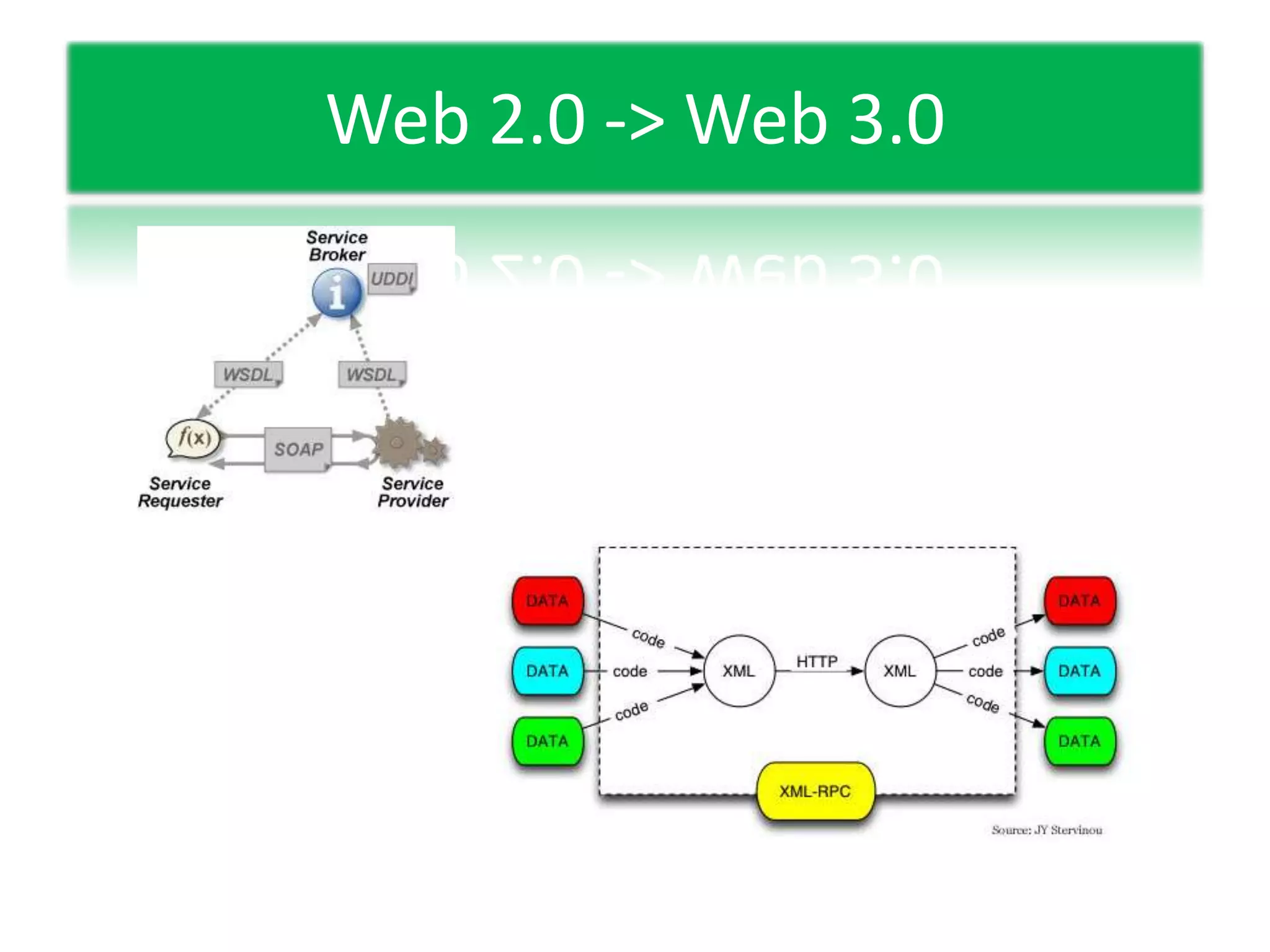
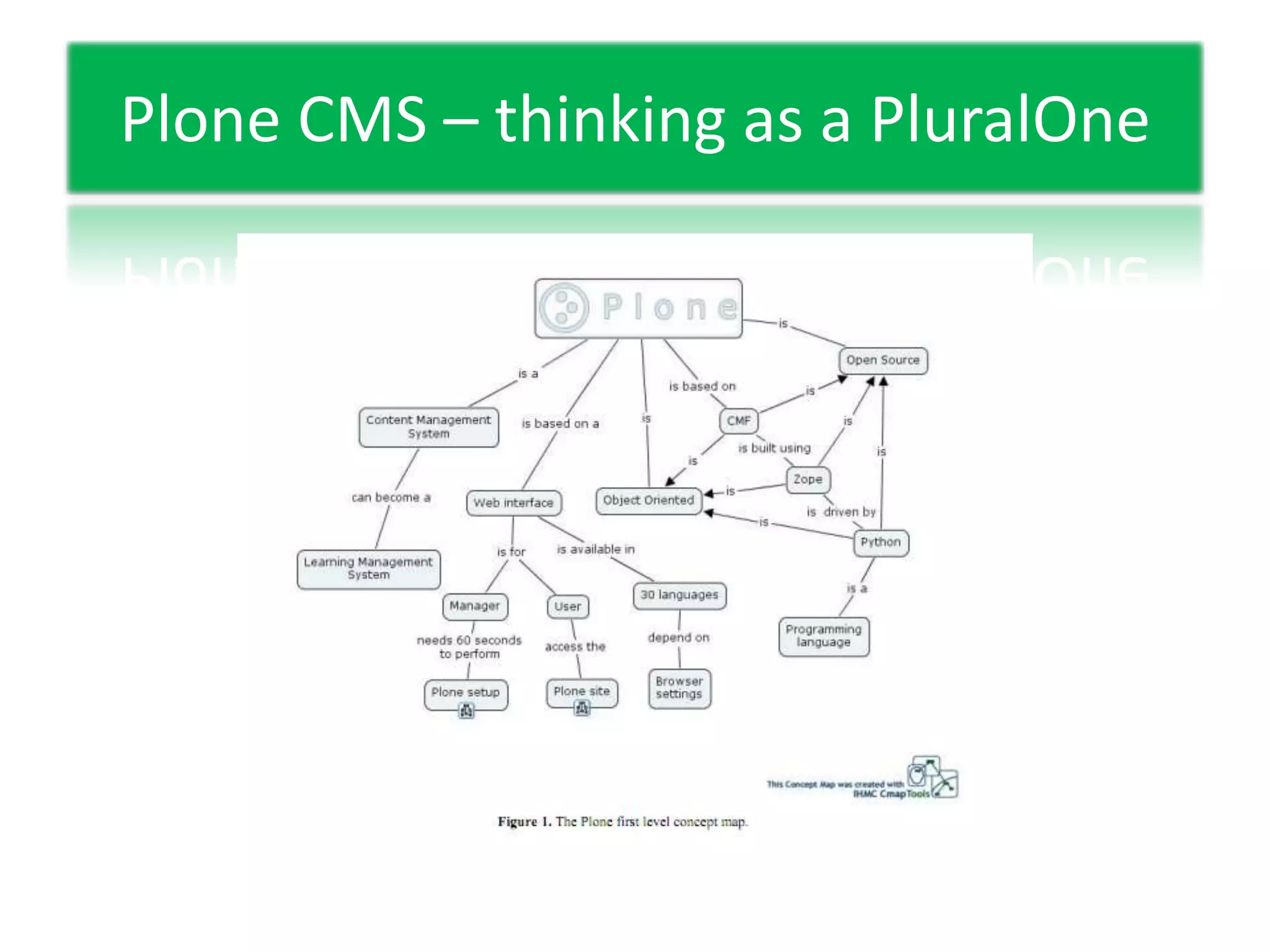
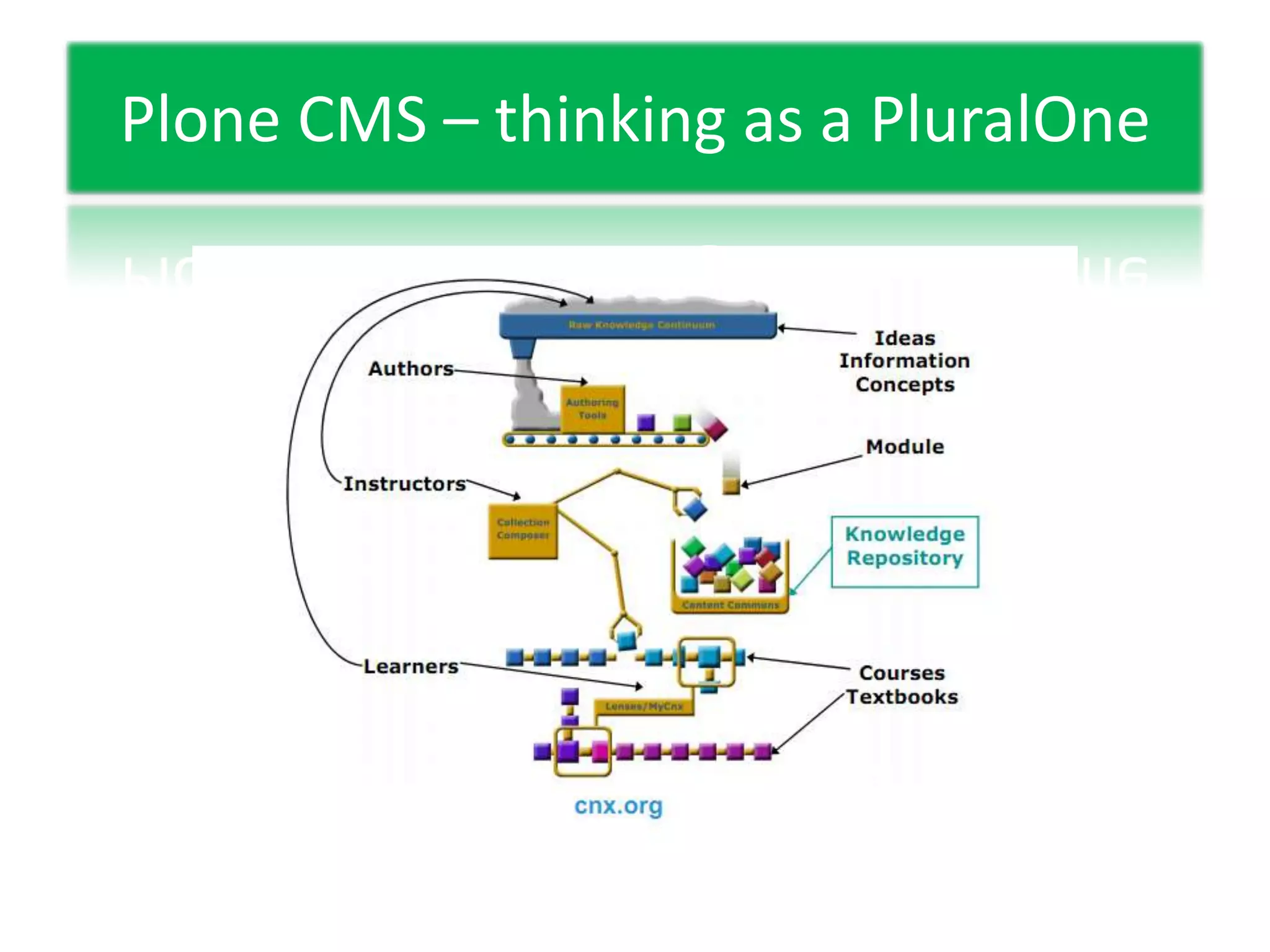
This document discusses experiential learning and learning styles. It explains that people perceive and process new information in different ways, either through concrete experiences or abstract conceptualization, and either through reflective observation or active experimentation. These dimensions present choices in how we learn, and we develop preferred patterns or learning styles. The document also provides an overview of the basics of web-based learning, including a brief history of email and e-learning leading into greater use of web-based learning through Web 2.0 and 3.0 technologies. It suggests using a password manager like LastPass when working online.