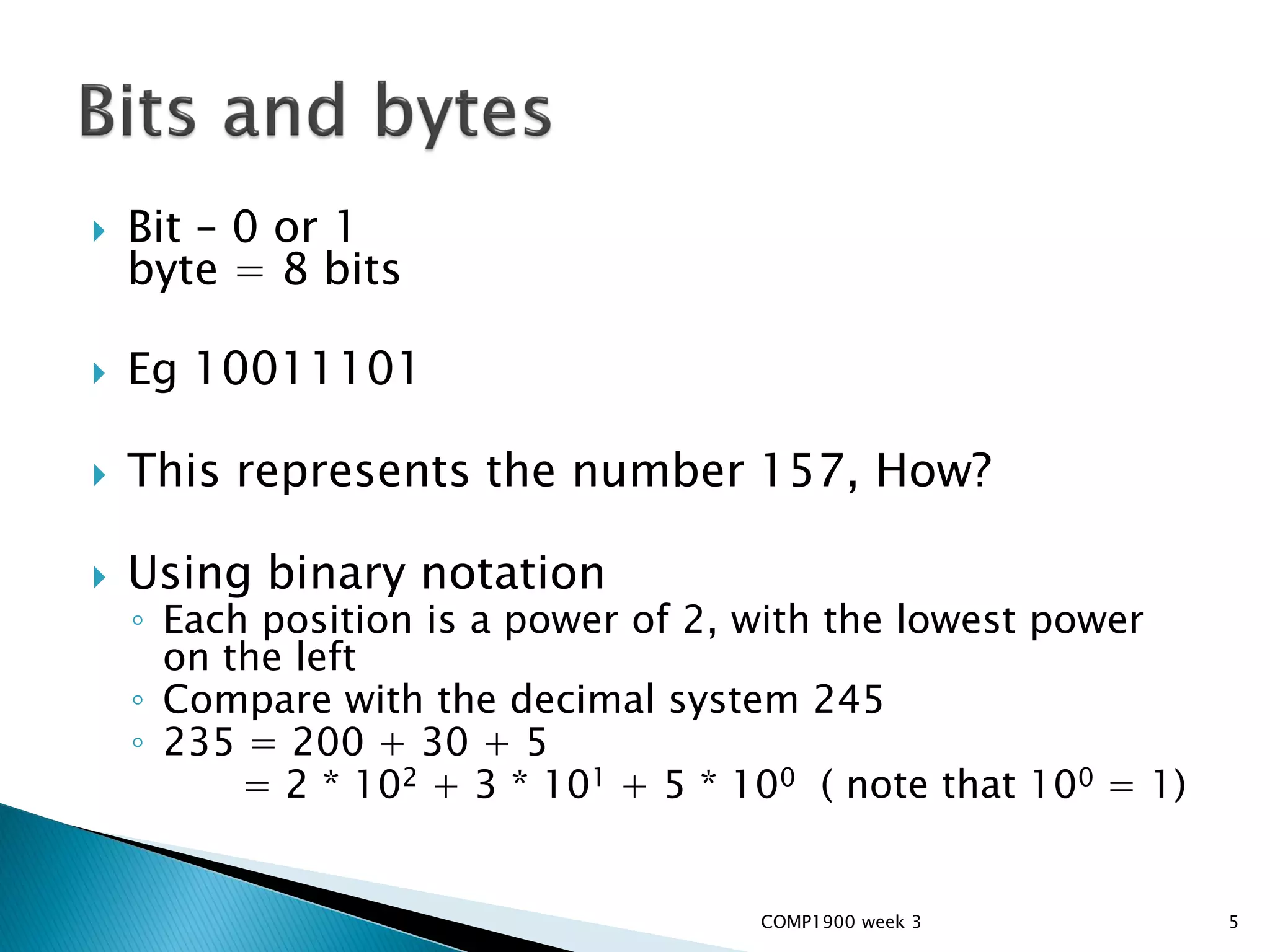
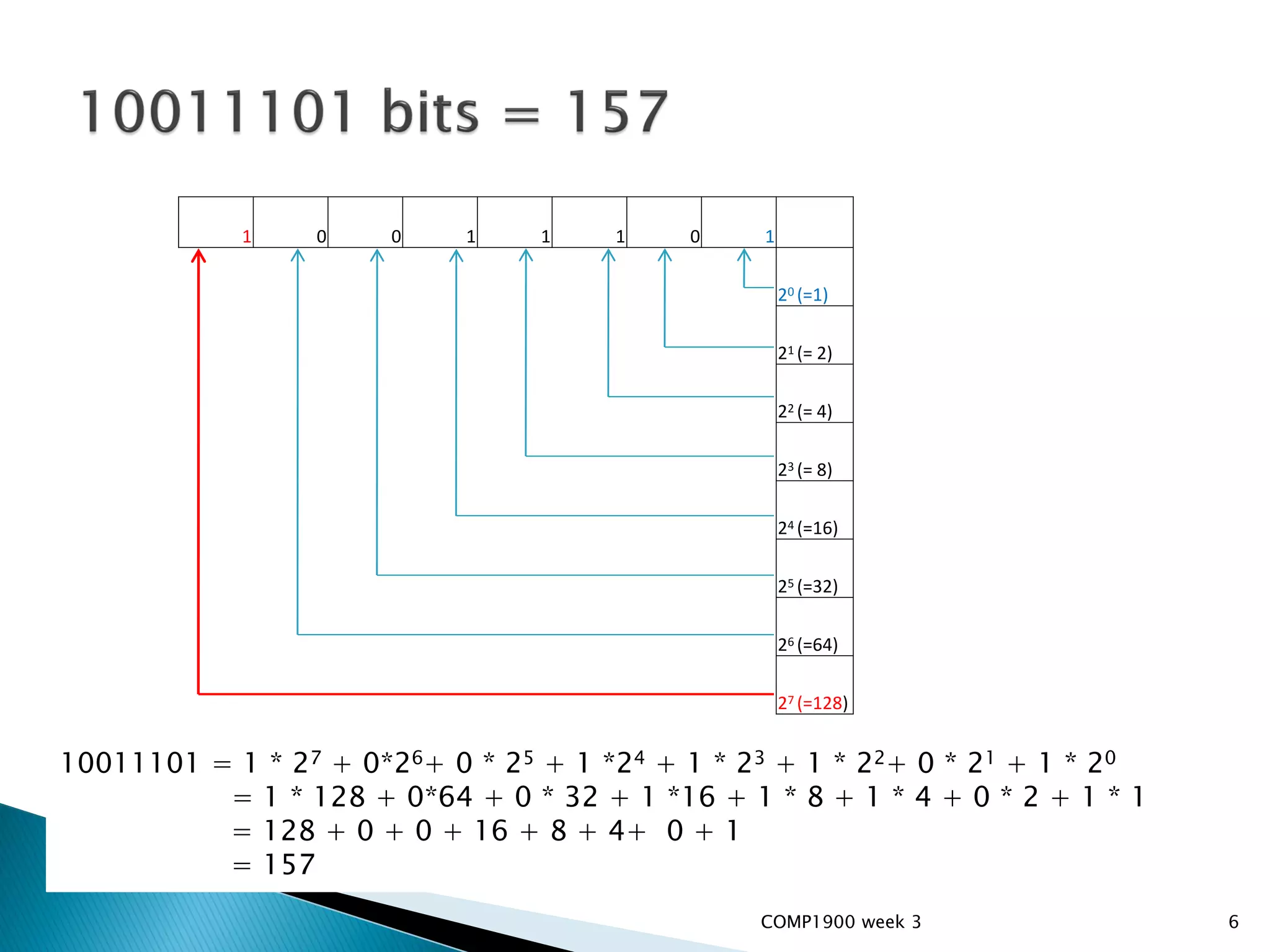
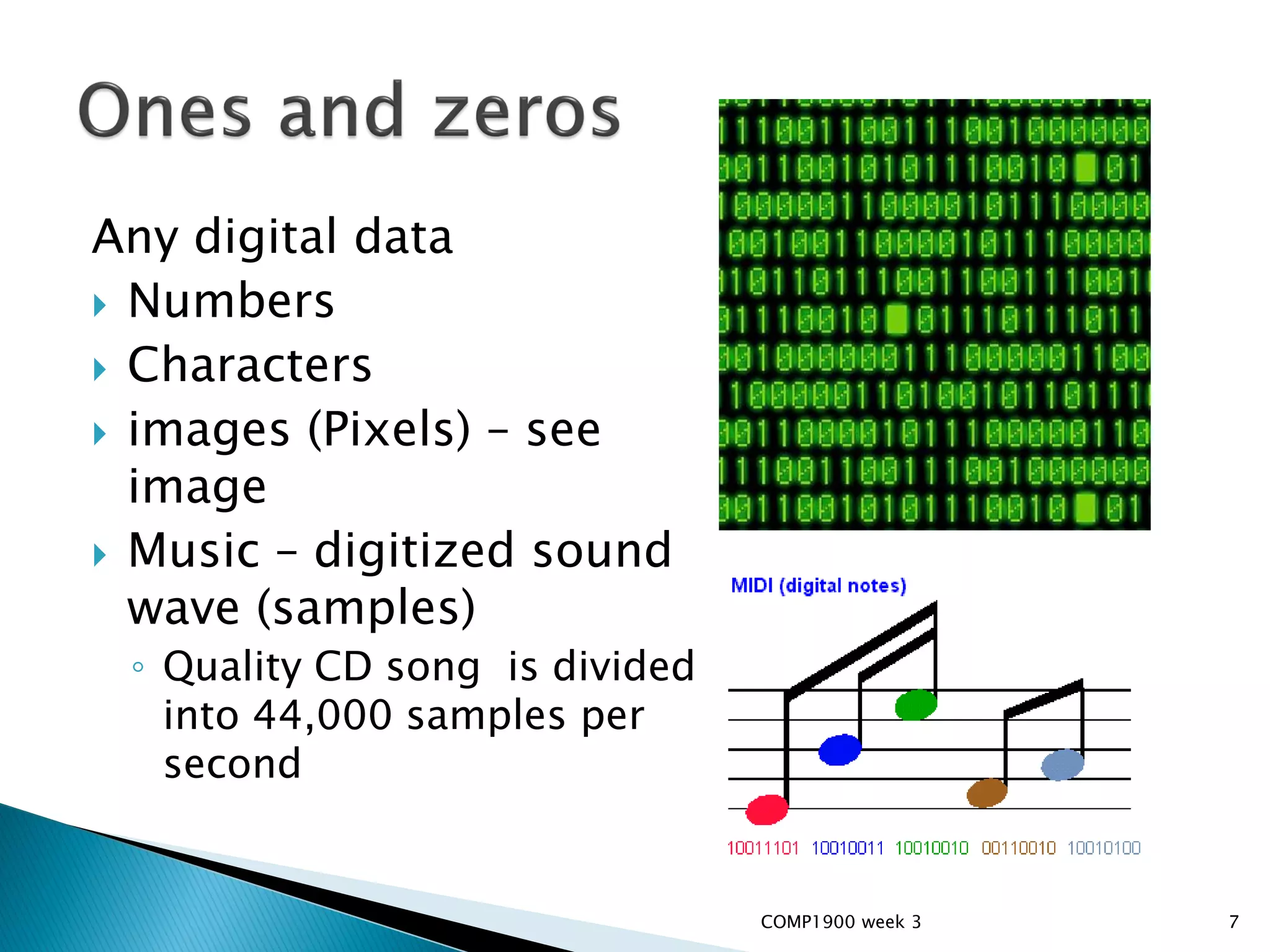
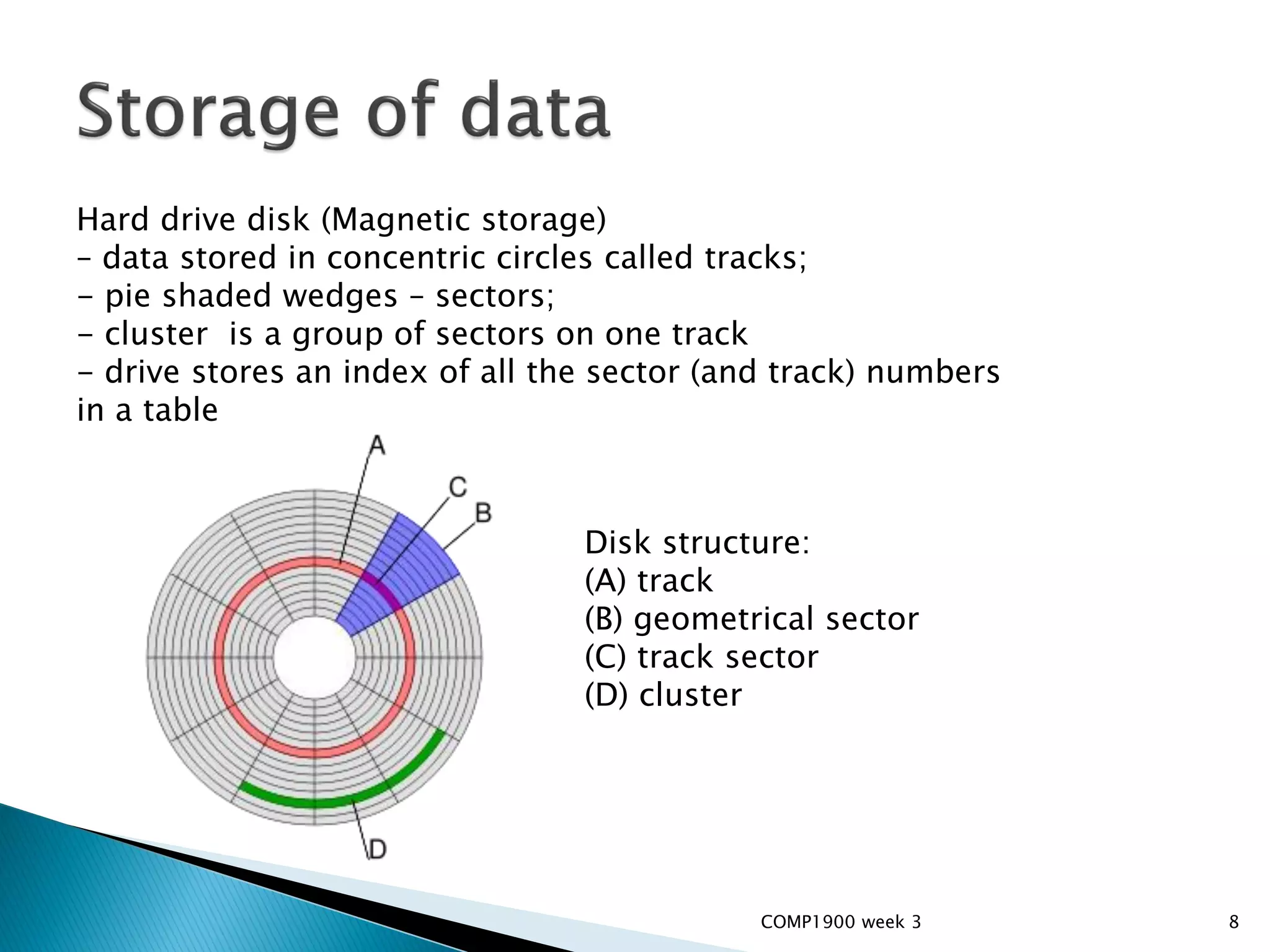
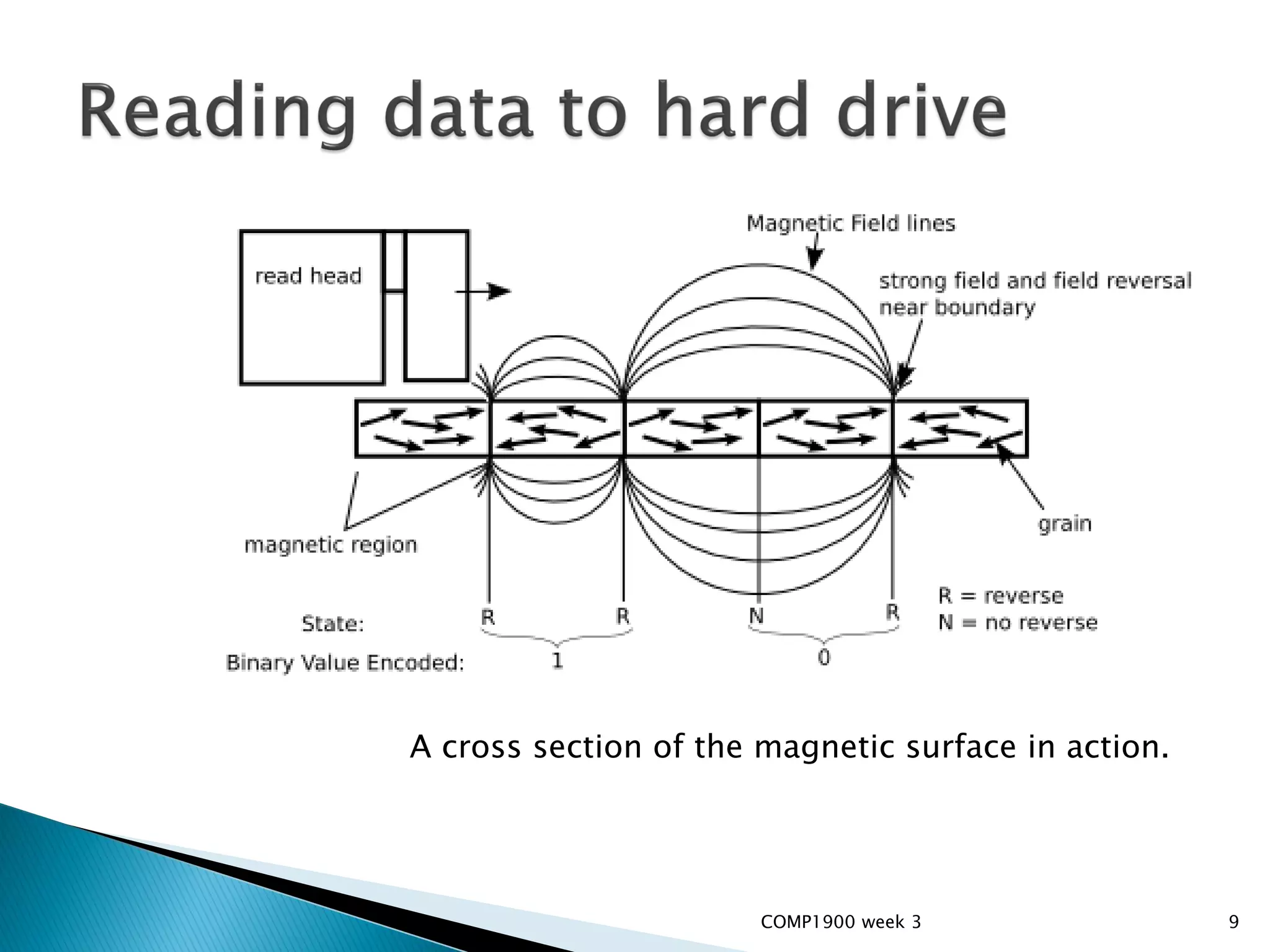
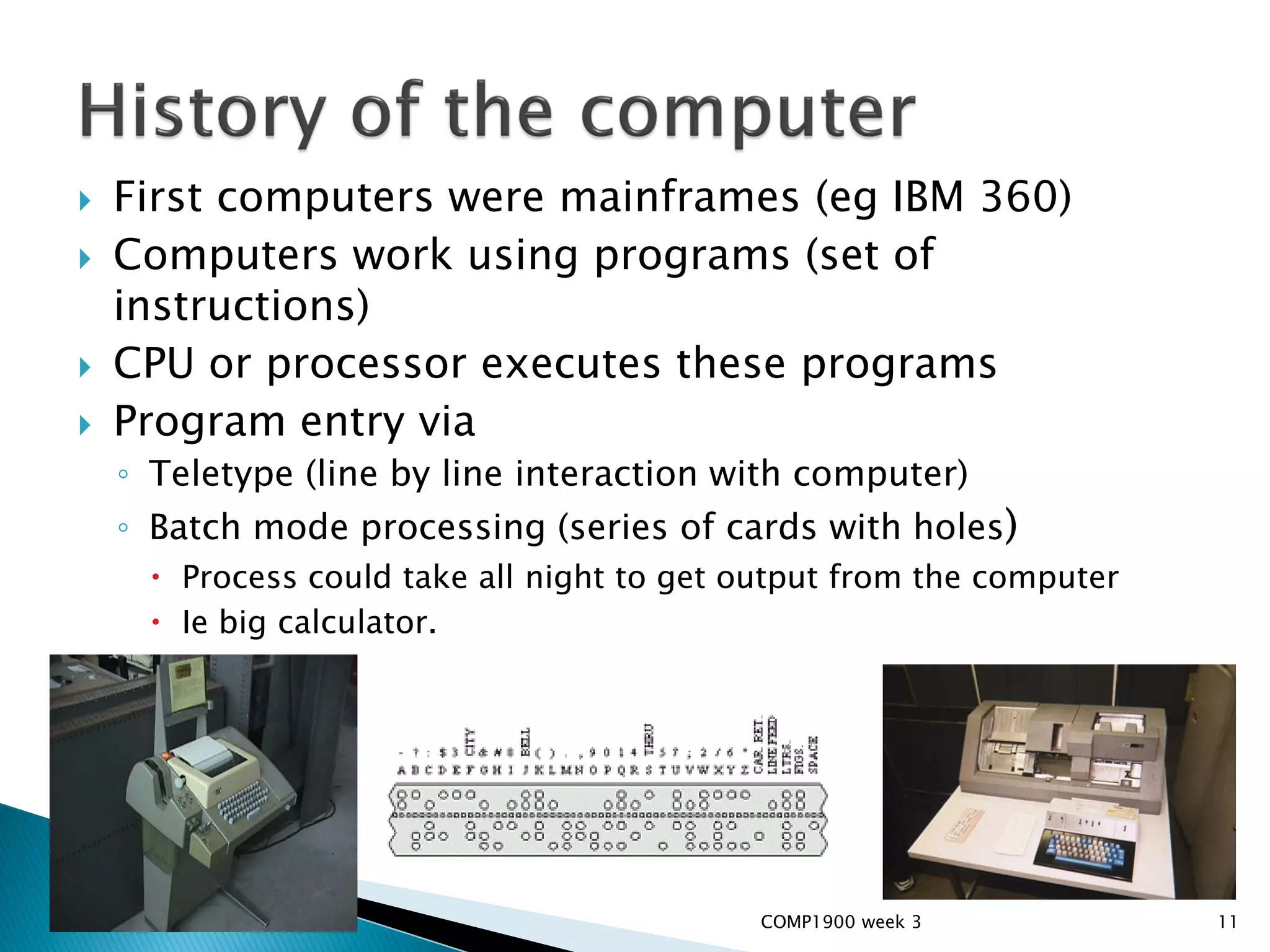
This document is a series of lecture slides on computer fundamentals. It covers topics like the history of computers from mainframes to microprocessors, operating systems like Windows, Mac OS, Linux, and Sugar OS. It discusses computer hardware components like the CPU, memory, storage, and input/output devices. It also explains key concepts such as bits, bytes, binary notation, and how data is stored on a hard drive in sectors and clusters. The document compares command line and graphical user interface approaches and how operating systems act as intermediaries between users and hardware.