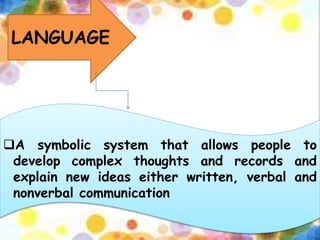
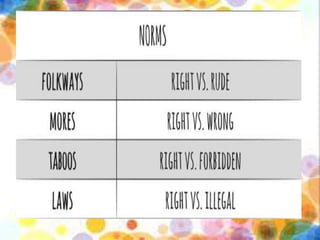
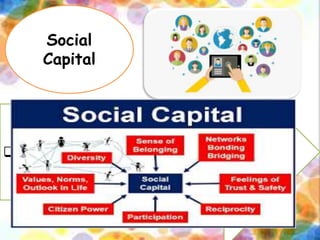
This document defines and describes the key elements of community structure, including social, cultural, political, and economic structures. The social structure includes social institutions, groups, statuses, and roles. Cultural structure comprises symbols, language, norms, values, beliefs, rituals, and artifacts. Political structure involves organizations, power relations, and leadership. Economic structure consists of capital assets, vulnerability context, business climate, and trade.