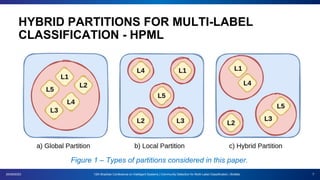
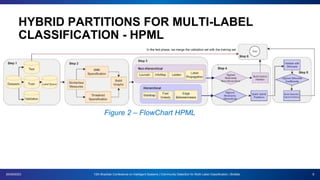
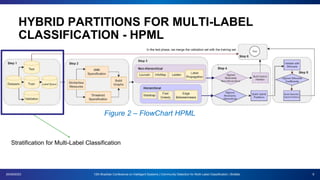
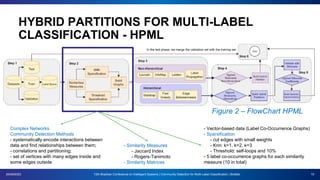
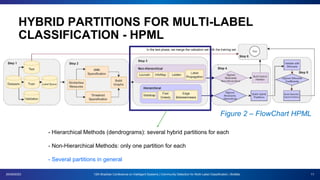
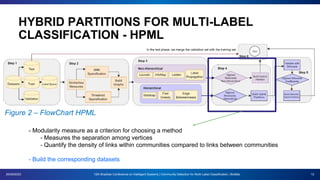
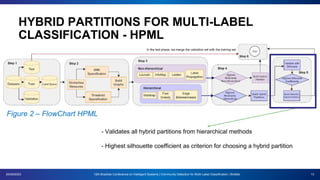
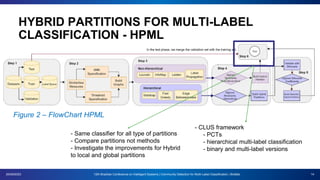
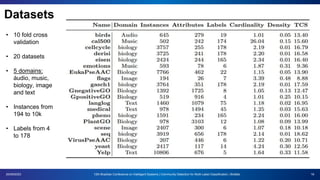
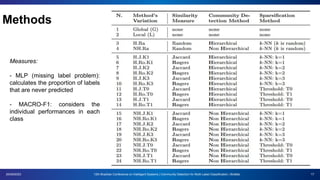
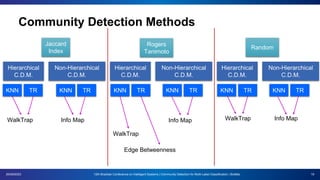
The document presents a proposal for using community detection methods to generate hybrid partitions for multi-label classification. It introduces the limitations of global and local multi-label approaches and proposes a hybrid approach called HPML. HPML uses community detection on label co-occurrence graphs to identify correlated groups of labels and generate partitions for classification. Experiments applying HPML to 20 datasets show its partitions perform competitively with local and better than global partitions on average, demonstrating the value of exploring label correlations through community detection for multi-label classification. However, room for improvement remains as classifiers still struggle with some datasets, suggesting further research is needed on multi-label methods and evaluation.