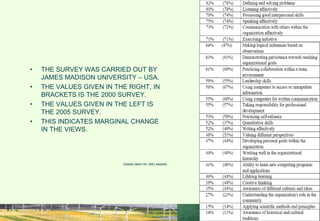
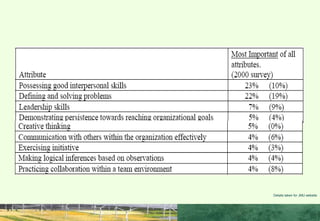
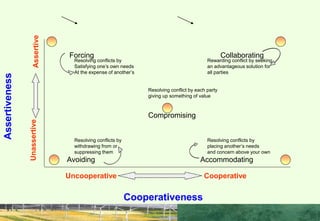
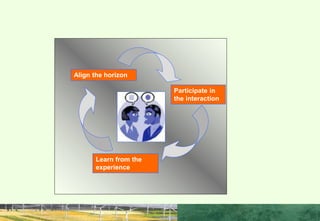
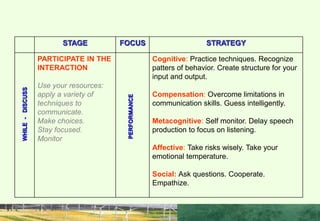
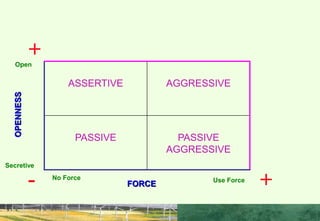
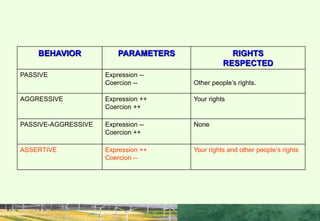
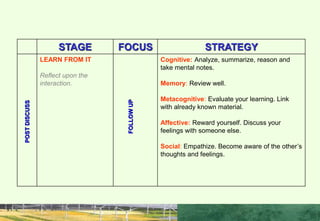
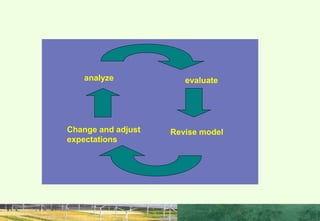
This document discusses the importance of interpersonal skills for employees and networking. It notes that employers value interpersonal skills highly in surveys. Good interpersonal skills allow for effective networking and teamwork. The document provides tips for improving interpersonal skills, such as planning, self-promotion, communication, creativity, organization and following through. It also outlines rules for good networking, including being open, prepared, treating others as equals and saying thank you. Positive and negative examples of networking are also discussed.