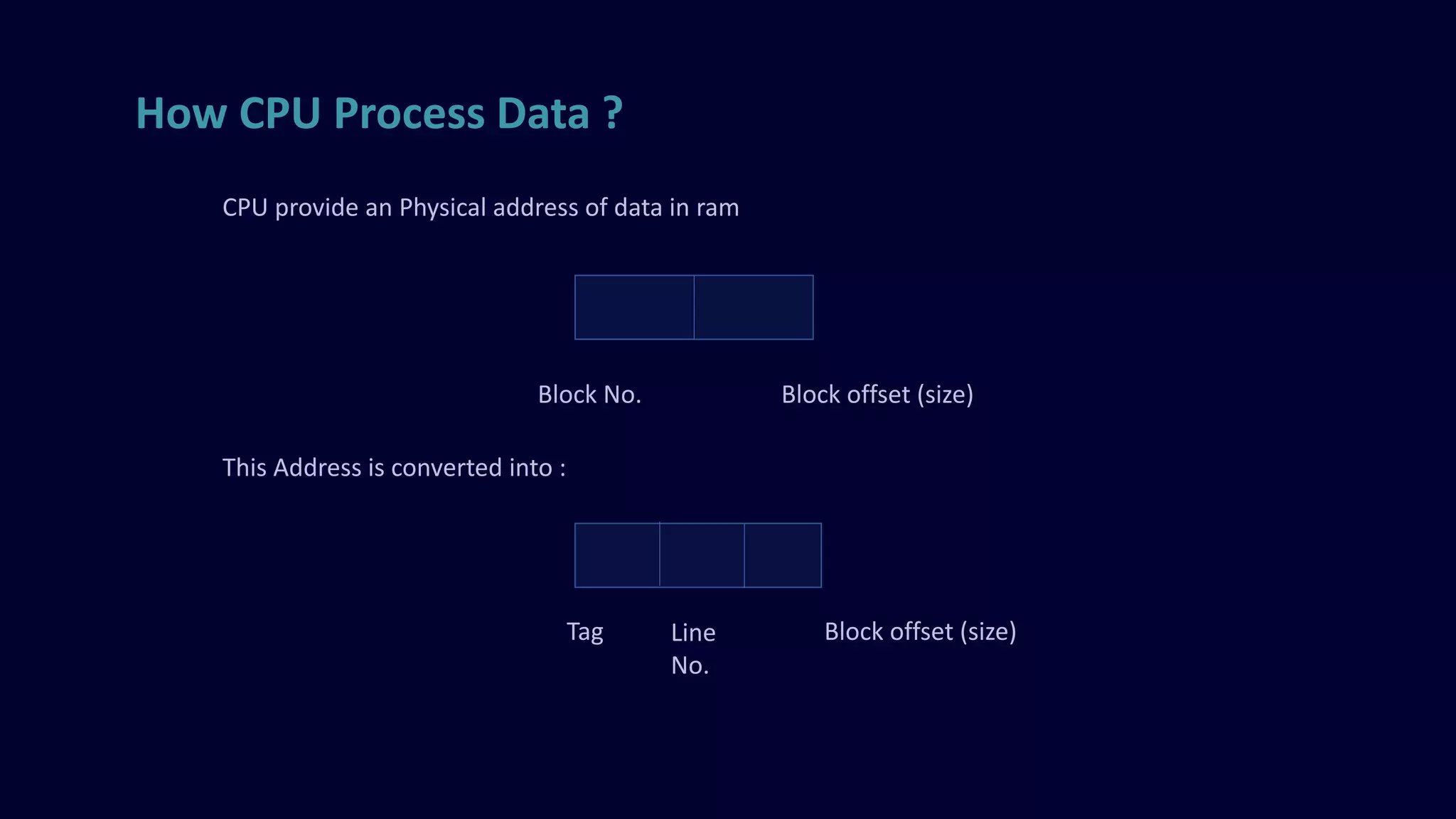
The document discusses cache memory mapping types, including direct mapping, fully associative mapping, and k-way set associative mapping, each with their pros and cons. It explains how cache mapping brings content from main memory into cache and provides mechanisms for how CPUs process data via physical addresses. Additionally, the document includes technical details such as the number of bits required for indexing and tag bits in direct mapped cache examples.