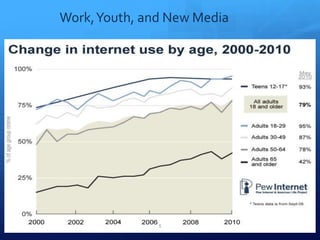
The document discusses how new media and technology impact youth work and learning opportunities. It notes that privileged youth integrate computers seamlessly at home, while lower-income youth often move directly from intensive high school jobs to full-time work. However, digital media have created new entrepreneurial avenues for youth to market their skills. While some view new media training as job preparation, others see it as busywork. Some youth monetize their media skills or hobbies, but most engage in amateur non-market activities for enjoyment rather than pay. In conclusion, socioeconomic status influences how youth experience and utilize new technologies.