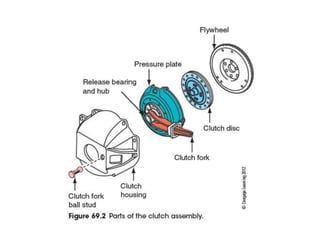
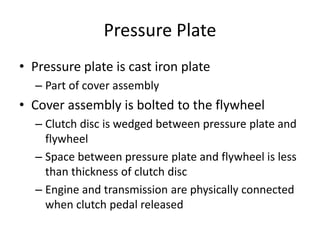
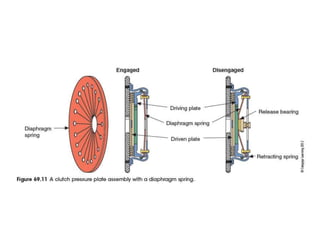
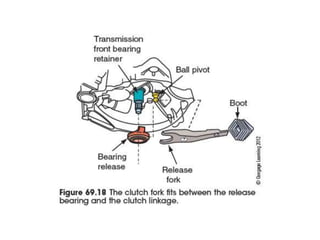
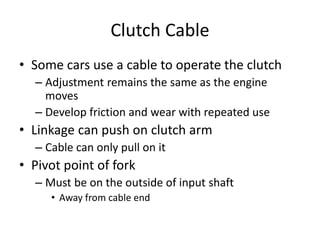
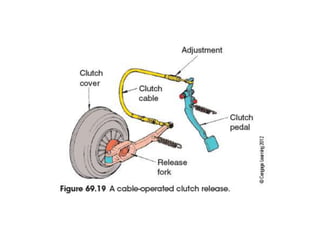
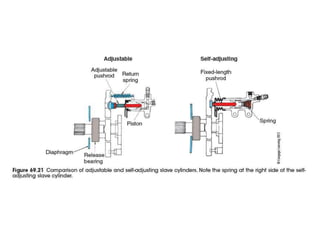
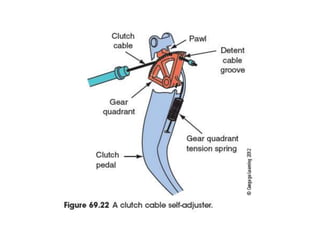
The document discusses the basic parts and operation of a vehicle clutch system. It describes the key components of a clutch including the flywheel, pressure plate, friction disc, and release mechanism. It explains how the clutch couples and decouples the engine from the transmission to allow for gear changes. The document also compares different clutch designs, such as coil spring and diaphragm clutches, and various methods for releasing the clutch, including linkages, cables, and hydraulic cylinders.