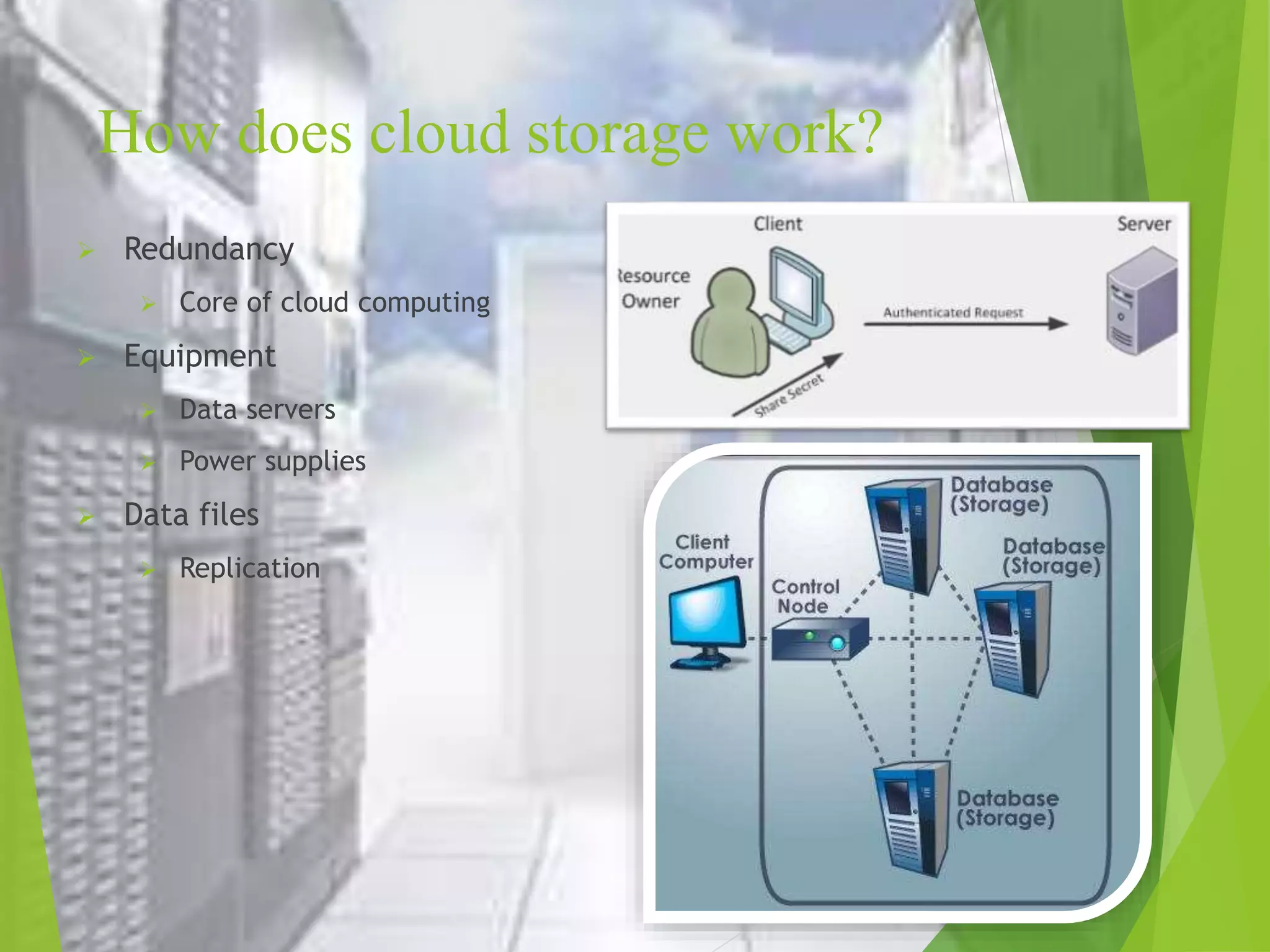
This document provides an overview of cloud storage, including what it is, how it works, the benefits and costs for personal and business use, different types of cloud storage, and advantages and disadvantages. Cloud storage stores digital data in logical pools across multiple servers owned by hosting companies, allowing access from anywhere at any time. It provides benefits like lower costs than physical storage, automatic updates and data accessibility from any device, as well as redundancy and disaster recovery. However, it also relies on internet access and offers less control and privacy than physical storage.