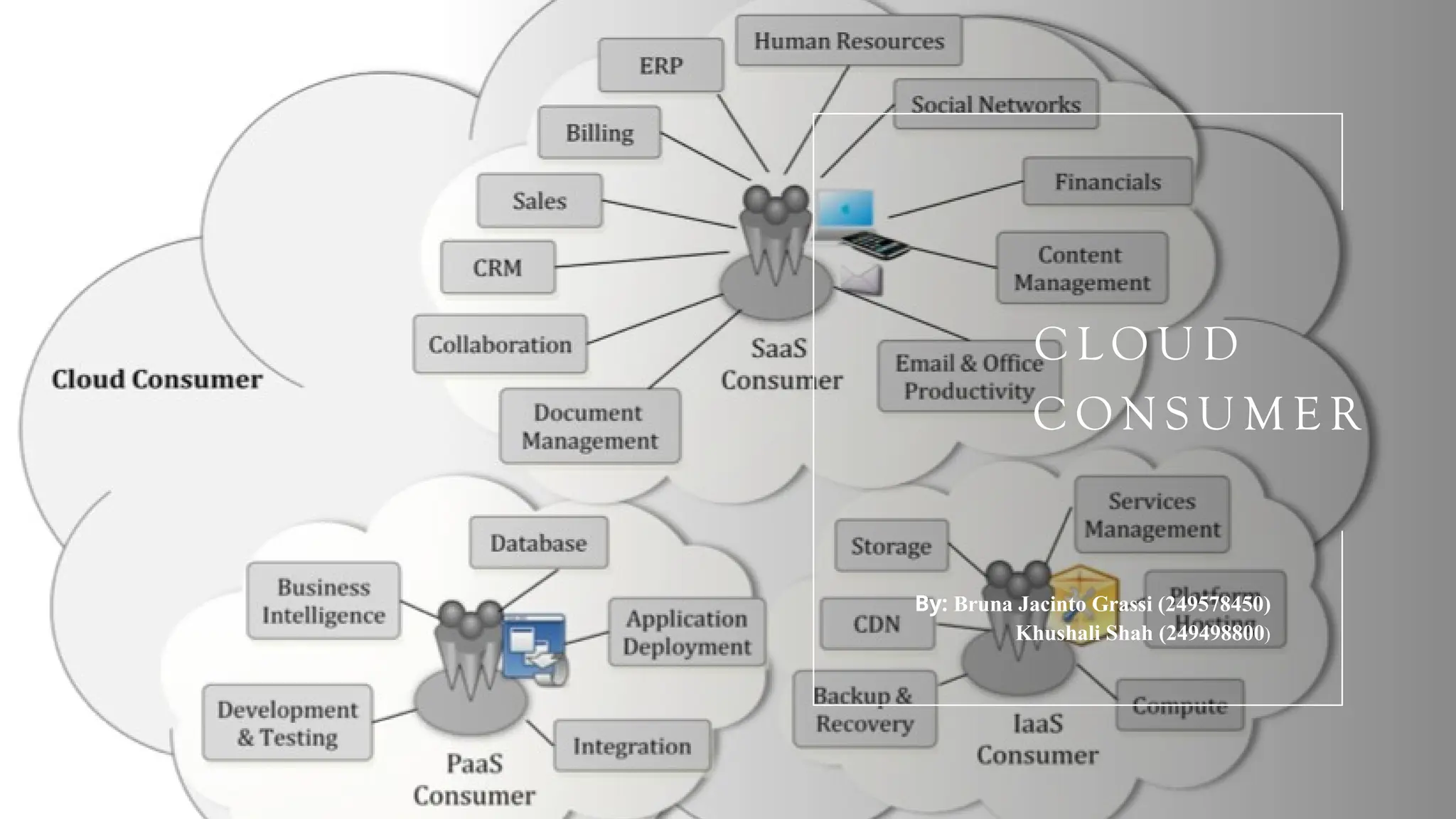
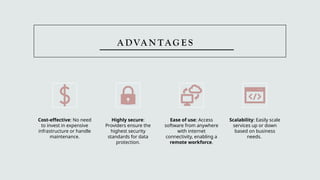
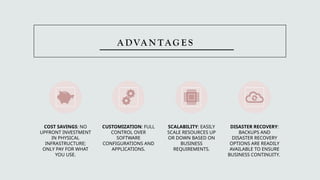
The document outlines the concept of cloud consumers and the three primary service models: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It explains the benefits of each model, their ideal use cases, and how service level agreements (SLAs) regulate expectations between providers and consumers. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of selecting a cloud service model based on organizational needs, budget, and technical resources.