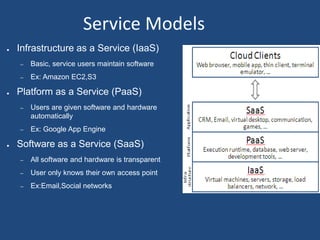
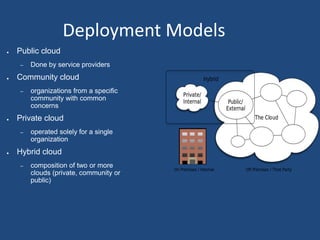
Cloud computing allows sharing of data, storage, and access to computer resources over the internet. It has three main service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides basic services and hardware that users maintain; Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides software, hardware, and platforms automatically; and Software as a Service (SaaS) provides transparent access to software and hardware. Cloud computing also has four deployment models: public, community, private, and hybrid clouds. While cloud computing provides benefits, it also faces challenges regarding privacy, compliance with regulations, security, and potential abuse.